|

Telecom Dictionary - Definitions of terms
International System of Units (SI)
International System of Units (SI) - The modern form of the metric system, which has been adopted by the United States and most other nations. Note: The SI is constructed from seven base units for independent physical quantities. Tables showing these values are included below and are current as of Fall 1995.
SI Prefixes. The common metric prefixes are;
| Multiplication Factor |
Prefix Name |
Prefix |
Symbol |
| 1 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 = |
1024 |
yotta |
Y |
| 1 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 = |
1021 |
zetta |
Z |
| 1 000 000 000 000 000 000 = |
1018 |
exa |
E |
| 1 000 000 000 000 000 = |
1015 |
peta |
P |
| 1 000 000 000 000 = |
1012 |
tera |
T |
| 1 000 000 000 = |
109 |
giga |
G |
| 1 000 000 = |
106 |
mega |
M |
| 1 000 = |
103 |
kilo |
k |
| 100 = |
102 |
hecto |
h |
| 10 = |
101 |
deka |
da |
| 0.1 = |
10-1 |
deci |
d |
| 0.01 = |
10-2 |
centi |
c |
| 0.001 = |
10-3 |
milli |
m |
| 0.000 001 = |
10-6 |
micro |
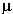 |
| 0.000 000 001 = |
10-9 |
nano |
n |
| 0.000 000 000 001 = |
10-12 |
pico |
p |
| 0.000 000 000 000 001 = |
10-15 |
femto |
f |
| 0.000 000 000 000 000 001 = |
10-18 |
atto |
a |
| 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 001 = |
10-21 |
zepto |
z |
| 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 001 = |
10-24 |
yocto |
y |
SI derived units. Derived units are formed by combining base units and other derived units according to the algebraic relations linking the corresponding quantities. The symbols for derived units are obtained by means of the mathematical signs for multiplication, division, and use of exponents. For example, the SI unit for velocity is the meter per second (m/s or m•s-1), and that for angular velocity is the radian per second (rad /s or rad•s-1). Some derived SI units have been given special names and symbols, as listed in this table.
SI derived units
| Quantity |
Unit Name |
Unit Symbol |
Expression in Terms of Other SI Units |
| Absorbed dose, specific energy imparted, kerma, absorbed dose index |
gray |
Gy |
J/kg |
| Activity (of a radionuclide) |
becquerel |
Bq |
1/s |
| Celsius temperature |
degree Celsius |
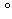 C C |
K |
| Dose equivalent |
sievert |
Sv |
J/kg |
| Electric capacitance |
farad |
F |
C/V |
| Electric charge, quantity of electricity |
coulomb |
C |
A•s |
| Electric conductance |
siemens |
S |
A/V |
| Electric inductance |
henry |
H |
Wb/A |
| Electric potential, potential difference, electromotive force |
volt |
V |
W/A |
| Electric resistance |
ohm |
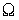 |
V/A |
| Energy, work, quantity of heat |
joule |
J |
N•m |
| Force |
newton |
N |
kg•m/s2 |
| Frequency (of a periodic phenomenon) |
hertz |
Hz |
1/s |
| Illuminance |
lux |
lx |
lm/m2 |
| Luminous flux |
lumen |
lm |
cd•sr |
| Magnetic flux |
weber |
Wb |
V•s |
| Magnetic flux density |
tesla |
T |
Wb/m2 |
| Plane angle |
radian |
rad |
m/m |
| Power, radiant flux |
watt |
W |
J/s |
| Pressure, stress |
pascal |
Pa |
N/m2 |
| Solid angle |
steradian |
sr |
m2/m2 |
|
