
Telecom Dictionary - Definitions of terms
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
B
b - Abbreviation for bit. (binary digit) The smallest unit of computer information.
B - Abbreviation for bel, byte. A byte is combination of bits that represents a single character (approximately 8 bits equal one byte).
B8ZS (bipolar 8-zero substitution, also called binary 8-zero substitution, clear channel, and clear 64) - is an encoding method used on T1 circuits that inserts two successive ones of the same voltage - referred to as a
bipolar violation - into a signal whenever eight consecutive zeros are transmitted. The device receiving the signal interprets the bipolar violation as a timing mark, which keeps the transmitting and receiving devices synchronized. Ordinarily, when successive ones are transmitted, one has a positive voltage and the other has a negative voltage.B8ZS is based on an older encoding method called alternate mark inversion (
AMI ). AMI is used with Dataphone Digital Service, the oldest data service still in use that uses 64 Kbps channels. AMI, however, requires the use of 8 Kbps of the 64 Kbps of each channel to maintain synchronization. In a T1 circuit, there are 24 channels. This loss adds up to 192 Kbps, which means that in reality only 56 Kbps is available for data transmission. B8ZS uses bipolar violations to synchronize devices, a solution that does not require the use of extra bits, which means a T1 circuit using B8ZS can use the full 64 Kbps for each channel for data. B8ZS is not compatible with older AMI equipment.T1 technology is used in the United States and Japan. In Europe, a comparable technology called E1 provides 32 channels instead of 24 and uses an encoding scheme called high-density bipolar 3 (HDB3) instead of B8ZS.
Babble - In transmission systems, the aggregate of crosstalk induced in a given line by all other lines.
Backbone - 1. The high-traffic-density connectivity portion of any communications network. 2. In packet-switched networks, a primary forward-direction path traced sequentially through two or more major relay or switching stations. Note: In packet-switched networks, a backbone consists primarily of switches and interswitch trunks.
Backbone - A series of high-speed network connections through which other networks connect.
Back Door - Synonym trapdoor. A hidden software or hardware mechanism, usually created for testing and troubleshooting, that may be used to circumvent computer security.
Background - 1. In Web pages, an image or color, usually defined in HTML, that serves as the underlying color or imagery for a Web page. Note: Browsers may also be configured to dictate backgrounds. 2. In computer display systems, the underlying color or imagery for the main screen or for the fundamental window of a computer's operating system.
Background Noise - The total system noise in the absence of information transmission.
Background Processing - The execution of lower priority computer programs when higher priority programs are not using the system resources. Note: Priorities may be assigned by system software, application software, or the operator.
Backhaul - 1. The practice of routing telecommunications traffic beyond its intended destination, and then back to the intended destination, usually for the purpose of taking advantage of tariffs or prices that are lower than those afforded by direct routing. 2. In security, to bring a call that has been routed along a particular path (usually via satellite) to some earlier position in the switching sequence (also using satellites). Note: The technique supports CALEA, the Communications Assistance to Law Enforcement Act and LAES, Lawfully Authorized Electronic Surveillance. 3. In commercial telephone networks, referring to a trunk or line between two central offices that may not share the same facilities or geographic location, and which trunk is used to support special services, e.g., orderwires, off-premises extensions, common exchange number routing, or least-cost routing of customer centrex services. 4. In mission programs requiring contingency networking, referring to a link that provides feedback to the mission control center to verify that the transmission via a primary communications has been successful. Note: In cases where the primary path fails to deliver the transmission, the communications may occur over the backhaul connection or an alternative network connection. 5. In contingency networking, an alternative connection that is routed via a diversified path, e.g., an alternative frequency, satellite facility, cable, trunk, or time slot.
Backscattering - 1. Radio wave propagation in which the direction of the incident and scattered waves, resolved along a reference direction (usually horizontal) are oppositely directed. A signal received by backscattering is often referred to as "backscatter." 2. In optics, the scattering of light into a direction generally opposite to the original one.
Back-to-Back Connection - 1. A direct connection between the output of a transmitting device and the input of an associated receiving device. Note: When used for equipment measurements or testing purposes, such a back-to-back connection eliminates the effects of the transmission channel or medium. 2. A direct connection between the output of a receiving device and the input to a transmitting device. Note: The term "direct," as used in both definitions, may be construed as permitting a passive device such as a pad (attenuator) to accommodate power level constraints.
Backup - 1. [A] copy of files and programs made to facilitate recovery, if necessary. 2. See backup file.
Backup File - A copy of a file made for purposes of later reconstruction of the file, if necessary. Note: A backup file may be used for preserving the integrity of the original file and may be recorded on any suitable medium. Synonym job-recovery control file.
Backward Channel - 1. In data transmission, a secondary channel in which the direction of transmission is constrained to be opposite to that of the primary, i.e., the forward (user-information) channel. Note: The direction of transmission in the backward channel is restricted by the control interchange circuit that controls the direction of transmission in the primary channel. 2. In a data circuit, the channel that passes data in a direction opposite to that of its associated forward channel. Note 1: The backward channel is usually used for transmission of supervisory, acknowledgement, or error-control signals. The direction of flow of these signals is opposite to that in which user information is being transferred. Note 2: The backward-channel bandwidth is usually less than that of the primary channel, i.e., the forward (user information) channel.
Backward Indicator Bit (BIB) - A signal unit (or sequence of bits) that (by changing its status) is used to request retransmission by the remote end whenever it receives a signal unit that is out of sequence.
Backward Recovery - The reconstruction of an earlier version of a file by using a newer version of data recorded in a journal.
Backward Sequence Number (BSN) - A field in a signal unit that contains the forward sequence number of a correctly received signal unit being acknowledged in the signal unit that is being returned to the sender.
Backward Signal - A signal sent from the called to the calling station, i.e., from the original data sink to the original data source. Note: Backward signals are usually sent via a backward channel and may consist of supervisory, acknowledgment, or control signals.
Backward Supervision - The use of supervisory signal sequences from a secondary to a primary station.
Bacterium - A program that attempts to propagate itself by e-mailing a copy of itself to e-mail addresses found on a recipient's hard drive. This is done without the consent or knowledge of the recipient. Note: In many cases, this type of program does not attempt to cause any direct damage to user's system, but rather attempts to overload the e-mail distribution system, much as a successful chain letter would do to the postal system. Synonym [in cryptosystems] chain letter.
Bad Sectoring - A technique for copy protection in which bad sectors are intentionally written on a diskette.
Balance - In electrical circuits and networks, to adjust the impedance to achieve specific objectives, such as to reach specified return loss objectives at a hybrid junction of two-wire and four-wire circuits.
Balanced - Pertaining to electrical symmetry.
Balanced Code - 1. In PCM systems, a code constructed so that the frequency spectrum resulting from the transmission of any code word has no dc component. 2. In PCM, a code that has a finite digital sum variation.
Balanced Line - A transmission line consisting of two conductors in the presence of ground, capable of being operated in such a way that when the voltages of the two conductors at all transverse planes are equal in magnitude and opposite in polarity with respect to ground, the currents in the two conductors are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Note: A balanced line may be operated in an unbalanced condition. Synonym balanced signal pair.
Balanced Modulator - A modulator constructed so that the carrier is suppressed and any associated carrier noise is balanced out. Note 1: The balanced modulator output contains only the sidebands. Note 2: Balanced modulators are used in AM transmission systems.
Balanced Signal Pair - Synonym balanced line. A transmission line consisting of two conductors in the presence of ground, capable of being operated in such a way that when the voltages of the two conductors at all transverse planes are equal in magnitude and opposite in polarity with respect to ground, the currents in the two conductors are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Note: A balanced line may be operated in an unbalanced condition.
Balance Return Loss - 1. A measure of the degree of balance between two impedances connected to two conjugate sides of a hybrid set, coil, network, or junction. 2. A measure of the effectiveness with which a balancing network simulates the impedance of a two-wire circuit at a hybrid coil.
Balancing Network - 1. In a hybrid set, hybrid coil, or resistance hybrid, a circuit used to match, i.e., to balance, the impedance of a uniform transmission line, i.e., twisted metallic pair, over a selected range of frequencies. Note: A balancing network is required to ensure isolation between the two ports of the four-wire side of the hybrid. 2. A device used between a balanced device or line and an unbalanced device or line for the purpose of transforming from balanced to unbalanced or from unbalanced to balanced.
Balun - Abbreviation for balanced to unbalanced. In radio frequency usage, a device used to couple a balanced device or line to an unbalanced device or line.
Band - 1. In communications, the frequency spectrum between two defined limits. 2. A group of tracks on a magnetic drum or on one side of a magnetic disk. 3. A set of frequencies authorized for use in a geographical area defined for common carriers for purposes of communications system management.
Band-Elimination Filter - Synonym band-stop filter. A filter that attenuates, usually to very low levels, all frequencies between two non-zero, finite limits and passes all frequencies not within the limits. Note: A band-stop filter may be designed to stop the specified band of frequencies but usually only attenuates them below some specified level.
Bandpass Filter - A filter that ideally passes all frequencies between two non-zero finite limits and bars all frequencies not within the limits. Note: The cutoff frequencies are usually taken to be the 3-dB points.
Band-Rejection Filter - Synonym band-stop filter. A filter that attenuates, usually to very low levels, all frequencies between two non-zero, finite limits and passes all frequencies not within the limits. Note: A band-stop filter may be designed to stop the specified band of frequencies but usually only attenuates them below some specified level.
Band-Stop Filter - A filter that attenuates, usually to very low levels, all frequencies between two non-zero, finite limits and passes all frequencies not within the limits. Note: A band-stop filter may be designed to stop the specified band of frequencies but usually only attenuates them below some specified level. Synonyms band-elimination filter, band-rejection filter, band-suppression filter, notched filter.
Band-Suppression Filter - Synonym band-stop filter. A filter that attenuates, usually to very low levels, all frequencies between two non-zero, finite limits and passes all frequencies not within the limits. Note: A band-stop filter may be designed to stop the specified band of frequencies but usually only attenuates them below some specified level.
Bandwidth - According to Webster's: a range within a band of wavelengths, frequencies, or energies; esp: a range of radio frequencies which is occupied by a modulated carrier wave, which is assigned to a service, or over which a device can operate. In Internet terms, bandwidth commonly refers to the amount of information that can be sent through a connection.In computer networks, bandwidth is often used as a synonym for data transfer rate - the amount of data that can be carried from one point to another in a given time period (usually a second). This kind of bandwidth is usually expressed in bits (of data) per second (bps). Occasionally, it's expressed as
bytes per second (Bps). A modem that works at 57,600 bps has twice the bandwidth of a modem that works at 28,800 bps. In general, a link with a high bandwidth is one that may be able to carry enough information to sustain the succession of images in a video presentation.It should be remembered that a real communications path usually consists of a succession of links, each with its own bandwidth. If one of these is much slower than the rest, it is said to be a bandwidth bottleneck.
Bandwidth Balancing Mechanism - In a distributed-queue dual-bus network, a procedure in which a node occasionally skips the use of empty queued arbitrated slots, and which procedure effects sharing of the bandwidth mechanisms.
Bandwidth Compression - 1. The reduction of the bandwidth needed to transmit a given amount of data in a given time. 2. The reduction of the time needed to transmit a given amount of data in a given bandwidth. Note: Bandwidth compression implies a reduction in normal bandwidth of an information-carrying signal without reducing the information content of the signal.
Bandwidth•Distance Product - Of an optical fiber, under specified launching and cabling conditions, at a specified wavelength, a figure of merit equal to the product of the fiber's length and the 3-dB bandwidth of the optical signal. Note 1: The bandwidth•distance product is usually stated in megahertz • kilometer (MHz •km) or gigahertz •kilometer (GHz•km). Note 2: The bandwidth•distance product, which is normalized to 1 km, is a useful figure of merit for predicting the effective fiber bandwidth for other lengths, and for concatenated fibers. Synonym bandwidth•length product.
Bandwidth•Length Product - Synonym for bandwidth•distance product. - Of an optical fiber, under specified launching and cabling conditions, at a specified wavelength, a figure of merit equal to the product of the fiber's length and the 3-dB bandwidth of the optical signal. Note 1: The bandwidth•length product is usually stated in megahertz • kilometer (MHz •km) or gigahertz •kilometer (GHz•km). Note 2: The bandwidth•length product, which is normalized to 1 km, is a useful figure of merit for predicting the effective fiber bandwidth for other lengths, and for concatenated fibers.
Bandwidth-Limited Operation - The condition prevailing when the system bandwidth limits performance. Note: Bandwidth-limited operation occurs when the system distorts the signal waveform beyond specified limits. For linear systems, bandwidth-limited operation is equivalent to distortion-limited operation.
Bandwidth (of an optical fiber) - 1. The lowest modulation frequency at which the RMS peak-to-valley amplitude (optical power) difference of an intensity-modulated monochromatic signal decreases, at the output of the fiber, to a specified fraction (usually one-half) of the RMS peak-to-valley amplitude (optical power) difference of a nearly-zero (arbitrarily low) modulation frequency, both modulation frequencies having the same RMS peak-to-valley amplitude (optical power) difference at the fiber input. Note 1: In multimode fibers, multimode distortion is usually the most significant parameter limiting fiber bandwidth, although material dispersion may also play a significant role, especially in the first (850-nm) window. Note 2: In multimode fibers, the bandwidth•distance product (loosely, "fiber bandwidth") is customarily specified by vendors for the bandwidth as limited by multimode distortion only. The spectral width of the optical source is assumed to be extremely narrow. In practice, the effective fiber bandwidth will also be limited by dispersion, especially in the first (850-nm) window, where material dispersion is relatively high, because optical sources have a finite spectral width. Laser diodes typically have a spectral width of several nanometers, FWHM. LEDs typically have a spectral width of 35 to 100 nm, FWHM. Note 3: The effective risetime of multimode fibers may be estimated fairly accurately as the square root of the sum of the squares of the material-dispersion-limited risetime and the multimode-distortion-limited risetime. Note 4: In single-mode fibers, the most important parameters affecting fiber bandwidth are material dispersion and waveguide dispersion. Practical fibers are designed so that material dispersion and waveguide dispersion cancel one another at the wavelength of interest. Note 5: Regarding effective fiber bandwidth as it affects overall system performance, it should be recognized that optical detectors such as PIN diodes are square-law devices. Their photocurrent is proportional to the optical power of the detected signal. Because electrical power is a function of the square of the current, when the optical power decreases by one-half (a 3-dB decrease), the electrical power decreases by three-fourths (a 6-dB decrease). 2. Loosely, synonym bandwidth•distance product.
Bang - The exclamation point character (!) used in early addressing schemes to separate the names of individual machines. Note: Bang-style addressing is no longer common. Synonym scream.
Banner - 1. An HTML tag that creates scrolling text on a Web page. 2. Scrolling or fixed text used as an advertisement on a Web page, e.g., banner advertising. 3. In computer networking, a page that is automatically prefixed to, and printed out as part of, a printing job, as a means of identifying uniquely the output belonging to a given user of a shared printer. Note: A banner may, in addition to identifying the owner of the printout, also identify the file name, queue, and server involved. Synonym banner page. 4. [A] display on an information system (IS) that sets parameters for system or data use.
Banner Page - Synonym banner. In computer networking, a page that is automatically prefixed to, and printed out as part of, a printing job, as a means of identifying uniquely the output belonging to a given user of a shared printer. Note: A banner may, in addition to identifying the owner of the printout, also identify the file name, queue, and server involved.
Bar Code - A code representing characters by sets of parallel bars of varying thickness and separation that are read optically by transverse scanning. Note: Bar code uses include identifying merchandise, sorting mail, and inventorying supplies.
Barge-In Protection- When installed on an incoming telephone line before ALL telephone equipment (extension wall jacks or multi-line phone systems), The Barge-In Protection feature will protect any voice or data call from being accessed by other telephone equipment on the same line. Any phone device that goes "off-hook" during a conversation or data transmission will receive a silent line or a busy signal depending on the product.
Barn Doors - This term is used in television production to describe the effect that occurs when a 4:3 image is viewed on a 16:9 screen. When this happens, viewers see black bars, or, "barn doors," on the sides of the screen.
Barrage Jamming - Jamming accomplished by transmitting a band of frequencies that is large with respect to the bandwidth of a single emitter. Note: Barrage jamming may be accomplished by presetting multiple jammers on adjacent frequencies or by using a single wideband transmitter. Barrage jamming makes it possible to jam emitters on different frequencies simultaneously and reduces the need for operator assistance or complex control equipment. These advantages are gained at the expense of reduced jamming power at any given frequency.
Base - 1. In the numeration system commonly used in scientific notation, the real number that is raised to a power denoted by the exponent and then multiplied by the coefficient to determine the value of the number represented without the use of exponents. Note: An example of a base is the number 6.25 in the expression 2.70 × 6.251.5
42.19. The 2.70 is the coefficient and the 1.5 is the exponent. In the decimal numeration system, the base is 10 and in the binary numeration system, the base is 2. The value e
2.718 is the natural base. 2. A reference value. 3. A number that is multiplied by itself as many times as indicated by an exponent.
Base Address - 1. An address that is used as the origin in the calculation of addresses in the execution of a computer program. 2. A given address from which an absolute address is derived by combination with a relative address. Note: Base addresses are primarily used by computer programmers rather than by computer users.
Baseband - 1. The original band of frequencies produced by a transducer, such as a microphone, telegraph key, or other signal-initiating device, prior to initial modulation. Note 1: In transmission systems, the baseband signal is usually used to modulate a carrier. Note 2: Demodulation re-creates the baseband signal. Note 3: Baseband describes the signal state prior to modulation, prior to multiplexing, following demultiplexing, and following demodulation. Note 4: Baseband frequencies are usually characterized by being much lower in frequency than the frequencies that result when the baseband signal is used to modulate a carrier or subcarrier. 2. In facsimile, the frequency of a signal equal in bandwidth to that between zero frequency and maximum keying frequency.
Baseband Local Area Network - A local area network in which information is encoded, multiplexed, and transmitted without modulation of carriers.
Baseband Modulation - Intensity modulation of an optical source, e.g., LED or ILD, directly, without first modulating the signal of interest onto an electrical carrier wave.
Baseband Signaling - Transmission of a digital or analog signal at its original frequencies; i.e., a signal in its original form, not changed by modulation.
Basecom - Abbreviation for base communications. - Communications services, such as the installation, operation, maintenance, augmentation, modification, and rehabilitation of communications networks, systems, facilities, and equipment, including off-post extensions, provided for the operation of a military post, camp, installation, station, or activity.
Base Communications (basecom) - Communications services, such as the installation, operation, maintenance, augmentation, modification, and rehabilitation of communications networks, systems, facilities, and equipment, including off-post extensions, provided for the operation of a military post, camp, installation, station, or activity. Synonym communications base station.
Base Earth Station - An Earth station in the fixed-satellite service or, in some cases, in the land mobile-satellite service, located at a specified fixed point or within a specified area on land to provide a feeder link for the land mobile-satellite service.
Base Key - A key used to derive (to compute cryptographically) or to decrypt transaction keys.
Base Station - 1. A land station in the land mobile service. 2. In personal communication service, the common name for all the radio equipment located at one fixed location, and that is used for serving one or several cells.
Basic Access - A characterization of a simple standardized combination of access channels that constitute the access arrangements for the majority of ISDN users; specifically, any of the following combinations of access channels: (1) one D-channel, (2) one B-channel plus one D-channel, (3) two B-channels plus one D-channel.
Basic Call - A call between two users that does not include additional features (e.g., a plain telephone call).
Basic Call Process (BCP) - The sequence of activities used in processing a basic call attempt.
Basic Exchange Telecommunications Radio Service (BETRS) - A commercial service that can extend telephone service to rural areas by replacing the local loop with radio communications. Note: In the BETRS, non-government ultra high frequency (UHF) and very high frequency (VHF) common carrier and the private radio service frequencies are shared.
Basic Mode Link Control - Control of data links by use of the control characters of the 7-bit character set for information processing interchange as given in ISO Standard 646-1983 and CCITT (ITU-T) Recommendation
Basic Rate Interface (BRI) - An ITU-T Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) multipurpose user interface standard that denotes the capability of simultaneous voice and data services provided over two clear 64-kb/s channels and one clear 16-kb/s channel (2B+D) access arrangement to each user location. - In the Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN), there are two levels of service: the Basic Rate Interface (BRI), intended for the home and small enterprise, and the Primary Rate Interface (PRI), for larger users. Both rates include a number of B-channels and a D-channel. Each B-channel carries data, voice, and other services. The D-channel carries control and signaling information.
The Basic Rate Interface consists of two 64 Kbps B-channels and one 16 Kbps D-channel. Thus, a Basic Rate Interface user can have up to 128 Kbps service. The Primary Rate Interface consists of 23 B-channels and one 64 Kpbs D-channel in the United States or 30 B-channels and 1 D-channel in Europe.
Basic Service - 1. A pure transmission capability over a communication path that is virtually transparent in terms of its interaction with customer-supplied information. 2. The offering of transmission capacity between two or more points suitable for a user's transmission needs and subject only to the technical parameters of fidelity and distortion criteria, or other conditioning.
Basic Service Element (BSE) - 1. An optional unbundled feature, generally associated with the basic serving arrangement (BSA), that an enhanced-service provider (ESP) may require or find useful in configuring an enhanced service. 2. A fundamental (basic) communication network service; an optional network capability associated with a BSA. Note: BSEs constitute optional capabilities to which the customer may subscribe or decline to subscribe.
Basic Serving Arrangement (BSA) - 1. The fundamental tariffed switching and transmission (and other) services that an operating company must provide to an enhanced service provider (ESP) to connect with its customers through the company network. 2. In an open-network-architecture context, the fundamental underlying connection of an enhanced service provider (ESP) to and through the operating company's network including an ESP access link, the features and functions associated with that access link at the central office serving the ESP and/or other offices, and the transport (dedicated or switched) within the network that completes the connection from the ESP to the central office serving its customers or to capabilities associated with the customer's complementary network services. Note: Each component may have a number of categories of network characteristics. Within these categories of network characteristics are alternatives from among which the customer must choose. Examples of BSA components are ESP access link, transport and/or usage.
Basic Status - In data transmission, the status of the capability of a secondary station to send or receive a frame containing an information field.
Bastion Host - A host computer that, in a screened subnetwork, performs the functions of a firewall. Synonym screened-host gateway.
Batched Communications - Synonym batched transmission. - The transmission of two or more messages from one station to another without intervening responses from the receiving station.
Batched Transmission - The transmission of two or more messages from one station to another without intervening responses from the receiving station. Synonym batched communications.
Batch Processing - 1. The processing of data or the accomplishment of jobs accumulated in advance in such a manner that the user cannot further influence the processing while it is in progress. 2. The processing of data accumulated over a period of time. 3. Loosely, the execution of computer programs serially. 4. Pertaining to the technique of executing a set of computer programs such that each is completed before the next program of the set is started. 5. Pertaining to the sequential input of computer programs or data.
Baud (Bd) - 1. A unit of modulation rate. Note: One baud corresponds to a rate of one unit interval per second, where the modulation rate is expressed as the reciprocal of the duration in seconds of the shortest unit interval. 2. A unit of signaling speed equal to the number of discrete signal conditions, variations, or events per second. Note 1: If the duration of the unit interval is 20 milliseconds, the signaling speed is 50 bauds. If the signal transmitted during each unit interval can take on any one of n discrete states, the bit rate is equal to the rate in bauds times log 2 n. . The technique used to encode the allowable signal states may be any combination of amplitude, frequency, or phase modulation, but it cannot use a further time-division multiplexing technique to subdivide the unit intervals into multiple subintervals. In some signaling systems, non-information-carrying signals may be inserted to facilitate synchronization; e.g., in certain forms of binary modulation coding, there is a forced inversion of the signal state at the center of the bit interval. In these cases, the synchronization signals are included in the calculation of the rate in bauds but not in the computation of bit rate. Note 2: Baud is sometimes used as a synonym for bit-per-second. This usage is deprecated.
Baudot Code - A synchronous code in which five equal-length bits represent one character. Note 1: The Baudot code, which was developed circa 1880, has been replaced by the start-stop asynchronous International Alphabet No. 2 (IA No. 2). Note 2: IA No. 2 is not, and should not be identified as, the Baudot code. Note 3: The Baudot code has been widely used in teletypewriter systems.
BCC - Abbreviation for block check character. - A character added to a transmission block to facilitate error detection. Note: In longitudinal redundancy checking and cyclic redundancy checking, block check characters are computed for, and added to, each message block transmitted. This block check character is compared with a second block check character computed by the receiver to determine whether the transmission is error free.
BCD - Abbreviation for binary-coded decimal code. See binary-coded decimal notation.
B-channel - In the Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN), the B-channel is the channel that carries the main data. (The "B" stands for "bearer" channel.)
In ISDN, there are two levels of service: the Basic Rate Interface, intended for the home and small enterprise, and the Primary Rate Interface, for larger users. Both rates include a number of B- (bearer) channels and a D-channel. The B-channels carry data, voice, and other services. The D-channel carries control and signaling information.
The Basic Rate Interface consists of two 64 Kbps B-channels and one 16 Kbps D-channel. Thus, a Basic Rate Interface user can have up to 128 Kbps service. The Primary Rate Interface consists of 23 B-channels and one 64 Kpbs D-channel in the United States or 30 B-channels and 1 D-channel in Europe.
B channel - 1. A communications channel used for the transmission of an aggregate signal generated by multichannel transmitting equipment. 2. The CCITT (now, ITU-T) designation for a clear channel, 64-kb/s service capability provided to a subscriber under the Integrated Services Digital Network offering. Note: The B channel, also called the bearer channel, is intended for transport of user information, as opposed to signaling information.
BCH code - Abbreviation for Bose-Chaudhuri-Hochquenghem code . A multilevel, cyclic, error-correcting, variable-length digital code used to correct errors up to approximately 25% of the total number of digits. Note: BCH codes are not limited to binary codes, but may be used with multilevel phase-shift keying whenever the number of levels is a prime number or a power of a prime number, such as 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 11, and 13. A BCH code in 11 levels has been used to represent the 10 decimal digits plus a sign digit.
BCI - Abbreviation for bit-count integrity. - 1. In message communications, the preservation of the exact number of bits that are in the original message. 2. In connection-oriented services, preservation of the number of bits per unit time. Note: Bit-count integrity is not the same as bit integrity, which requires that the delivered bits correspond exactly with the original bits.
Beacon - See radiobeacon station. - A station in the radionavigation service the emissions of which are intended to enable a mobile station to determine its bearing or direction in relation to the radiobeacon station.
Beam - 1. The main lobe of an antenna radiation pattern. 2. A column of light. Note: A beam may be parallel, divergent, or convergent.
Beam Diameter - Of an electromagnetic beam, along any specified line that (a) intersects the beam axis and (b) lies in any specified plane normal to the beam axis, the distance between the two diametrically opposite points at which the irradiance is a specified fraction, e.g., ½ or 1/
, of the beam's peak irradiance. Note 1: Beam diameter is usually used to characterize electromagnetic beams in the optical regime, and occasionally in the microwave regime, i.e., cases in which the aperture from which the beam emerges is very large with respect to the wavelength. Note 2: Beam diameter usually refers to a beam of circular cross section, but not necessarily so. A beam may, for example, have an elliptical cross section, in which case the orientation of the beam diameter must be specified, e.g., with respect to the major or minor axis of the elliptical cross section.
Beam Divergence - Of an electromagnetic beam, in any plane that intersects the beam axis, the increase in beam diameter with distance from the aperture from which the beam emerges. Note 1: Beam divergence is usually used to characterize electromagnetic beams in the optical regime, i.e., cases in which the aperture from which the beam emerges is very large with respect to the wavelength. Note 2: Beam divergence usually refers to a beam of circular cross section, but not necessarily so. A beam may, for example, have an elliptical cross section, in which case the orientation of the beam divergence must be specified, e.g., with respect to the major or minor axis of the elliptical
Beamsplitter - A device for dividing an optical beam into two or more separate beams. Note: An example of a beamsplitter is a partially reflecting mirror.
Beam Steering - Changing the direction of the main lobe of a radiation pattern. Note: In radio systems, beam steering may be accomplished by switching antenna elements or by changing the relative phases of the rf signals driving the elements. In optical systems, beam steering may be accomplished by changing the refractive index of the medium through which the beam is transmitted or by the use of mirrors or lenses.
Beamwidth - 1. In the radio regime, of an antenna pattern, the angle between the half-power (3-dB) points of the main lobe, when referenced to the peak effective radiated power of the main lobe. Note: Beamwidth is usually expressed in degrees. It is usually expressed for the horizontal plane, but may also be expressed for the vertical plane. 2. For the optical regime, see beam divergence.
Bearer Channel - See B channel. - In the Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN), the B-channel is the channel that carries the main data. (The "B" stands for "bearer" channel.)
In ISDN, there are two levels of service: the Basic Rate Interface, intended for the home and small enterprise, and the Primary Rate Interface, for larger users. Both rates include a number of B- (bearer) channels and a D-channel. The B-channels carry data, voice, and other services. The D-channel carries control and signaling information.
Bearer Service - A telecommunications service that allows transmission of user-information signals between user-network interfaces. See B channel, service access.
Beating - See heterodyne. - 1. To generate new frequencies by mixing two or more signals in a nonlinear device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode mixer. Note: A superheterodyne receiver converts any selected incoming frequency by heterodyne action to a common intermediate frequency where amplification and selectivity (filtering) are provided. 2. A frequency produced by mixing two or more signals in a nonlinear device.
Beeping - Synonym paging, radio paging. - The use of a pocket-size radio receiver capable of alerting its wearer that there is a phone call, either from a displayed phone number or to a predesignated number. Note: Beeping (Radio paging) may be considered a subset of paging.
B8ZS (bipolar 8-zero substitution, also called binary 8-zero substitution, clear channel, and clear 64) - is an encoding method used on T1 circuits that inserts two successive ones of the same voltage - referred to as a
bipolar violation - into a signal whenever eight consecutive zeros are transmitted. The device receiving the signal interprets the bipolar violation as a timing mark, which keeps the transmitting and receiving devices synchronized. Ordinarily, when successive ones are transmitted, one has a positive voltage and the other has a negative voltage.B8ZS is based on an older encoding method called alternate mark inversion (
AMI ). AMI is used with Dataphone Digital Service, the oldest data service still in use that uses 64 Kbps channels. AMI, however, requires the use of 8 Kbps of the 64 Kbps of each channel to maintain synchronization. In a T1 circuit, there are 24 channels. This loss adds up to 192 Kbps, which means that in reality only 56 Kbps is available for data transmission. B8ZS uses bipolar violations to synchronize devices, a solution that does not require the use of extra bits, which means a T1 circuit using B8ZS can use the full 64 Kbps for each channel for data. B8ZS is not compatible with older AMI equipment.T1 technology is used in the United States and Japan. In Europe, a comparable technology called E1 provides 32 channels instead of 24 and uses an encoding scheme called high-density bipolar 3 (HDB3) instead of B8ZS.
A T-carrier line code in which bipolar violations are deliberately inserted if user data contains a string of 8 or more consecutive zeros. Note 1: B8ZS is used to ensure a sufficient number of transitions to maintain system synchronization when the user data stream contains an insufficient number of "ones" to do so. Note 2: B8ZS is used in the European hierarchy at the T1 rate.
bel (B): A unit of measure of ratios of power levels, i.e., relative power levels. Note 1: The number of bels for a given ratio of power levels is calculated by taking the logarithm, to the base 10, of the ratio. Mathematically, the number of bels is calculated as B = log10(P 1/P 2) where P 1 and P 2 are power levels. Note 2: The dB, equal to 0.1 B, is a more commonly used unit.
Bell (BEL) Character - A transmission control character that is used when there is a need to call for user or operator attention in a communications system, and that usually activates an audio or visual alarm or other attention-getting device.
Bell-La Padula Security Model - [A] formal state-transition model of a computer security policy that describes a formal set of access controls based on information sensitivity and subject authorizations.
Bell Operating Company - (see BOC). Historically, any of the 22 operating companies that were divested from AT&T by court order. Note: Cincinnati Bell Telephone Co. and Southern New England Bell Telephone Co. were not included.
Bell Operating Company is a term for any of the 22 original companies (or their successors) that were created when AT&T was broken up in 1983 and given the right to provide local telephone service in a given geographic area. The companies had previously existed as subsidiaries of AT&T and were called the "Bell System." The purpose of the breakup was to create competition at both the local and long-distance service levels. BOCs compete with other, independent companies to sell local phone service. In certain areas, long-distance companies, including AT&T, can now compete for local service. Collectively, companies offering local phone service are referred to legally as local exchange carriers (local exchange carrier).
BOCs are not allowed to manufacture equipment and were initially not allowed to provide long-distance service. The Telecommunications Act of 1996 now permits them to engage in long-distance business under certain circumstances. As of 1996, the BOCs consisted of original and successor companies to:
Bell Telephone Company of Nevada, Illinois Bell, Indiana Bell, Michigan Bell, New England Telephone and Telegraph Company, New Jersey Bell, New York Telephone Company, U S West Communications Company, South Central Bell, Southern Bell, Southwestern Bell, Bell Telephone of Pennsylvania, The Chesapeake and Potomac Telephone Company, The Chesapeake and Potomac Telephone Company of Maryland, The Chesapeake and Potomac Telephone Company of Virginia, The Diamond State Telephone Company, The Ohio Bell Telephone Company, The Pacific Telephone and Telegraph Company, and the Wisconsin Telephone Company.
Bend Loss - See macrobend loss, microbend loss. In an optical fiber, that loss attributable to macrobending. Synonym curvature loss.
Benign - A condition of cryptographic data that cannot be compromised by human access.
Benign Environment - [In security, a] nonhostile environment that may be protected from external hostile elements by physical, personnel, and procedural security countermeasures.
BER (bit error rate) - In telecommunication transmission, the BER is the percentage of bits that have errors relative to the total number of bits received in a transmission, usually expressed as ten to a negative power. For example, a transmission might have a BER of 10 to the minus 6, meaning that, out of 1,000,000 bits transmitted, one bit was in error. The BER is an indication of how often a packet or other data unit has to be retransmitted because of an error. Too high a BER may indicate that a slower data rate would actually improve overall transmission time for a given amount of transmitted data since the BER might be reduced, lowering the number of packets that had to be resent. BER - Abbreviation for bit error ratio.
BERT - Acronym for bit error ratio tester. - A testing device that compares a received data pattern with a known transmitted pattern to determine the level of transmission quality.
Beta Test - A secondary software product test involving select or voluntary participants before the product is marketed to the general public. Note: Participants agree to provide detailed feedback to the product's manufacturer in return for their being allowed to preview, use, and contribute to the final form of the product.
BETRS - Abbreviation for basic exchange telecommunications radio service. - A commercial service that can extend telephone service to rural areas by replacing the local loop with radio communications. Note: In the BETRS, non-government ultra high frequency (UHF) and very high frequency (VHF) common carrier and the private radio service frequencies are shared.
Between-the-lines Entry - Unauthorized access to a momentarily inactive terminal, of a legitimate user, assigned to a communications channel.
BEX - Abbreviation for broadband exchange. A communications switch capable of interconnecting channels having bandwidths greater than voice bandwidth.
B Frame - An MPEG video frame type that provides bidirectional interframe compression. Note: A b frame derives its content from the closest 1 or P frame, one in the past and one in the future. Generating b frames requires greater computing power than does generating 1 or P frames. The use of b frames enables compression ratios of 200:1. Robust MPEG encoders employ a combination of b, 1, and P frame encoding.
Bias - 1. A systematic deviation of a value from a reference value. 2. The amount by which the average of a set of values departs from a reference value. 3. Electrical, mechanical, magnetic, or other force (field) applied to a device to establish a reference level to operate the device. 4. In telegraph signaling systems, the development of a positive or negative dc voltage at a point on a line that should remain at a specified reference level, such as zero. Note: A bias may be applied or produced by (i) the electrical characteristics of the line, (ii) the terminal equipment, and (iii) the signaling scheme.
Bias Distortion - 1. Signal distortion resulting from a shift in the bias. 2. In binary signaling, distortion of the signal in which all the significant intervals have uniformly longer or shorter durations than their theoretical durations. Note: Bias distortion is expressed in percent of the system-specified unit interval.
Biased - In the generation of pseudorandom or random numbers, pertaining to or describing a condition that renders the more likely occurrence of some numbers or patterns than others.
Biconical Antenna - An antenna consisting of two conical conductors, having a common axis and vertex, and extending in opposite directions. Note 1: In a biconical antenna, excitation is applied at the common vertex. Note 2: If one of the cones is reduced to a plane, the antenna is called a discone.
Bidirectional Asymmetry - In data transmission, the condition that exists when information flow characteristics are different in each direction.
Bidirectional Connection - Association established between two higher layer entities for which information is transmitted between both entities.
Bidirectional Coupler - See directional coupler. A transmission coupling device for separately sampling (through a known coupling loss) either the forward (incident) or the backward (reflected) wave in a transmission line. Note: A directional coupler may be used to sample either a forward or backward wave in a transmission line. A unidirectional coupler has available terminals or connections for sampling only one direction of transmission; a bidirectional coupler has available terminals for sampling both directions.
Bidirectional Symmetry - The condition that exists when information flow characteristics are the same in each direction.
Big-Endian - A format for transmission or storage of binary data in which the most significant byte (bit) appears first.
BIH - French abbreviation for International Time Bureau. See International Atomic Time. The time scale established by the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM--International Bureau of Weights and Measures in Sevres, France) on the basis of atomic clock data supplied by cooperating institutions.
Bilateral Control - Synonym bilateral synchronization. - A synchronization control system between exchanges A and B in which the clock at exchange A controls the data received at exchange B and the clock at exchange B controls the data received at exchange A. Note: Bilateral control is usually implemented by deriving the timing from the incoming bit stream.
Bilateral Synchronization - A synchronization control system between exchanges A and B in which the clock at exchange A controls the data received at exchange B and the clock at exchange B controls the data received at exchange A. Note: Bilateral synchronization is usually implemented by deriving the timing from the incoming bit stream. Synonym bilateral control.
Billboard Antenna - An array of parallel dipole antennas with flat reflectors, usually positioned in a line or plane. Note 1: The spacing and dimensions of the dipoles depend on the wavelength. Note 2: The main lobe of a fixed billboard antenna may, within limits, be steered by appropriate phasing of the respective signals to individual elements of the array. Synonym broadside antenna.
Billed Number Screening - Allows you to restrict billing of Collect and/or Third Number Billing calls to your residential or business telephone account.
Binary - 1. Pertaining to a selection, choice, or condition that has two possible different values or states. 2. Pertaining to a fixed radix numeration system that has a radix of 2.
Binary Code - A code, the elements of which can assume either one of two possible states.
Binary-Coded Decimal Code - Synonym binary-coded decimal notation. - A binary notation in which each of the decimal digits is represented by a binary numeral.
Binary-Coded Decimal Interchange Code - See binary-coded decimal notation.
Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) Notation - A binary notation in which each of the decimal digits is represented by a binary numeral. Synonyms binary-coded decimal code, binary-coded decimal representation.
Binary-Coded Decimal Representation - Synonym binary-coded decimal notation. A binary notation in which each of the decimal digits is represented by a binary numeral.
Binary Digit (bit) - See bit. The smallest unit of computer information.
Binary Element - A constituent element of data that takes either of two values or states. Note: Binary element should not be confused with binary digit.
Binary Exponential Backoff - See truncated binary exponential backoff. - In carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) networks and in carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) networks, the algorithm used to schedule retransmission after a collision such that the retransmission is delayed by an amount of time derived from the slot time and the number of attempts to retransmit.
Binary Modulation - The process of varying a parameter of a carrier as a function of two finite, discrete states.
Binary Notation - 1. Any notation that uses two different characters, usually the digits 0 and 1. Note: Data encoded in binary notation need not be in the form of a pure binary numeration system; e.g., they may be represented by a Gray code. 2. A scheme for representing numbers, which scheme is characterized by the arrangements of digits in sequence, with the understanding that successive digits are interpreted as coefficients of successive powers of base 2.
Binary Number - A number that is expressed in binary notation and is usually characterized by the arrangement of bits in sequence, with the understanding that successive bits are interpreted as coefficients of successive powers of the base 2.
Binary String - Synonym bit string. - A sequence of bits. Note: In a bit stream, individual bit strings may be separated by data delimiters.
Binary Synchronous (bi-sync) Communication - A character-oriented, data-link-layer protocol. Note: The bi-sync protocol is being phased out of most computer communication networks in favor of bit-oriented protocols such as SDLC, HDLC, and ADCCP.
Binding - 1. In computer, communications, and automatic data processing systems, assigning a value or referent to an identifier. Note: Examples of binding include assigning a value to a parameter, assigning an absolute address to a virtual or relative address, and assigning a device identifier to a symbolic address or label. 2. [In security, the] process of associating a specific communications terminal with a specific cryptographic key or associating two related elements of information.
Biometric - Any specific and uniquely identifiable physical human characteristic, e.g., of the retina, iris, acoustic spectrum of the voice (i.e., voiceprint), fingerprint(s), handwriting, pattern of finger lengths, etc., that may be used to validate the identity of an individual. Note: Biometrics provide a highly secure means of identification, for purposes of security involving, e.g., Internet communications and cryptosystems.
Biometrics - Automated methods of authenticating or verifying an individual based upon a physical or behavioral characteristic.
Biphase Modulation - Synonym phase-shift keying. - 1. In digital transmission, angle modulation in which the phase of the carrier is discretely varied in relation either to a reference phase or to the phase of the immediately preceding signal element, in accordance with data being transmitted. 2. In a communications system, the representing of characters, such as bits or quaternary digits, by a shift in the phase of an electromagnetic carrier wave with respect to a reference, by an amount corresponding to the symbol being encoded. Note 1: For example, when encoding bits, the phase shift could be 0° for encoding a "0," and 180° for encoding a "1," or the phase shift could be -90
for "0" and +90° for a "1," thus making the representations for "0" and "1" a total of 180° apart. Note 2: In PSK systems designed so that the carrier can assume only two different phase angles, each change of phase carries one bit of information, i.e., the bit rate equals the modulation rate. If the number of recognizable phase angles is increased to 4, then 2 bits of information can be encoded into each signal element; likewise, 8 phase angles can encode 3 bits in each signal element.
Bipolar 8-Zero Substitution (B8ZS, binary 8-zero substitution, clear channel, and clear 64) - is an encoding method used on T1 circuits that inserts two successive ones of the same voltage - referred to as a
bipolar violation - into a signal whenever eight consecutive zeros are transmitted. The device receiving the signal interprets the bipolar violation as a timing mark, which keeps the transmitting and receiving devices synchronized. Ordinarily, when successive ones are transmitted, one has a positive voltage and the other has a negative voltage (see B8ZS).Bipolar Signal - 1. A signal that may assume either of two polarities, neither of which is zero. Note 1: A bipolar signal may have a two-state non-return-to-zero (NRZ) or a three-state return-to-zero (RZ) binary coding scheme. Note 2: A bipolar signal is usually symmetrical with respect to zero amplitude, i.e., the absolute values of the positive and negative signal states are nominally equal. 2. A pseudoternary signal, conveying binary digits, in which successive "ones" (marks, pulses) are of alternating, positive (+) and negative (-) polarity, equal in amplitude, and in which a "zero" (space, no pulse) is of zero amplitude.Synonym alternate mark inversion signal.
Bipolar Violation - In a bipolar alternate mark inversion (AMI) signal, a "one" condition (mark, pulse) having the same polarity as its predecessor.
Birefringence - In a transparent material, anisotropism of the refractive index, which varies as a function of polarization as well as orientation with respect to the incident ray. Note 1: The term "birefringence" means, literally, " double refraction." Note 2: All crystals except those of cubic lattice structure exhibit some degree of anisotropy with regard to their physical properties, including refractive index. Other materials, such as glasses or plastics, become birefringent when subjected to mechanical strain. Note 3: Birefringent materials, including crystals, have the ability to refract an unpolarized incident ray into two separate, orthogonally polarized rays, which in the general case take different paths, depending on orientation of the material with respect to the incident ray. The refracted rays are referred to as the "ordinary," or "O" ray, which obeys Snell's Law, and the "extraordinary," or "E" ray, which does not. Synonym double refraction.
Birefringent Medium - See birefringence.
Birthday Phenomenon - The phenomenon stating that, for a category size of 365 (the number of days in a year), after only 23 people are gathered, the probability is greater than 0.5 that at least two people have a common birthday (month and day). Note: The birthday phenomenon applied to DES encryption means that where category size is 264, this same probability of a repeat (match) occurs at approximately r=232. The theory behind this principle applies that for a 64-bit block encryption operation with a fixed key, if one has a text dictionary of 232 plaintext/ciphertext pairs and 232 blocks of ciphertext produced from random input, then it should be expected that one block of unknown ciphertext will be found in the dictionary.
B-ISDN - Abbreviation for broadband ISDN.
Bistable - Pertaining to a device capable of assuming either one of two stable states.
Bistable Circuit - Synonym flip-flop. - A device that may assume either one of two reversible, stable states. Note 1: The bistable circuit is used as a basic control element in computer and communications systems. Note 2: In a bistable circuit, the transition from one stable state to the other is unstable, i.e., for the very short period during which the transition takes place, both outputs may assume the same state, which state may be unpredictable.
Bistable Multivibrator - Synonym flip-flop. - A device that may assume either one of two reversible, stable states. Note 1: The bistable multivibrator is used as a basic control element in computer and communications systems. Note 2: In a bistable multivibrator, the transition from one stable state to the other is unstable, i.e., for the very short period during which the transition takes place, both outputs may assume the same state, which state may be unpredictable.
Bistable Trigger Circuit - Synonym flip-flop. - A device that may assume either one of two reversible, stable states. Note 1: The bistable trigger circuit is used as a basic control element in computer and communications systems. Note 2: In a bistable trigger circuit, the transition from one stable state to the other is unstable, i.e., for the very short period during which the transition takes place, both outputs may assume the same state, which state may be unpredictable.
Bi-Sync - Abbreviation for binary synchronous (bi-sync) communication. - A character-oriented, data-link-layer protocol. Note: The bi-sync protocol is being phased out of most computer communication networks in favor of bit-oriented protocols such as SDLC, HDLC, and ADCCP.
Bit - (binary digit) The smallest unit of computer information.
Bit-by-Bit Asynchronous Operation - In data transmission, an operation in which manual, semiautomatic, or automatic shifts in the data modulation rate are accomplished by gating or slewing the clock modulation rate. Note: For example, bit-by-bit asynchronous operation may be at 50 b/s one moment and at 1200 b/s the next moment.
Bit Configuration - The sequence of bits used to encode a character.
Bit-Count Integrity (BCI) - 1. In message communications, the preservation of the exact number of bits that are in the original message. 2. In connection-oriented services, preservation of the number of bits per unit time. Note: Bit-count integrity is not the same as bit integrity, which requires that the delivered bits correspond exactly with the original bits.
Bit Density - The number of bits recorded per unit length, area, or volume. Note: Bit density is the reciprocal of bit pitch. Synonym recording density.
Bit Depth - Synonym bits per pixel. - In a digitized image, the number of bits used to represent the luminance (brightness, gray scale) and chroma (color) information contained in each pixel.
Biternary Transmission - Digital transmission in which two binary pulse trains are combined for transmission over a channel in which the available bandwidth is sufficient for transmission of only one of the two pulse trains at a time if they remain in binary form.
Bit Error - A bit that is transferred from the source to the destination within the assigned time slot, but that, when delivered, is of a different value from that sent from the source.
Bit Error Rate - (See BER)
Bit Error Ratio (BER) - The number of erroneous bits divided by the total number of bits transmitted, received, or processed over some stipulated period. Note 1: Examples of bit error ratio are (a) transmission BER, i.e., the number of erroneous bits received divided by the total number of bits transmitted; and (b) information BER, i.e., the number of erroneous decoded (corrected) bits divided by the total number of decoded (corrected) bits. Note 2: The BER is usually expressed as a coefficient and a power of 10; for example, 2.5 erroneous bits out of 100,000 bits transmitted would be 2.5 out of 105 or 2.5 × 10-5.
Bit Error Ratio Tester (BERT) - A testing device that compares a received data pattern with a known transmitted pattern to determine the level of transmission quality.
Bit Interleaved Parity N (BIP-N): A method of error monitoring. If even parity is used, an N bit code is generated by the transmitting equipment over a specified portion of the signal in such a manner that the first bit of the code provides even parity over the first bit of all N-bit sequences in the covered portion of the signal, the second bit provides even parity over the second bits of all N-bit sequences within the specified portion, and so on. Even parity is generated by setting the BIP-N bits so that there are an even number of 1s in each of all N-bit sequences including the BIP-N.
Bit Interval - See bit, character interval, unit interval.
Bit Inversion - 1. The changing of the state of a bit to the opposite state. 2. The changing of the state that represents a given bit, i.e., a 0 or a 1, to the opposite state. Note: For example, if a 1 is represented by a given polarity or phase at one stage in a circuit, the 1 is represented by the opposite polarity or phase at the next stage.
Bitmap - In computer graphics, a representation of an image (which category includes characters) by code or a coding scheme that defines (a) the position of pixels by row (horizontal position) and column (vertical position), and (b) individual pixel characteristics such as gray scale and color. Loosely synonymous with raster.
Bitmapped Graphics - In computer graphics, an image created with, or represented by, a matrix of pixels. Synonym [loosely] raster graphics.
Bit Masking - In embedded ADPCM (adaptive differential pulse-code modulation), the process of discarding the enhancement bits.
BITNET - Abbreviation for Because It's Time NETwork. An early (ca. 1981) store-and-forward digital communications network interconnecting universities and research institutions worldwide. Note: BITNET, which is now obsolete, had a purpose akin to that of the present Internet, but was not nearly so robust, and at a speed of only 9600 b/s, it could not support the data rates presently attainable via the Internet.
Bit Padding - is the addition of one or more extra bits to a transmission or storage unit to make it conform to a standard size. Some sources identify bit padding as a type of bit stuffing.
Bit Pairing - The practice of establishing, within a code set, a number of subsets that have an identical bit representation except for the state of a specified bit. Note: An example of bit pairing occurs in the International Alphabet No. 5 and the American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII), where the upper case letters are related to their respective lower case letters by the state of bit six.
Bit Period (T) - The amount of time required to transmit a logical one or a logical zero
Bit Position - A character position in a word in a binary notation.
Bit Rate (BR) - 1. In a bit stream, the number of bits occurring per unit time, usually expressed in bits per second. Note: For n-ary operation, the bit rate is equal to log 2 n times the rate (in bauds), where n is the number of significant conditions in the signal. 2. The rate of transmission of information in binary (two state) form in bits per unit time.
Bit-Rate•Distance Product - See bandwidth•distance product. - Of an optical fiber, under specified launching and cabling conditions, at a specified wavelength, a figure of merit equal to the product of the fiber's length and the 3-dB bandwidth of the optical signal. Note 1: The bit-rate•distance product is usually stated in megahertz • kilometer (MHz •km) or gigahertz •kilometer (GHz•km). Note 2: The bit-rate•distance product, which is normalized to 1 km, is a useful figure of merit for predicting the effective fiber bandwidth for other lengths, and for concatenated fibers.
Bit Robbing - In digital carrier systems, the practice or technique of preempting, at regular intervals and for the purpose of transmitting signaling information, one digit time slot that (a) is associated with the given user channel for which signaling is required, and (b) is used primarily for transporting encoded speech via that channel. Note 1: Bit robbing is an option in networks compatible with T-carrier, e.g., an ISDN. Note 2: In conventional T-carrier systems, bit robbing uses, in every sixth frame, the time slot associated with the least significant bit. Synonym speech digit signaling.
Bit Robbing - is a technique used in signaling on the T-carrier system, the widely-used system for transmitting both voice and data in digital form in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and in private networks. In the basic T-1 system, a 193 bit frame, serving 24 channels, is transmitted in a sequence of 12 frames that are referred to as a superframe. Special signaling information, such as whether a voice channel is on-hook or off-hook, is included within the superframe by using a bit (called the a bit) that is "robbed" from the sixth frame as a signaling bit and another bit (the b bit) that is robbed from the 12th frame.
Bit robbing is acceptable for voice conversations or data transmissions that are received by a modem but not for "pure" data transmission (where every bit is significant). Bit robbing is the reason that a 64 Kbps channel only carries 56 Kbps of usable data. Bit robbing is a form of in-band signalling.
Bit-Sequence Independence - A characteristic of some digital data transmission systems that impose no restrictions on, or modification of, the transmitted bit sequence. Note: Bit-sequence-independent protocols are in contrast to protocols that reserve certain bit sequences for special meanings, such as the flag sequence, 01111110, for HDLC, SDLC, and ADCCP protocols.
Bit Slip - In digital transmission, the loss of a bit or bits, caused by variations in the respective clock rates of the transmitting and receiving devices. Note: One cause of bit slippage is overflow of a receive buffer that occurs when the transmitter's clock rate exceeds that of the receiver. This causes one or more bits to be dropped for lack of storage capacity.
Bits Per Inch (b/in) - A unit used to express the linear bit density of data in storage. Note: The abbreviation " bpi" is not in accordance with international standards, and is therefore deprecated.
Bits Per Pixel (BPP) - In a digitized image, the number of bits used to represent the luminance (brightness, gray scale) and chroma (color) information contained in each pixel. Synonym bit depth.
Bits Per Second (bps or bit/sec) - In data communications, bits per second is a common measure of data speed for computer modems and transmission carriers. As the term implies, the speed in bps is equal to the number of bits transmitted or received each second.
Larger units are sometimes used to denote high data speeds. One kilobit per second (abbreviated Kbps in the U.S.; kbps elsewhere) is equal to 1,000 bps. One megabit per second (Mbps) is equal to 1,000,000 bps or 1,000 Kbps.
Bit-Stepped - Pertaining to the control of digital equipment in which operations are performed one step at a time at the applicable bit rate.
Bit-Stream Transmission - 1. In bit-oriented systems, the transmission of bit strings. 2. In character-oriented systems, the transmission of bit streams that represent characters. Note: In bit-stream transmission, the bits usually occur at fixed time intervals, start and stop signals are not used, and the bit patterns follow each other in sequence without interruption.
Bit String - A sequence of bits. Note: In a bit stream, individual bit strings may be separated by data delimiters. Synonym binary string.
Bit Stuffing - is the insertion of one or more bits into a transmission unit as a way to provide signaling information to a receiver. The receiver knows how to detect and remove or disregard the stuffed bits. Bit stuffing is the insertion of noninformation bits into data.
For example, the timing or bit rate of T-carrier system signals is constantly synchronized between any terminal device and an adjacent repeater or between any two repeaters. The synchronization is achieved by detecting the transition in polarity for 1 bits in the data stream. (T-1 signalling uses bipolar signaling, where each successive bit with a value of 1 is represented by voltage with a reverse polarity from the previous bit. Bits with a value of 0 are represented by a no-voltage time slot.) If more than 15 bits in a row are sent with a 0 value, this "lull" in 1 bits that the system depends on for synchronization may be long enough for two end points to become out of synchronization. To handle this situation (the sequence of more than 15 0 bits), the signal is "stuffed" with a short, unique bit pattern (which includes some 1 bits) that is recognized as a synchronization pattern. The receiving end removes the stuffed bits and restores the bit stream to its original sequence.
In another example of bit stuffing, a standard HDLC packet begins and ends with 01111110. To make sure this sequence doesn't appear again before the end of the packet, a 0 is inserted after every five consecutive 1s.
Bit stuffing is defined by some to include bit padding or the addition of bits to a tranmission to make the tranmission unit conform to a standard size.
Note 1: Stuffed bits should not be confused with overhead bits. Note 2: In data transmission, bit stuffing is used for various purposes, such as for synchronizing bit streams that do not necessarily have the same or rationally related bit rates, or to fill buffers or frames. The location of the stuffing bits is communicated to the receiving end of the data link, where these extra bits are removed to return the bit streams to their original bit rates or form. Bit stuffing may be used to synchronize several channels before multiplexing or to rate-match two single channels to each other. Synonym positive justification.
Bit Stuffing Rate - See nominal bit stuffing rate. - The rate at which stuffing bits are inserted when both the input and output bit rates are at their nominal values.
Bit Synchronization - Synchronization in which the decision instant is brought into alignment with the received bit, i.e., the basic signaling element.
Bit Synchronous Operation - Operation in which data circuit terminating equipment (DCE), data terminal equipment (DTE), and transmitting circuits are all operated in bit synchronism with a clock. Note 1: In bit synchronous operation, clock timing is usually delivered at twice the modulation rate, and one bit is transmitted or received during each clock cycle. Note 2: Bit synchronous operation is sometimes erroneously referred to as digital synchronization.
BIU - Abbreviation for bus interface unit. See network interface device.
BLACK - 1. [A] designation applied to telecommunications and automated information systems, and to associated areas, circuits, components, and equipment, in which only unclassified signals are processed. Note: Encrypted signals are unclassified. 2. Designation applied to information systems, and to associated areas, circuits, components, and equipment, in which national security information is not processed.
Blackbody - A totally absorbing body that does not reflect radiation. Note: In thermal equilibrium, a blackbody absorbs and radiates at the same rate; the radiation will just equal absorption when thermal equilibrium is maintained.
Black Box - is any device, sometimes highly important, whose workings are not understood by or accessible to its user. According to Edward Tenner, writing in The Washington Post, the first black box was a gun sight carried on World War II Flying Fortresses, with hidden components that corrected for environmental variables, such as wind speed. The crew probably didn't know how the device worked, but they knew it might be crucial to their survival. Nowadays, there are two types of black box carried on aircraft, which may be combined into a single device: a flight data recorder (FDR), which logs information such as speed and altitude, and a cockpit voice recorder (CVR), which logs all voice communication in the cockpit. These black boxes also carry beacons to help find the aircraft in a rescue situation.
Black box is a generic term for a single-purpose device having limited functionality. Note: A black box is usually represented in schematic drawings as a geometric figure, possibly with defined connector (s), but no details with respect to the type or number of internal components that enable it to perform its defined task.
Black Burst - A composite color video signal comprised of sync, color burst, and black video. Note: Black burst is used to synchronize (genlock) other video sources to the same sync and color information. Black burst generators are used in video studios to "lock" the entire facility to a common signal ("house sync" or "house black").
Black Facsimile Transmission - 1. In facsimile systems using amplitude modulation, that form of transmission in which the maximum transmitted power corresponds to the maximum density of the subject. 2. In facsimile systems using frequency modulation, that form of transmission in which the lowest transmitted frequency corresponds to the maximum density of the subject.
Black Level - Of a television baseband signal (e.g., NTSC composite video), the voltage level corresponding to black or to the maximum limit of black peaks.
Black Noise - Noise that has a frequency spectrum of predominately zero power level over all frequencies except for a few narrow bands or spikes. Note: An example of black noise in a facsimile transmission system is the spectrum that might be obtained when scanning a black area in which there are a few random white spots. Thus, in the time domain, a few random pulses occur while scanning.
Black Recording - 1. In facsimile systems using amplitude modulation, recording in which the maximum received power corresponds to the maximum density of the record medium. 2. In a facsimile system using frequency modulation, recording in which the lowest received frequency corresponds to the maximum density of the record medium.
Black Signal - In facsimile, the signal resulting from scanning a maximum-density area of the object.
BLACK signal - A signal that represents only unclassified or encrypted information, usually in cryptographic systems.
Blanketing - The interference that is caused by the presence of an AM broadcast signal of one volt per meter (V/m) or greater strengths in the area adjacent to the antenna of the transmitting station. The 1 V/m contour is referred to as the blanket contour and the area within this contour is referred to as the "blanket area."
Blanketing Area - In the vicinity of a transmitting antenna, the area in which the signal from that antenna interferes with the reception of other signals. Note: The blanketing area around a given transmitting antenna depends on the selectivity and sensitivity of the receiver, and on the respective levels of the other signals in question.
Blanking - 1. The period of time in which no video image is displayed. 2. In graphic display, the suppression of the display of one or more display elements or display segments.
Blanking Interval - In raster-scanned television technology, the period between (a) the end of one horizontal scanning line and the beginning of the next (the horizontal blanking interval), or (b) the end of one field and the beginning of the next (the vertical blanking interval), during which the display of picture information is suppressed. Note 1: Blanking intervals were a necessary part of the original NTSC and other, similar, television signal structures, which were based on the state of the art of electronics in the 1930s and even earlier. Both the camera and display (television receiver) were dependent upon specialized electron tubes that employed an electron beam that was swept (scanned) across the photosensitive or photoemissive area, respectively, of the tube in question. It was necessary that the beam be turned off during its return sweep (trace), to avoid marring the image (trace). While television cameras based on charge-coupled devices (CCDs), which have no such constraint, have supplanted cameras based on electron beams, most receivers still depend upon beam-based tubes. Note 2: To support a smooth transition (avoid obsolescence of older receivers) as the state of the art improved, the basic original signal structure was retained, with modifications (e.g., the superposition of signals necessary to support color).
Blanking Level - In a baseband television signal, the DC level (nominally 0 volts) from which the amplitudes of the various components of the signal are measured. Conventionally, the viewable parts of the signal (except subcarriers) are positive with respect to blanking, while the synchronizing pulses are negative with respect to blanking. In North American NTSC signals, the darkest portions of the image (black level) are offset positively with respect to blanking level. This offset is called either pedestal or setup, depending on how it is generated. In almost all other television signals, including component RGB, there is no setup, so black level is the same voltage as blanking level. Synonym pedestal.
Blind Transmission - Transmission without obtaining a receipt, i.e., acknowledgement of reception, from the intended receiving station. Note: Blind transmission may occur or be necessary when security constraints, such as radio silence, are imposed, when technical difficulties with a sender's receiver or receiver's transmitter occur, or when lack of time precludes the delay caused by waiting for receipts.
Blinking - In graphic display devices, an intentional periodic change in the intensity of one or more display elements or display segments.
Block - 1. A group of bits or digits that is transmitted as a unit and that may be encoded for error-control purposes. 2. A string of records, words, or characters, that for technical or logical purposes are treated as a unit. Note 1: Blocks (a) are separated by interblock gaps, (b) are delimited by an end-of-block signal, and (c) may contain one or more records. Note 2: A block is usually subjected to some type of block processing, such as multidimensional parity checking, associated with it. 3. In programming languages, a subdivision of a program that serves to group related statements, delimit routines, specify storage allocation, delineate the applicability of labels, or segment parts of the program for other purposes.
Block Character - See end-of-transmission-block character. - A transmission control character used to indicate the end of a transmission block of data when data are divided into such blocks for transmission purposes.
Block Check - In the processing or transmission of digital data, an error-control procedure that is used to determine whether a block of data is structured according to given rules.
Block Check Character (BCC) - A character added to a transmission block to facilitate error detection. Note: In longitudinal redundancy checking and cyclic redundancy checking, block check characters are computed for, and added to, each message block transmitted. This block check character is compared with a second block check character computed by the receiver to determine whether the transmission is error free.
Block Code - An error detection and/or correction code in which the encoded block consists of N symbols, containing K information symbols (K <N) and N-K redundant check symbols, such that most naturally occurring errors can be detected and/or corrected.
Block Diagram - A diagram of a system, a computer, or a device in which the principal parts are represented by suitably annotated geometrical figures to show both the basic functions of the parts and their functional relationships.
Block Distortion - In the received image in video systems, distortion characterized by the appearance of an underlying block encoding structure.
Block Dropping - A process by which one or more of the less significant bits of all the samples stored in a packet are dropped to alleviate congestion.
Block Efficiency - In a block, the ratio of the number of user information bits to the total number of bits. Note: For a given block scheme, block efficiency represents the maximum possible efficiency for a given block scheme transmitted over a perfect transmission link.
Block Error - A block within which at least one bit error occurs when the block is transferred from the source to the destination within the time slot assigned.
Block-Error Probability - The expected block-error ratio.
Block-Error Ratio - 1. The ratio of the number of incorrectly received blocks to the total number of blocks transferred. Note: The block-error ratio is calculated using empirical measurements. Multiple block-error ratios may be used to predict block-error probability. 2. The ratio of the number of blocks that contain at least one bit in error to the total number of blocks transmitted in a given time interval.
Blocking - 1. The formatting of data into blocks for purposes of transmission, storage, checking, or other functions. 2. Denying access to, or use of, a facility, system, or component. 3. The failure of a telecommunications network to meet a user service demand, because of the lack of an available communications path.
Blocking Criterion - In telephone traffic engineering, a criterion that specifies the maximum number of calls or service demands that fail to receive immediate service. Note: The blocking criterion is usually expressed in probabilistic notation, such as P.001.
Blocking Factor - The number of records in a block. Note: The blocking factor is calculated by dividing the block length by the length of each record contained in the block. If the records are not of the same length, the average record length may be used to compute the blocking factor. Synonym grouping factor.
Blocking Formula - A specific probability distribution function intended to model calling patterns of users who fail to find available facilities. Note: There are several blocking formulas. The applicability of each to a given situation depends on its underlying assumptions regarding caller behavior.
Blocking Network - In telecommunications, a network that has fewer transmission paths than would be required if all users were to communicate simultaneously. Note: Blocking networks are used because not all users require service simultaneously. Certain statistical distributions apply to the patterns of user demand.
Blocking Options - Local phone companys may offer several blocking options that you may subscribe to such as Anonymous Call Rejection, Billed Number Screening, Call Block 900/976 Restriction, Call Block Full Restriction, Call Block International Restriction, Call Block Long Distance Toll Restriction, Caller ID - Block Per Line, Caller ID - Block Per Call, and Pay Per Use Feature Blocking. Monthly Recurring Charges may apply. Most phone companies must provide and cannot charge local customers for Caller ID Per-Call Blocking of their number.
Block Length - The number of data units, such as bits, bytes, characters, or records, in a block.
Block-Loss Probability - The ratio of the number of lost blocks to the total number of block transfer attempts during a specified period.
Block-Misdelivery Probability - The ratio of the number of misdelivered blocks to the total number of block transfer attempts during a specified period.
Block Parity - The designation of one or more bits in a block as parity bits used to force the block into a selected parity, either odd or even. Note: Block parity is used to assist in error detection or correction.
Block Transfer - The process, initiated by a single action, of transferring one or more blocks of data.
Block Transfer Attempt - A coordinated sequence of user and telecommunication system activities undertaken to effect transfer of an individual block from a source user to a destination user. Note: A block transfer attempt begins when the first bit of the block crosses the functional interface between the source user and the telecommunication system. A block transfer attempt ends either in successful block transfer or in block transfer failure.
Block Transfer Efficiency - The average ratio of user information bits to total bits in successfully transferred blocks.
Block Transfer Failure - Failure to deliver a block successfully. Note: The principal block transfer failure outcomes are: lost block, misdelivered block, and added block.
Block Transfer Rate - The number of successful block transfers during a performance measurement period divided by the duration of the period.
Block Transfer Time - The average value of the duration of a successful block transfer attempt. Note: A block transfer attempt is successful if (a) the transmitted block is delivered to the intended destination user within the maximum allowable performance period and (b) the contents of the delivered block are correct.
Blue Noise - In a spectrum of frequencies, a region in which the spectral density, i.e., power per hertz, is proportional to the frequency.
Blue-Screening - See chroma keying. - . Note 1: Chroma keying is used to create an overlay effect in the final picture, e.g., to insert a false background, such as a weather map or scenic view, behind the principal subject being photographed. Note 2: The principal subject is photographed against a background having a single color or a relatively narrow range of colors, usually in the blue or green. When the phase of the chroma signal corresponds to the preprogrammed state or states associated with the background color, or range of colors, behind the principal subject, the signal from the alternate, i.e., false, background is inserted in the composite signal and presented at the output. When the phase of the chroma signal deviates from that associated with the background color(s) behind the principal subject, video associated with the principal subject is presented at the output.
Bluetooth - A low-power, short-range, rf technology that allows the connection of intelligent communications devices or appliances in a household or an office in a short-range wireless network. Examples of Bluetooth applications are transferring data between cell phones, radios, pagers, personal digital assistants, notebook computers, video and still cameras, audio players, and local area networks.
Blurring - In television and video systems, a global distortion over the entire image, characterized by reduced sharpness of edges and limited spatial detail.
BNC connector - A type of bayonet (twist-lock) coaxial connector commonly used in applications involving small (e.g., RG-59, RG-62) coaxial cables.
Board - In computers, a board, depending on usage, can be short for motherboard, the physical arrangement of a computer's basic components and circuitry, or it can refer to an expansion board (or card or adapter), which fits into one of the computer's expansion slots and provides expanded capability.
BOC (Bell operating company) Abbreviation for Bell Operating Company. - is a term for any of the 22 original companies (or their successors) that were created when AT&T was broken up in 1983 and given the right to provide local telephone service in a given geographic area. The companies had previously existed as subsidiaries of AT&T and were called the "Bell System." The purpose of the breakup was to create competition at both the local and long-distance service levels. BOCs compete with other, independent companies to sell local phone service. In certain areas, long-distance companies, including AT&T, can now compete for local service. Collectively, companies offering local phone service are referred to legally as local exchange carriers (local exchange carrier).
BOCs are not allowed to manufacture equipment and were initially not allowed to provide long-distance service. The Telecommunications Act of 1996 now permits them to engage in long-distance business under certain circumstances. As of 1996, the BOCs consisted of original and successor companies to:
Bell Telephone Company of Nevada, Illinois Bell, Indiana Bell, Michigan Bell, New England Telephone and Telegraph Company, New Jersey Bell, New York Telephone Company, U S West Communications Company, South Central Bell, Southern Bell, Southwestern Bell, Bell Telephone of Pennsylvania, The Chesapeake and Potomac Telephone Company, The Chesapeake and Potomac Telephone Company of Maryland, The Chesapeake and Potomac Telephone Company of Virginia, The Diamond State Telephone Company, The Ohio Bell Telephone Company, The Pacific Telephone and Telegraph Company, and the Wisconsin Telephone Company.
Historically, a BOC is any of the 22 operating companies that were divested from AT&T by court order. Note: Cincinnati Bell Telephone Co. and Southern New England Bell Telephone Co. were not included.
Boltzmann's Constant (k): The number that relates the average energy of a molecule to its absolute temperature. Note: Boltzmann's constant is approximately 1.38 × 10-23 J/K (joules/ kelvin).
Bond - An electrical connection that provides a low-resistance path between two conducting surfaces.
Bonding - 1. In electrical engineering, the process of connecting together metal parts so that they make low resistance electrical contact for direct current and lower frequency alternating currents. [JP1] 2. The process of establishing the required degree of electrical continuity between two or more conductive surfaces that are to be joined.
Bookmark - A name or address of an Internet resource, stored in a software file at a user's site, e.g., in a desktop computer, for convenient future use. Note: An example of a bookmark is an entry in a bookmark file (or bookmark list) such as maintained within or by a Web browser for the convenience of the user in revisiting a previously visited Web site.
Bookmark List - Synonym hotlist. - A list of frequently used web locations and URLs (Uniform Resource Locators). Note: Hotlists may consist of a) lists of bookmarks accessed by a browser or b) lists of URLs at a web site for linking to other relevant web sites. Synonyms hotlist, go list, history list.
Boolean function - 1. A mathematical function that describes Boolean operations. 2. A switching function in which the number of possible values of the function and each of its independent variables is two.
Boolean operation - 1. Any operation in which each of the operands and the result take one of two values. Note: Typical states are "0 or 1," "on or off," "open or closed," or "present or absent." 2. An operation that follows the rules of Boolean Algebra.
Bootstrap - 1. A technique or device designed to bring about a desired state by means of its own action. 2. That part of a computer program that may be used to establish another version of the computer program. 3. The automatic procedure whereby the basic operating system of a processor is reloaded following a complete shutdown or loss of memory. 4. A set of instructions that cause additional instructions to be loaded until the complete computer program is in storage. 5. To initialize a system by means of a bootstrap.
Bootup - In computer science, the initial sequence of events (usually preprogrammed in firmware present in the computer) that are necessary to start a computer; i.e., to initialize its operating system, load programs into memory, etc., when (a) it is first powered up, or (b) when already powered up, upon some kind of assenting action by the user.
Boot Up - To take some kind of assenting action to initiate computer bootup, e.g., to turn on the primary power (often referred to as initiating a cold bootup) or restart a powered-up computer (often referred to as initiating a hot bootup or hot reboot).
Bose-Chaudhuri-Hochquenghem code - See BCH code. A multilevel, cyclic, error-correcting, variable-length digital code used to correct errors up to approximately 25% of the total number of digits. Note: BCH codes are not limited to binary codes, but may be used with multilevel phase-shift keying whenever the number of levels is a prime number or a power of a prime number, such as 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 11, and 13. A BCH code in 11 levels has been used to represent the 10 decimal digits plus a sign digit.
Bot - Abbreviation for robot. A relatively small and focused computer application that (a) runs continuously, in the background (i.e., simultaneously), as other programs are being run, and (b) responds automatically to a user's activity. Synonyms agent, droid, infobot. Note 1: Many bots are created for the benefit of the user, e.g., those that send information upon request, perform automated searches, or monitor messages in a network forum. Other robots (e.g., a computer virus) are intended to harm the user or to spam the user (e.g., with advertising). Note 2: Many bots have nicknames that loosely describe their function. Some examples of bots are:
adbot A bot that searches newsgroups and other on-line documents for email addresses. When one is found, an advertisement is automatically sent to that address. The address is usually saved in a database for sale to other advertisers. Alternatively, an adbot can be one that automatically posts advertisements to newsgroups and other network forums. crawler Synonym web crawler. knowbot Abbreviation for knowledge robot. A bot that automatically searches on-line information for data relevant to a user's previous search criteria. knowledge robot See knowbot. list server A bot that accepts messages from users and then sends a copy of that messages to all members of the related mailing list. The list server will also allow list members to customize the way messages are sent to them (e.g., the messages can be sent as they are received by the list server or saved, compiled, and then sent). pokerbot A bot that automatically plays the game of poker in various on-line forums. Note: Many on-line games have had bots designed to play them, e.g., a chessbot or a bridgebot. portal A bot that serves as a starting point for browsers. A portal will often include a search engine. robot See bot. robotic librarian Synonym search engine. search bot Synonym search engine. search engine A bot that accepts words or phrases from an Internet user via a browser, searches a database for matching web pages, and displays a list of those pages that match the search criteria. spambot A bot that sends unwanted, unrequested, and usually repetitive e-mail or messages directly to a user or to a message forum. In most cases, this unwanted information is commercial advertisements, although the message can be propaganda supporting a cause or nonsense messages designed to fill up a user's mailbox. spider Synonym web crawler. web crawler A bot that searches the world wide web for new and updated web pages. Found pages are categorized by subject and placed in a database. Typically, an associated search engine will access that database. wizard A bot that has some ability to make informed decisions. For example, a wizard might determine the city from which you are accessing the network and provide to you the current weather report for your area. Bounce - To return, to the sender, e-mail that is, for whatever reason, undeliverable to its intended destination. Note 1: There are various reasons why e-mail may be bounced. Examples are an incorrect address, problems with local network facilities, and problems with telecommunications links. Note 2: Bounced e-mail is often accompanied by an error message describing the reason that it was not delivered.
Bouncing Busy Hour (BBH) - The hour in which the highest usage is measured for any day. The readings are on the hour or half hour. The selected clock hour will vary from day to day, depending on the measured usage.
Boundary - 1. [In security,] Software, hardware, or a physical barrier that limits access to a system or part of a system.2. Synonym [in networking] section boundary.
Bound Mode - In an optical fiber, a mode that (a) has a field intensity that decays monotonically in the transverse direction everywhere external to the core and (b) does not lose power to radiation. Note: Except for single-mode fibers, the power in bound modes is predominantly contained in the core of the fiber.Synonyms guided mode, trapped mode.
Bound Ray - In an optical fiber, a ray that is confined primarily to the core. Note: A guided ray satisfies the relation given by
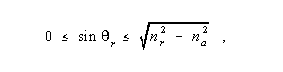
where
r is the angle the ray makes with the fiber axis, r is the radial position, i.e., radial distance, of the ray from the fiber axis, nr is the refractive index at the radial distance r from the fiber axis, and na is the refractive index at the core radius, a, i.e., at the core-cladding interface. Guided rays correspond to bound modes, i.e., guided modes, in terms of modes rather than rays. Synonyms guided ray, trapped ray.
BPI ( bpi) - See bits per inch. - A unit used to express the linear bit density of data in storage. Note: The abbreviation " bpi" is not in accordance with international standards, and is therefore deprecated.
BPS - (See bits per second). - In data communications, bits per second is a common measure of data speed for computer modems and transmission carriers. As the term implies, the speed in bps is equal to the number of bits transmitted or received each second.
Braid - 1. An essential part of many fiber-optic cable designs, consisting of a layer of woven yarn. Note: In the case of single-fiber loose-buffered or two-fiber "zip-cord" loose-buffered fiber-optic cables, the braid is situated between the buffer tube and jacket. In the case of cables having multiple buffer tubes, the braid is usually situated between the inner jacket and outer jacket. 2. Loosely, an unwoven parallel bundle of yarn situated around the tight buffer of a single-fiber or two-fiber "zip-cord" fiber-optic cable. Note 1: The braid serves to add tensile strength to the cable. The braid may also be anchored to an optical connector or splice organizer assembly to secure the end of the cable. Note 2: The braid is often of an aramid yarn.
Branch - 1. In a computer program, a conditional jump or departure from the implicit or declared order in which instructions are being executed. 2. To select a branch, as in definition #1. 3. A direct path joining two nodes of a network or graph. 4. In a power distribution system, a circuit from a distribution device (power panel) of a lower power handling capability than that of the input circuits to the device.
Branching Network - A network used for transmission or reception of signals over two or more channels.
Branching Repeater - A repeater with two or more outputs for each input.
Branch Point - A network point where two or more possible routes through different intermediate networks from the origination network to destination network physically diverge. A branch point may occur in any network except the destination network.
Breach - The circumvention or disablement of some element of computer security, with or without detection, which could result in a penetration of (a) the affected computer's software or data base (s), or (b) another device or network to which the affected computer may also be connected.
Breadboard - 1. An assembly of circuits or parts used to prove the feasibility of a device, circuit, system, or principle with little or no regard to the final configuration or packaging of the parts. 2. To prepare a breadboard.
Break Interval - 1. In dial-pulse signaling, that portion of the dial pulse in which the pulsing circuit is in its high-impedance condition. 2. In dial-pulse signaling, that portion of the dial pulse in which the pulsing circuit is on-hook.
Break Out - To separate the individual fibers or buffer tubes of a fiber-optic cable for the purpose of splicing or installing optical connectors. Synonyms fan out, furcate.
Break-Out Box - A testing device that permits a user to access individual leads of an interface cable, using jumper wires, in order to monitor, switch, or patch the electrical output of the cable.
Breakout Cable - A multifiber fiber-optic cable design in which individual fibers, usually tight-buffered, are surrounded by separate strength members and jackets, which are in turn enveloped by a common jacket. Note 1: The breakout cable facilitates easy installation of fiber-optic connectors. All that need be done to prepare the ends of the cable to receive connectors is to remove the outer jacket, exposing what are essentially individual single-fiber cables. Note 2: Because it tends to induce bends in the fibers, the breakout cable design usually results in slightly higher transmission losses, for a given fiber, than loose-buffer designs. Synonym fanout cable.
Breakout Kit - A kit of materials, composed of an outer jacket in which is contained a strength member consisting of a bundle of usually aramid yarn, which jacket and yarn may be slipped over a loose buffer tube containing a single fiber, to convert the buffer tube and fiber to a complete single-fiber cable to which a fiber-optic connector may be directly attached. Note 1: A heat-shrinkable plastic boot may also be used for cosmetic purposes, strain relief, and to seal the point where the individual cables so created, merge. Note 2: Use of a breakout kit enables a fiber-optic cable containing multiple loose buffer tubes to receive connectors without the splicing of pigtails.
Brewster's angle - For a plane electromagnetic wavefront incident on a plane boundary between two dielectric media having different refractive indices, the angle of incidence at which transmittance from one medium to the other is unity when the wavefront is linearly polarized with its electric vector parallel to the plane of incidence. Note 1: Brewster's angle
B, is given by
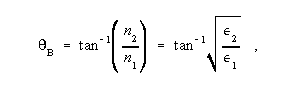
where n 1 and n 2 are the refractive indices of the respective media, and
1 and
2, their respective electric permittivities. Note 2: For a randomly polarized ray incident at Brewster's angle, the reflected and refracted rays are at 90° with respect to one another.
Brewster's law - See Brewster's angle.
BRI - Abbreviation for basic rate interface.
Brick - An informal name for a hand-held radiotelephone unit. Synonyms personal terminal, radio personal terminal.
Brick Wall Filter - A low-pass filter with a steep cut-off (such as 20 dB /octave or greater), such that a negligible amount of higher frequency information passes. Note: A brick wall filter typically has uniform group delay.
Bridge - 1. In communications networks, a device that (a) links or routes signals from one ring or bus to another or from one network to another, (b) may extend the distance span and capacity of a single LAN system, (c) performs no modification to packets or messages, (d) operates at the data-link layer of the OSI--Reference Model (Layer 2), (e) reads packets, and (f) passes only those with addresses on the same segment of the network as the originating user. 2. A functional unit that interconnects two local area networks that use the same logical link control procedure, but may use different medium access control procedures. 3. A balanced electrical network, e.g., a Wheatstone bridge. Note: A bridge may be used for electrical measurements, especially resistances or impedances. 4. See hybrid coil.
Bridged Ringing - The part of a signaling system in which ringers associated with a particular line are connected across that line.
Bridged Tap - Any portion of a loop that is not in the direct talking path between the central office and the service user's terminating equipment. A bridged tap may be an unused cable pair connected at an intermediate point or an extension of the circuit beyond the service user's location. Note: A bridged tap creates an impedance mismatch within the transmission line, which creates signal reflections. These reflections are generally not noticed in standard (POTS) voicegrade service, but become significant with high frequency (x DSL--which can be A DSL, asynchronous DSL, or S DSL, synchronous DSL, etc.) and digital transmission (DDS and DS1) services.
Bridge Lifter - A device that electrically or physically removes bridged telephone pairs. Note: Relays, saturable inductors, and semiconductors are used as bridge lifters.
Bridge-to-Bridge Station - A ship station operating in the port operations service in which messages are restricted to navigational communications and which is capable of operation from the ship's navigational bridge or, in the case of a dredge, from its main control station, operating on a frequency or frequencies in the 156-162 MHz band.
Bridge Transformer - Synonym hybrid coil. - A single transformer that effectively has three windings, and which is designed to be configured as a circuit having four branches, i.e., ports, that are conjugate in pairs. Note: The primary use of a hybrid coil is to convert between 2-wire and 4-wire operation in concatenated sections of a communications circuit. Such conversion is necessary when repeaters are introduced in a 2-wire circuit.
Bridging Connection - A parallel connection used to extract some of the signal energy from a circuit, usually with negligible effect on the normal operation of the circuit.
Bridging Loss - At a given frequency, the loss that results when an impedance is connected across a transmission line. Note: Bridging loss is expressed as the ratio, in dB, of the signal power delivered, prior to bridging, to a given point in a system downstream from the bridging point, to the signal power delivered to the given point after bridging.
Brightness - An attribute of visual perception in which a source appears to emit a given amount of light. Note 1: "Brightness" should be used only for nonquantitative references to physiological sensations and perceptions of light. Note 2: "Brightness" was formerly used as a synonym for the photometric term "luminance" and (incorrectly) for the radiometric term " radiance."
Brillouin Diagram - See Brillouin scattering. - In a physical medium, scattering of lightwaves, caused by thermally driven density fluctuations. Note: Brillouin scattering may cause frequency shifts of several gigahertz at room temperature.
Brillouin Scattering - In a physical medium, scattering of lightwaves, caused by thermally driven density fluctuations. Note: Brillouin scattering may cause frequency shifts of several gigahertz at room temperature.
Broadband - 1. Synonym [in analog technology] wideband. 2. A descriptive term for evolving digital technologies that provide consumers a signal-switched facility offering integrated access to voice, high-speed data service, video-demand services, and interactive delivery services.
Broadband Exchange (BEX) - A communications switch capable of interconnecting channels having bandwidths greater than voice bandwidth.
Broadband Internet Connection - A connection capable of carrying high quality VoIP conversations, and is much more cheap and efficient than a traditional telephone line.
Broadband ISDN (B-ISDN) - An Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) offering broadband capabilities. Note 1: B-ISDN is an ITU-T proposed (originally a CCITT-proposed) service that may (a) include interfaces operating at data rates from 150 to 600 Mb/s, (b) use asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) to carry all services over a single, integrated, high-speed packet-switched network, (c) have LAN interconnection capability, (d) provide access to a remote, shared disk server, (e) provide voice/ video /data teleconferencing, (f) provide transport for programming services, such as cable TV, (g) provide single-user controlled access to remote video sources, (h) handle voice/video telephone calls, and (i) access shop-at-home and other information services. Note 2: Techniques used in the B-ISDN include code conversion, information compression, multipoint connections, and multiple-connection calls. Current proposals use a service-independent call structure that allows flexible arrangement and modular control of access and transport edges. The service components of a connection can provide each user with independent control of access features and can serve as the basis of a simplified control structure for multipoint and multiconnection calls. Such a network might be expected to offer a variety of ancillary information processing functions.
Broadband Phone - is a type of voice based communications system, which can be created using a regular touch tone telephone, a broadband connection, and a connecting adapter.
Broadband System - See [in analog technology] wideband.
Broadcasting-Satellite Service - A radiocommunication service in which signals transmitted or retransmitted by space stations are intended for direct reception by the general public. In the broadcasting-satellite service, the term "direct reception" shall encompass both individual reception and community reception.
Broadcasting Satellite Space Station - A space station in the broadcasting-satellite service (sound broadcasting).
Broadcasting Service - A radiocommunication service in which the transmissions are intended for direct reception by the general public. This service may include sound transmissions, television transmissions or other types of transmissions.
Broadcasting Station - A station in the broadcasting service.
Broadcast Operation - The transmission of signals that may be simultaneously received by stations that usually make no acknowledgement.
Broadcast Spectrum - An entire range of frequencies used for radio and television transmission.
Broadcasting - Using radio waves to distribute radio or TV programs, which are available for reception by the general public.
Broadside Antenna - Synonym billboard antenna. - An array of parallel dipole antennas with flat reflectors, usually positioned in a line or plane. Note 1: The spacing and dimensions of the dipoles depend on the wavelength. Note 2: The main lobe of a fixed billboard antenna may, within limits, be steered by appropriate phasing of the respective signals to individual elements of the array.
Brouter - A combined bridge and router that operates without protocol restrictions, routes data using a protocol it supports, and bridges data it cannot route.
Browser - A software program that allows you to view HTML documents and navigate on the WWW. Any computer software program for reading hypertext. Note 1: Browsers are usually associated with the Internet and the World Wide Web (WWW). Note 2: A browser may be able to access information in many formats, and through different services including HTTP and FTP.
Browsing - [The] act of searching through information-system (IS) storage to locate or acquire information without necessarily knowing of the existence or the format of the information being sought.
Brute-Force Attack - In security, an attack that requires trying all (or a large fraction of all) possible values until the right value is found. Synonym [loosely] exhaustive attack.
b/s - Abbreviation for bits per second.
BSA - Abbreviation for basic serving arrangement.
BSE - Abbreviation for basic service element.
BSI - Abbreviation for British Standards Institution.
B6ZS - Abbreviation for bipolar with six-zero substitution. A T-carrier line code in which bipolar violations are deliberately inserted if user data contain a string of 6 or more consecutive zeros. Note 1: B6ZS is used to ensure a sufficient number of transitions to maintain system synchronization when the user data stream contains an insufficient number of "ones" to do so. Note 2: B6ZS is used in the North American hierarchy at the T2 rate.
B3ZS - Abbreviation for bipolar with three-zero substitution. A T-carrier line code in which bipolar violations are deliberately inserted if user data contain a string of 3 or more consecutive zeros. Note 1: B3ZS is used to ensure a sufficient number of transitions to maintain system synchronization when the user data stream contains an insufficient number of "ones" to do so. Note 2: B3ZS is used in the North American hierarchy at the T3 rate.
Budgeting - Synonym proration. The proportional distribution or allocation of parameters, such as noise power and transmission losses, among a number of tandem-connected items, such as equipment, cables, links, or trunks, in order to balance the performance of communications circuits.
Buffer - 1. A routine or storage medium used to compensate for a difference in rate of flow of data, or time of occurrence of events, when transferring data from one device to another. Note: Buffers are used for many purposes, such as (a) interconnecting two digital circuits operating at different rates, (b) holding data for use at a later time, (c) allowing timing corrections to be made on a data stream, (d) collecting binary data bits into groups that can then be operated on as a unit, (e) delaying the transit time of a signal in order to allow other operations to occur. 2. To use a buffer or buffers. 3. An isolating circuit, often an amplifier, used to minimize the influence of a driven circuit on the driving circuit. Synonym buffer amplifier. 4. In a fiber optic communication cable, one type of component used to encapsulate one or more optical fibers for the purpose of providing such functions as mechanical isolation, protection from physical damage and fiber identification. Note: The buffer may take the form of a miniature conduit, contained within the cable and called a loose buffer, or loose buffer tube, in which one or more fibers may be enclosed, often with a lubricating gel. A tight buffer consists of a polymer coating in intimate contact with the primary coating applied to the fiber during manufacture.
Buffer Amplifier - Synonym buffer.
Bug - 1. A concealed microphone or listening device or other audiosurveillance device.2. A mistake in a computer program. 3. To install means for audiosurveillance. 4. A semiautomatic telegraph key. 5. A mistake or malfunction.
Building Out - The process of adding a combination of inductance, capacitance, and resistance to a cable pair so that its electrical length may be increased by a desired amount to control impedance and loss characteristics. Synonym line buildout.
Build-Out Delay - The maximum variable transmission and processing delay that is permitted in a wideband network. Each PVP (packetized voice protocol) node records the delay that it adds and updates accordingly the TS (time stamp) value in the packet header. When the terminating endpoint of a PVP node receives a voice packet, the provisioned build-out and the time stamp value are compared. If the TS value is larger than the build-out, the PVP node drops the packet. If the delay is less than the provisioned build-out, the packet is delayed by the difference between the two values.
Bulk Encryption - Simultaneous encryption of all channels of a multichannel telecommunications link. Note: A single encryption device can be used to encrypt the output signal from a multiplexer.
Bulletin Board - A form of electronic messaging in which addressed messages or files are entered by users into a computer or network of computers. Note: Other users may obtain, at their convenience and request, messages or files available to them. Synonym electronic bulletin board.
Bunched Frame-Alignment Signal - A frame-alignment signal in which the signal elements occupy consecutive digit positions.
Bundle - 1. A group of optical fibers or electrical conductors, such as wires and coaxial cables, usually in a single jacket. Note: Multiple bundles of optical fibers or electrical conductors may be placed in the same cable. 2. In cryptography, the three cryptographic keys (K1, K2, K3) used with a TDEA mode.
Buried Cable - See direct-buried cable.
Buried Plant - See direct-buried cable.
Burst - 1. In data communications, a sequence of signals, noise, or interference counted as a unit in accordance with some specific criterion or measure. 2. To separate continuous-form or multipart paper into discrete sheets.
Burst Isochronous - Deprecated synonym for isochronous burst transmission.
Burst Switching - In a packet-switched network, a switching capability in which each network switch extracts routing instructions from an incoming packet header to establish and maintain the appropriate switch connection for the duration of the packet, following which the connection is automatically released. Note: In concept, burst switching is similar to connectionless mode transmission, but it differs from the latter in that burst switching implies an intent to establish the switch connection in near real time so that only minimum buffering is required at the node switch.
Burst Transmission - 1. Transmission that combines a very high data signaling rate with very short transmission times. 2. Operation of a data network in which data transmission is interrupted at intervals. Note: Burst transmission enables communications between data terminal equipment (DTEs) and a data network operating at dissimilar data signaling rates. Synonym data burst.
Bus - One or more conductors or optical fibers that serve as a common connection for a group of related devices.
Business Systems - The set of voice, data, and Internet products that provide communication solutions and services to business customers. The products usually reside within the customer's place of business.
Bus Interface Unit (BIU): See network interface device. - 1. A device that performs interface functions, such as code conversion, protocol conversion, and buffering, required for communications to and from a network. 2. A device used primarily within a local area network (LAN) to allow a number of independent devices, with varying protocols, to communicate with each other. Note 1: An NID converts each device protocol into a common transmission protocol. Note 2: The transmission protocol may be chosen to accommodate directly a number of the devices used within the network without the need for protocol conversion for those devices by the NID. Synonym network interface unit.
Bus Network - See network topology. A network topology in which all nodes, i.e., stations, are connected together by a single bus.
Bus Topology - See network topology. A network topology in which all nodes, i.e., stations, are connected together by a single bus.
Busy Back - Deprecated term. See busy signal.
Busy Hour - In a communications system, the sliding 60-minute period during which occurs the maximum total traffic load in a given 24-hour period. Note 1: The busy hour is determined by fitting a horizontal line segment equivalent to one hour under the traffic load curve about the peak load point. Note 2: If the service time interval is less than 60 minutes, the busy hour is the 60-minute interval that contains the service timer interval. Note 3: In cases where more than one busy hour occurs in a 24-hour period, i.e., when saturation occurs, the busy hour or hours most applicable to the particular situation are used. Synonym peak busy hour.
Busy Verification - In a public switched telephone network, a network-provided service feature that permits an attendant to verify the busy or idle state of station lines and to break into the conversation. Note: A 440-Hz tone is applied to the line for 2 seconds, followed by a 0.5-second burst every 10 seconds, to alert both parties that the attendant is connected to the circuit.
Busy Season - During a 1-year cycle, the period of 3 consecutive months having the highest busy hour traffic.
Busy Signal - 1. In telephony, an audible or visual signal that indicates that no transmission path to the called number is available. Synonym busy tone. 2. In telephony, an audible or visual signal that indicates that the called number is occupied or otherwise unavailable. Synonym reorder tone.
Busy Test - In telephony, a test made to determine whether certain facilities, such as a subscriber line or a central office trunk, are available for use.
Busy Tone - Synonym busy signal. In telephony, an audible or visual signal that indicates that no transmission path to the called number is available.
BW - Abbreviation for bandwidth.
Bypass - 1. The use of any telecommunications facilities or services that circumvents those of the local exchange common carrier. Note: Bypass facilities or services may be either customer-provided or vendor-supplied. 2. An alternate circuit that is routed around equipment or system component. Note: Bypasses are often used to allow system operation to continue when the bypassed equipment or a system component is inoperable or unavailable.
Byte - A combination of bits that represents a single character (approximately 8 bits equal one byte). A sequence of contiguous bits (usually 8) considered as a unit. Note: In pre-1970 literature, "byte" referred to a variable-length bit string. Since that time, the usage has changed so that now it almost always refers to an 8-bit string. This usage predominates in computer and data transmission literature; when so used, the term is synonymous with " octet."
Fax Switch Products
|
*Note: All prices include shipping and handling in the continental US and most of Canada. We reserve the right to charge up to the actual price of shipping on all orders outside the continental United States. Customer is responsible for any taxes, duties or brokerage charges that may apply. All orders shipped UPS Ground unless specified. For air and express shipments, appropriate charges will be applied to your order.
Need Help?
- Call now for free phone consultation at 1-866-337-0965.
Click here if you want to share 2 devices on 1 line and don't know which device to choose.
Click here if you want to share 3 or more devices on one line and don't know what type to choose.
"Albert Einstein Presents Fax Switch "
Can't find your phone equipment here?
Please visit our sister company, SuperPhoneStore.com for wholesale to the public telephones, phone accessories or the latest electronics. We have over 4500 different products in stock.
![]()
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z