
Telecom Dictionary - Definitions of terms
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
N
NA - Abbreviation for numerical aperture. 1. The sine of the vertex angle of the largest cone of meridional rays that can enter or leave an optical system or element, multiplied by the refractive index of the medium in which the vertex of the cone is located. Note: The NA is generally measured with respect to an object or image point and will vary as that point is moved. 2. For an optical fiber in which the refractive index decreases monotonically from n 1 on the axis to n 2 in the cladding, an expression of the extent of the fiber's ability to accept, in its bound modes, non-normal incident rays, given by NA = ( n 1 2 - n 2 2 ) ½ . Note: In multimode fibers, the term equilibrium numerical aperture is sometimes used. This refers to the numerical aperture with respect to the extreme exit angle of a ray emerging from a fiber in which equilibrium mode distribution has been established. 3. Loosely, the sine of the radiation or acceptance angle of an optical fiber, multiplied by the refractive index of the material in contact with the exit or entrance face. Note: This usage is approximate and imprecise, but is often encountered.
Nailed-Up Circuit - Deprecated term. See dedicated circuit, permanent virtual circuit. A circuit designated for exclusive use by specified users. Note: DOD normally considers a dedicated circuit to be between two users only. A virtual circuit used to establish a long-term connection between data terminal equipments (DTE). Note 1: In a PVC, the long-term association is identical to the data transfer phase of a virtual call. Note 2: Permanent virtual circuits eliminate the need for repeated call set-up and clearing.
NAK - Acronym for negative-acknowledge character . A transmission control character sent by a station as a negative response to the station with which the connection has been set up. Note 1: In binary synchronous communication protocol , the NAK is used to indicate that an error was detected in the previously received block and that the receiver is ready to accept retransmission of that block. Note 2: In multipoint systems, the NAK is used as the not-ready reply to a poll.
NAK Attack - In communications security systems, a security penetration technique that makes use of the negative-acknowledge transmission - control character and capitalizes on a potential weakness in a system that handles asynchronous transmission interruption in such a manner that the system is in an unprotected state against unauthorized access during certain periods.
Naming Authority - With respect to Internet addressing, an entity responsible for the allocation of names. Note: Such naming is typically hierarchical, so that the authority to allocate domain names is restricted to a particular level within a domain, such as ".com", ".net", or ".gov".
NAP - See Network Access Point. A centralized point where Internet traffic is exchanged or shared.
Narrative Traffic - Traffic consisting of plain or encrypted messages written in a natural language and transmitted in accordance with standard formats and procedures. Note: Examples of narrative traffic include (a) messages that are placed on paper tape and transmitted via a teletypewriter ( TTY ), and on reception, are converted back to a printed page on another teletypewriter or teleprinter and (b) messages printed on a sheet of paper, transmitted via optical character recognition ( OCR ) equipment, and on reception, converted back to a printed page on a printer.
Narrowband Modem - A modem whose modulated output signal has an essential frequency spectrum that is limited to that which can be wholly contained within, and faithfully transmitted through, a voice channel with a nominal 4- kHz bandwidth . Note: High frequency (HF) modems are limited to operation over a voice channel with a nominal 3-kHz bandwidth.
Narrowband Radio Voice Frequency (NBRVF) - In narrowband radio, the nominal 3- kHz bandwidth allocated for single channel radio that provides a transmission path for analog and quasi-analog signals.
Narrowband Signal - Any analog signal or analog representation of a digital signal whose essential spectral content is limited to that which can be contained within a voice channel of nominal 4- kHz bandwidth. Note: Narrowband radio uses a voice channel with a nominal 3-kHz bandwidth.
n-ary code - A code that has n significant conditions, where n is a positive integer greater than 1. Note 1: The integer substituted for n indicates the specific number of significant conditions, i.e., quantization states, in the code. For example, an 8-ary code has eight significant conditions and can convey three bits per code symbol. Note 2: A prefix that indicates an integer, e.g., "bi," "tern," or "quater," may be used in lieu of a numeral, to produce "binary," "ternary," or "quaternary" (2, 3, and 4 states respectively).
n-ary signaling - See n-ary code.
NATA - Abbreviation for North American Telecommunications Association.
National Communications System (NCS) -1. The organization established by Section 1(a) of Executive Order No. 12472 to assist the President, the National Security Council, the Director of the Office of Science and Technology Policy, and the Director of the Office of Management and Budget, in the discharge of their national security emergency preparedness telecommunications functions. The NCS consists of both the telecommunications assets of the entities represented on the NCS Committee of Principals and an administrative structure consisting of the Executive Agent, the NCS Committee of Principals, and the Manager. 2. The telecommunications system that results from the technical and operational integration of the separate telecommunications systems of the several executive branch departments and agencies having a significant telecommunications capability.
National Coordinating Center (NCC) for Telecommunications - The joint telecommunications industry/Federal Government operation established by the National Communications System to assist in the initiation, coordination, restoration, and reconstitution of National Security or Emergency Preparedness (NS/EP) telecommunications services or facilities.
National Electric Code® (NEC) - A standard that governs the use of electrical wire, cable, and fixtures, and electrical and optical communications cable installed in buildings. Note: The NEC was developed by the NEC Committee of the American National Standards Institute ( ANSI ), was sponsored by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), and is identified by the description ANSI/NFPA 70-XXXX, the last four digits representing the year of the NEC revision.
National Information Infrastructure (NII) - A proposed, advanced, seamless web of public and private communications networks, interactive services, interoperable hardware and software, computers, databases, and consumer electronics to put vast amounts of information at users' fingertips. Note: NII includes more than just the physical facilities (more than the cameras, scanners, keyboards, telephones, fax machines, computers, switches, compact disks, video and audio tape, cable, wire, satellites, optical fiber transmission lines, microwave nets , switches, televisions, monitors, and printers) used to transmit, store, process, and display voice, data, and images; it encompasses a wide range of interactive functions, user -tailored services, and multimedia databases that are interconnected in a technology-neutral manner that will favor no one industry over any other. Synonym information superhighway.
National Number - The number identifying a calling user line within an area designated by a country code.
National Prefix - A digit or combination of digits to be dialed by a calling subscriber, making a call to a subscriber in his own country but outside his own numbering area. It provides access to the automatic outgoing trunk equipment.
National Security Information (NSI) - Information that has been determined, pursuant to Executive Order 12958 or any predecessor order, to require protection against unauthorized disclosure.
National Security System - Any telecommunications or information system operated by the United States Government, the function, operation, or use of which: (a) involves intelligence activities; (b) involves cryptologic activities related to national security; (c) involves command and control of military forces; (d) involves equipment that is an integral part of a weapon or weapon system; or (e) is critical to the direct fulfillment of military or intelligence missions and does not include a system that is to be used for routine administrative and business applications (including payroll, finance, logistics, and personnel management applications). 40 U.S.C. Section 1452, Information Technology Management Reform Act of 1996.
National Security or Emergency Preparedness telecommunications - See NS/EP telecommunications.
National Television Standards Committee Standard - See NTSC standard. The North American standard (525-line interlaced raster -scanned video ) for the generation, transmission, and reception of television signals. Note 1: In the NTSC standard, picture information is transmitted in vestigial- sideband AM and sound information is transmitted in FM. Note 2: In addition to North America, the NTSC standard is used in Central America, a number of South American countries, and some Asian countries, including Japan.
Natural Frequency - The natural frequency of an antenna is the lowest frequency at which the antenna resonates without the addition of any inductance or capacitance.
Nautical Mile (nmi) - A unit of distance used in navigation and based on the length of one minute of arc taken along a great circle. Note 1: Because the Earth is not a perfect sphere, various values have been assigned to the nautical mile. The value 1852 meters (6076.1 ft.) has been adopted internationally. Note 2: The nautical mile is frequently confused with the geographical mile, which is equal to 1 min of arc on the Earth's equator (6087.15 ft.).
Navigate - To move around (a) within a series of Web pages, or (b) among different Web pages, by following hyperlinked paths within each document. Synonyms browsing, surfing.Navigation Assistant - Synonym droid. 1. In the Internet, an intelligent search tool that automatically seeks out relevant online information based on the user 's specifications. Synonyms agent, bot, crawler, hotbot, infobot, information agent, intelligent agent, Internet search engine, knowbot, knowledge robot, personal agent, robotic librarian, search robot, spider, Web crawler, Web spider, wizard. 2. In artificial intelligence, an entity with the ability to sense its environment and to act in such a way or to affect that environment; typically knowledge-based entities that can communicate with each other through some message -passing scheme.
Navigator - Synonym droid. 1. In the Internet, a navigator is an intelligent search tool that automatically seeks out relevant online information based on the user 's specifications. Synonyms agent, bot, crawler, hotbot, infobot, information agent, intelligent agent, Internet search engine, knowbot, knowledge robot, personal agent, robotic librarian, search robot, spider, Web crawler, Web spider, wizard. 2. In artificial intelligence, a navigator is an entity with the ability to sense its environment and to act in such a way or to affect that environment; typically knowledge-based entities that can communicate with each other through some message -passing scheme.
NBH - Abbreviation for network busy hour. See busy hour. In a communications system, NBH is the sliding 60-minute period during which occurs the maximum total traffic load in a given 24-hour period. Note 1: The busy hour is determined by fitting a horizontal line segment equivalent to one hour under the traffic load curve about the peak load point. Note 2: If the service time interval is less than 60 minutes, the busy hour is the 60-minute interval that contains the service timer interval. Note 3: In cases where more than one busy hour occurs in a 24-hour period, i.e., when saturation occurs, the busy hour or hours most applicable to the particular situation are used.
NBRVF - Abbreviation for narrowband radio voice frequency. In narrowband radio, the nominal 3- kHz bandwidth allocated for single channel radio that provides a transmission path for analog and quasi-analog signals.
NCC - Abbreviation for National Coordinating Center for Telecommunications. The NCC is the joint telecommunications industry/Federal Government operation established by the National Communications System to assist in the initiation, coordination, restoration, and reconstitution of National Security or Emergency Preparedness (NS/EP) telecommunications services or facilities.
NC Code - Abbreviation for network channel (NC) code . NC Code is a code used to identify both switched and nonswitched channel services. Included in this code set are customer options associated with individual channel services, or feature groups and other switched services.
NCI Code - Abbreviation for network channel interface code . An encoded representation used to identify 5 interface elements located at a point of termination ( POT ) at central office or customer location. The interface elements are: total conductors, protocol, impedance, protocol options, and transmission level points.
NC (no circuit) - A call disposition category for a call attempt that does not find an available outgoing trunk.
NCS - Abbreviation for National Communications System, net control station. 1. The organization established by Section 1(a) of Executive Order No. 12472 to assist the President, the National Security Council, the Director of the Office of Science and Technology Policy, and the Director of the Office of Management and Budget, in the discharge of their national security emergency preparedness telecommunications functions. The NCS consists of both the telecommunications assets of the entities represented on the NCS Committee of Principals and an administrative structure consisting of the Executive Agent, the NCS Committee of Principals, and the Manager. 2. The telecommunications system that results from the technical and operational integration of the separate telecommunications systems of the several executive branch departments and agencies having a significant telecommunications capability.
NDUB (network-determined user busy) - A condition of an interface, as determined by the network, based on the network's capability to terminate another call to that interface. The interface is said to be NDUB if any of the following conditions exist: (a) if the maximum number of information channels available has been reached and the network does not support the offering of additional calls beyond this number; (b) if the limit of additional offering had been reached; (c) if the maximum number of total calls supported for User B has been reached.
Near Absolute Immunity - Near Absolute Immunity is a central office or similar facility 's ability to maintain continuity of operations without any operationally significant interruption of service from either hardware or software failures in the presence of one or more HEMP ( high-altitude electromagnetic pulse ) events.
Near-End Crosstalk - Near-End Crosstalk is Crosstalk that is propagated in a disturbed channel in the direction opposite to the direction of propagation of a signal in the disturbing channel. Note: The terminals of the disturbed channel, at which the near-end crosstalk is present, and the energized terminal of the disturbing channel, are usually near each other.
Near Field - Synonym near-field region. Near Field is defined as 1. The close-in region of an antenna wherein the angular field distribution is dependent upon distance from the antenna. Synonym near zone. 2. In optical fiber communications, the region close to a source or aperture. Note: The diffraction pattern in this region typically differs significantly from that observed at infinity and varies with distance from the source.
Near-Field Diffraction Pattern - A Near-Field Diffraction Pattern is the diffraction pattern of an electromagnetic wave, which pattern is observed close to a source or aperture, as distinguished from a far- field diffraction pattern. Note: The pattern in the output plane is called the near-field radiation pattern. Synonym Fresnel diffraction pattern.
Near-Field Region - A Near-Field Region is defined as 1. The close-in region of an antenna wherein the angular field distribution is dependent upon distance from the antenna. Synonyms near field , near zone . 2. In optical fiber communications , the region close to a source or aperture . Note: The diffraction pattern in this region typically differs significantly from that observed at infinity and varies with distance from the source.
Near-Field Scanning - Near-Field Scanning is a technique for measuring the refractive- index profile of an optical fiber by using an extended source to illuminate an endface and measuring the point-by-point radiance at the exit face.
Near Real Time - Near Real Time is defined as 1. Pertaining to the delay introduced, by automated data processing, between the occurrence of an event and the use of the processed data, e.g., for display or feedback and control purposes. Note 1: For example, a near-real- time display depicts an event or situation as it existed at the current time less the processing time. Note 2: The distinction between near real time and real time is somewhat nebulous and must be defined for the situation at hand. 2. Pertaining to the timeliness of data or information which has been delayed by the time required for electronic communication and automatic data processing. This implies that there are no significant delays.
Near-Vertical-Incidence Skywave - In radio propagation , Near-Vertical-Incidence Skywave is a wave that is reflected from the ionosphere at a nearly vertical angle and that is used in short-range communications to reduce the area of the skip zone and thereby improve reception beyond the limits of the ground wave.
Near Zone - Synonym near-field region. Near Zone is defined as 1. The close-in region of an antenna wherein the angular field distribution is dependent upon distance from the antenna. Synonym near field. 2. In optical fiber communications, the region close to a source or aperture . Note: The diffraction pattern in this region typically differs significantly from that observed at infinity and varies with distance from the source.
NEC - Abbreviation for National Electric Code ® - NEC is a standard that governs the use of electrical wire, cable, and fixtures, and electrical and optical communications cable installed in buildings. Note: The NEC was developed by the NEC Committee of the American National Standards Institute ( ANSI ), was sponsored by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), and is identified by the description ANSI/NFPA 70-XXXX, the last four digits representing the year of the NEC revision.
Necessary Bandwidth -1. For a given class of emission, the width of the frequency band which is just sufficient to ensure the transmission of information at the rate and with the quality required under specified conditions. Note: Emissions useful for the adequate functioning of the receiving equipment, e.g., the emission corresponding to the carrier of reduced carrier systems, must be included in the necessary bandwidth. ( See Annex J of NTIA Manual of Regulations and Procedures for Federal Radio Frequency Management for formulas used to calculate necessary bandwidth.) 2. The calculated spectral width of an emission. Calculations are made using procedures set forth in part 2 of this chapter [of 47CFR ]. The bandwidth so calculated is considered to be the minimum necessary to convey information at the desired rate with the desired accuracy.
Need To Know -Need to Know is 1. The legitimate requirement of a person or organization to know, access, or possess sensitive or classified information that is critical to the performance of an authorized, assigned mission. 2. The necessity for access to, or knowledge or possession of, specific information required to carry out official duties.
Negation Circuit - Deprecated synonym for inverter. 1. In electrical engineering, a negation circuit is a device for converting direct current into alternating current. 2. In computers, a negation circuit is a device or circuit that inverts the polarity of a signal or pulse.
Negative-Acknowledge Character (NAK) - A Negative-Acknowledge Character is a transmission control character sent by a station as a negative response to the station with which the connection has been set up. Note 1: In binary synchronous communication protocol , the NAK is used to indicate that an error was detected in the previously received block and that the receiver is ready to accept retransmission of that block. Note 2: In multipoint systems, the NAK is used as the not-ready reply to a poll.
Negative Feedback - See feedback. If the feedback is degenerative (subtractive), it is called " negative feedback ," which reduces the gain and distortion, and increases linearity and stability. Note 1: Feedback may occur inadvertently, and be detrimental. 2. Information returned as a response to an originating source.
Negative Justification - Synonym de-stuffing. Negative justification is the controlled deletion of stuffing bits from a stuffed digital signal, to recover the original signal.
Negative Pulse Stuffing - Synonym de-stuffing. Negative Pulse Stuffing is the controlled deletion of stuffing bits from a stuffed digital signal, to recover the original signal.
N-Entity - An active element in the n -th layer of the Open Systems Interconnection--Reference Model ( OSI -RM) that (a) interacts directly with elements, i.e. , entities, of the layer immediately above or below the n -th layer, (b) is defined by a unique set of rules, i.e. , syntax, and information formats, including data and control formats, and (c) performs a defined set of functions. Note 1: The n refers to any one of the 7 layers of the OSI-RM. Note 2: In an existing layered open system, the n may refer to any given layer in the system. Note 3: Layers are conventionally numbered from the lowest, i.e., the physical layer, to the highest, so that the n + 1 layer is above the n -th layer and the n - 1 layer is below.
NEP - Abbreviation for noise equivalent power. At a given data - signaling rate or modulation frequency , operating wavelength, and effective noise bandwidth, the radiant power that produces a signal-to-noise ratio of unity at the output of a given optical detector. Note 1: Some manufacturers and authors define NEP as the minimum detectable power per square root bandwidth. When defined this way, NEP has the units of watts per ( hertz ) 1/2 . Therefore, the term is a misnomer, because the units of power are watts. Note 2: Some manufacturers define NEP as the radiant power that produces a signal-to-dark-current noise ratio of unity. The NEP measurement is valid only if the dark-current noise dominates the noise level.
Neper (Np) - A neper is a unit used to express ratios, such as gain, loss, and relative values. Note 1: The neper is analogous to the decibel, except that the Naperian base 2.718281828. . . is used in computing the ratio in nepers. Note 2: The value in nepers, Np , is given by Np = ln( x 1 / x 2 ), where x 1 and x 2 are the values of interest, and ln is the natural logarithm, i.e., logarithm to the base e. Note 3: One neper (Np) = 8.686 dB, where 8.686 = 20/(ln 10). Note 4: The neper is often used to express voltage and current ratios, whereas the decibel is usually used to express power ratios. Note 5: Like the dB, the Np is a dimensionless unit. Note 6: The ITU recognizes both units.
Nested Command Menu - A command menu within another command menu. See command menu.
Net - Synonym communications net. - An organization of stations capable of direct communication on a common channel or frequency.
Net Browser - Abbreviation for network browser. A computer program for browsing hyperlinked documents (especially on the Web ). Note 1: A network browser formats and displays information so obtained in a form useful to the viewer. Note 2: A network browser may function in a graphical mode or in a text-only mode.
Net Control Station (NCS) -1. A radio station that performs net control functions, such as controlling traffic and enforcing operational discipline. 2. A terminal in a secure telecommunications net responsible for distributing key in electronic form to the members of the net.
Net Gain - Net Gain is the overall gain of a transmission circuit. Note 1: Net gain is measured by applying a test signal at an appropriate power level (see Note 5) at the input port of a circuit and measuring the power delivered at the output port. The net gain in dB is calculated by taking 10 times the logarithm of the ratio of the output power to the input power. Note 2: The net gain expressed in dB may be positive or negative. Note 3: If the net gain expressed in dB is negative, it is also called the " net loss." Note 4: If the net gain is expressed as a ratio, and the ratio is less than unity, a net loss is indicated. Note 5: The test signal must be chosen so that its power level is within the usual operating range of the circuit being tested.
Netiquette - [Slang] A contraction of network etiquette. The written or unwritten rules of etiquette that govern online interaction between users on the Internet. Note: Some typical rules are a ban on profane or offensive language, a requirement to respect other users, and a ban on floods of unsolicited advertisements. Netiquette rules may be enforced by a moderator or may be self-policed by other users.
Net Loss - The overall loss of a transmission circuit.
Net Loss Variation - The maximum change in net loss occurring in a specified portion of a communication system during a specified period.
Net Operation - The operation of an organization of stations capable of direct communication on a common channel or frequency. Note: Net operations (a) allow participants to conduct ordered conferences among participants who usually have common information needs or related functions to perform, (b) are characterized by adherence to standard formats and procedures, and (c) are responsive to a common supervisory station, called the " net control station," which permits access to the net and maintains net operational discipline.
Net Radio Interface (NRI) - An interface between a single- channel radio station (usually in a radio net ) and switched communications systems.
NETS - Abbreviation for Nationwide Emergency Telecommunications Service. See Government Emergency Telecommunications Service.
Network - A network is the total infrastructure for transmitting phone and/or Internet messages. 1. An interconnection of three or more communicating entities. 2. An interconnection of usually passive electronic components that performs a specific function (which is usually limited in scope), e.g., to simulate a transmission line or to perform a mathematical function such as integration or differentiation. Note: A network may be part of a larger circuit. 3. In television, a communication system consisting of a group of broadcasting stations that all transmit the same programs. (ABC, CBS, NBC)Network Access Point (NAP) - A centralized point where Internet traffic is exchanged or shared.
Network Address - The signaling point code, containing for U.S. national networks, the network identification, network cluster, and network cluster member fields (24 bits).
Network Administration - A group of network management functions that (a) provide support services, (b) ensure that the network is used efficiently, and (c) ensure prescribed service -quality objectives are met. Note: Network administration may include activities such as network address assignment, assignment of routing protocols and routing table configuration, and directory service configuration.
Network Architecture - 1. The design principles, physical configuration, functional organization, operational procedures, and data formats used as the bases for the design, construction, modification, and operation of a communications network. 2. The structure of an existing communications network, including the physical configuration, facilities, operational structure, operational procedures, and the data formats in use.
Network Availability - The probability a network can perform its required functions.
Network Browser - A computer program for browsing hyperlinked documents (especially on the Web ). Note 1: A network browser formats and displays information so obtained in a form useful to the viewer. Note 2: A network browser may function in a graphical mode or in a text-only mode.
Network Busy Hour (NBH) - See busy hour. In a communications system, the sliding 60-minute period during which occurs the maximum total traffic load in a given 24-hour period. Note 1: The busy hour is determined by fitting a horizontal line segment equivalent to one hour under the traffic load curve about the peak load point. Note 2: If the service time interval is less than 60 minutes, the busy hour is the 60-minute interval that contains the service timer interval. Note 3: In cases where more than one busy hour occurs in a 24-hour period, i.e., when saturation occurs, the busy hour or hours most applicable to the particular situation are used.
Network Cluster - The field in the U.S. signaling point code structure that identifies groups of signaling points and individual STPs (signaling transfer points) of a signaling network.
Network Computer -1. Synonym thin client. 2. Any computer connected to a network.
Network Connectivity - The topological description of a network that specifies, in terms of circuit termination locations and quantities, the interconnection of the transmission nodes.
Network Control Program (NCP) - In a switch or network node , software designed to store and forward frames between nodes. Note: An NCP may be used in local area networks or larger networks.
Network Data - Data that are specific to the functionality of the network.
Network Element Function Block - A functional block that communicates with a telecommunications management network (TMN) for the purpose of being monitored, or controlled, or both.
Network Element Location (NE location) - A building (such as a central office ) or nonbuilding location housing NEs. Communication within an NE location may be accomplished with minimal attention to such factors as noise, lightning protection, or the cost of bandwidth; communication outside an NE location uses suitable modems and uses conventional communications services or an EOC ( embedded operations channel ).
Network Element (NE) - In integrated services digital networks, a piece of telecommunications equipment that provides support or services to the user.
Network Engineering -1. In telephony, the discipline concerned with (a) determining internetworking service requirements for switched networks, and (b) developing and implementing hardware and software to meet them. 2. In computer science, the discipline of hardware and software engineering to accomplish the design goals of a computer network. 3. In radio communications, the discipline concerned with developing network topologies.
Network Etiquette (netiquette): See netiquette. The written or unwritten rules of etiquette that govern online interaction between users on the Internet. Note: Some typical rules are a ban on profane or offensive language, a requirement to respect other users, and a ban on floods of unsolicited advertisements. Netiquette rules may be enforced by a moderator or may be self-policed by other users.
Network Facility - The connection between the radio port controller and the PCS (personal communications services) switching center.
Network Failure - A complete or partial failure of a component or components of a network because of malfunction or natural or human-caused disasters. Partial failures include degradation (and graceful degradation).
Network Failure Triple - A combination of the network 's unservability (U), duration (D), and extent (E) parameters that exceeds a threshold.
Network File System (NFS) - See NFS. 1. A file system that is distributed over a computer network. 2. A file system, on a single computer, that contains the low- level networking files for an entire network.
Network Identification - The field in the U.S. signaling point code structure that identifies signaling networks.
Network Indicator (NI) - Information within the service information octet of the message signal unit that permits discrimination between national and international messages.
Network Information Center (NIC) - See NIC. An entity that provides information management, technical support, and administrative services to users of a given network. Note: NICs can form a hierarchy. A specific NIC, designated at the " Internetwork information center" or " InterNIC," has been the authority that assigns the network numbers to the subnetworks that it connects to the Internet.
Network Integrity - See network survivability. The (a) ability of a network to maintain or restore an acceptable level of performance during network failures by applying various restoration techniques, and (b) mitigation or prevention of service outages from network failures by applying preventive techniques.
Network Interface - 1. The point of interconnection between a user terminal and a private or public network. 2. The point of interconnection between the public switched network and a privately owned terminal. Note: Code of Federal Regulations, Title 47, part 68, stipulates the interface parameters. 3. The point of interconnection between one network and another network. 4. The point of demarcation between the carrier's facilities and the customer installation, which establishes the technical interface and division of operational responsibility. In this definition, the term "customer" refers to the end-user.
Network Interface Card (NIC) - See NIC. A network interface device ( NID ) in the form of a circuit card that is installed in an expansion slot of a computer to provide network access. Note: Examples of NICs are cards that interface a computer with an Ethernet LAN and cards that interface a computer with an FDDI ring network.
Network Interface Device (NID) - 1. A device that performs interface functions, such as code conversion, protocol conversion, and buffering, required for communications to and from a network. 2. A device used primarily within a local area network (LAN) to allow a number of independent devices, with varying protocols, to communicate with each other. Note 1: An NID converts each device protocol into a common transmission protocol. Note 2: The transmission protocol may be chosen to accommodate directly a number of the devices used within the network without the need for protocol conversion for those devices by the NID. Synonym network interface unit.
Network Interface Unit (NIU) - Synonym network interface device.
Network Interworking - Cooperation among networks in the processing, management, and creation of services that span multiple networks.
Network Inward Dialing (NID) - Synonym direct inward dialing. A service feature that allows inward-directed calls to a PBX to reach a specific PBX extension without human intervention.
Network-Launched Application - In a computer networking environment, an application ( program ) that is centrally stored, e.g. , on a server, and copies of which may be accessed on demand by a client and used temporarily ( i.e. , for a single session) by the client ( e.g. , a desktop computer). Note: Multiple clients may make simultaneous use of a given network -launched application.
Network Layer - Layer 3. This layer responds to service requests from the Transport Layer and issues service requests to the Data Link Layer. The Network Layer provides the functional and procedural means of transferring variable length data sequences from a source to a destination via one or more networks while maintaining the quality of service requested by the Transport Layer. The Network Layer performs network routing, flow control, segmentation/desegmentation, and error control functions. See Open Systems Interconnection--Reference Model.
Network Layer Relay - A function within the network layer by means of which one correspondent network entity forwards data to another correspondent network entity.
Network Loss - Loss added to the network to control echo.
Network Management - The execution of the set of functions required for controlling, planning, allocating, deploying, coordinating, and monitoring the resources of a telecommunications network, including performing functions such as initial network planning, frequency allocation, predetermined traffic routing to support load balancing, cryptographic key distribution authorization , configuration management, fault management, security management, performance management, and accounting management. Note: Network management does not include user terminal equipment.
Network Manager - In network management, the entity that initiates requests for management information from managed systems or receives spontaneous management-related notifications from managed systems.
Network Node (NN) - A grouping of one or more network elements (at one or more sites) which provides network related functions, and is administered as a single entity. A single site may contain more than one network node. For the purpose of this glossary, a network node is considered synonymous with a network element, and is usually at a single site. This restriction simplifies the definition of the network node interface (NNI) and INI, which would not apply between network elements.
Network Number - An identification number, within a computer network or set of interconnected networks, that uniquely identifies a computer. Note: Under the Internet protocol system, the network number forms a part of the IP address of each computer in the network.
Network Operating System (NOS) - Software that (a) controls a network and its message (e.g., packet) traffic, and queues, (b) controls access by multiple users to network resources such as files, and (c) provides for certain administrative functions, including security. Note 1: A network operating system is most frequently used with local area networks and wide area networks, but could also have application to larger network systems. Note 2: The upper 5 layers of the OSI--Reference Model provide the foundation upon which many network operating systems are based.
Network Operation Center (NOC) - A round-the-clock operation where Network engineers monitor and troubleshoot technical equipment and connections.Network Operator - The operator responsible for the development, provision and maintenance of real- time networking services and for operating the corresponding networks.
Network Outpulsing State - A call state in which the network transmits the caller's emergency service ID (CESID) to the public service answering point (PSAP) customer installation (CI).
Network Outward Dialing (NOD) - Synonym direct outward dialing. An automated PBX service feature that provides for outgoing calls to be dialed directly from the user terminal.
Network Performance - The qualitative level at which a network fulfills its function.
Network Provided Number (NPN) - An ISDN number, supplied by the calling user 's or the redirecting user's network , which is associated with the calling user or the redirecting user. It is possible that the NPN may have the same value as the user provided number (UPN) especially in cases where delivery of two calling party numbers is supported. The NPN may also be accompanied by a subaddress.
Network Provider - The organization that maintains and operates the network components required for intelligent network (IN) functionality. A network provider may also take more than one role, e.g., also acting as service provider.
Network Reliability - See network survivability. The (a) ability of a network to maintain or restore an acceptable level of performance during network failures by applying various restoration techniques, and (b) mitigation or prevention of service outages from network failures by applying preventive techniques.
Network Restoration - Automatic or manual methods to return a network to its normal function in response to a network failure.
Network Section - The network components that provide a virtual connection between two circuit sections. A network section may be either an access network section or a transit network section.
Network Security: Protection of networks and their services from unauthorized modification, destruction, or disclosure. It provides assurance the network performs its critical functions correctly and there are no harmful side-effects.
Network Security Architecture - A subset of network architecture specifically addressing security -relevant issues.
Network Service Part - The combination of the MTP ( message transfer part ) and the SCCP ( signaling connection control part ).
Network Site -1. A collection of functional units that provide network services and that belong to one management domain and are considered as a whole. [2382-pt.35] 2. A specific location that houses telecommunications equipment entities and/or facility terminations at that location, or a specific location that houses administrative operations . A location is usually designated as a network site when it houses one or more network applications.
Network Surveillance - A process concerned with surveillance of the network as a whole. It includes activities for coordination and assigning priorities to maintenance actions. The information necessary to support this process comes from alarms, measurements, and indicators of operational (including congestion ) status.
Network Side - The side of the network interface or the network functions as seen from the interface.
Network Survivability - The (a) ability of a network to maintain or restore an acceptable level of performance during network failures by applying various restoration techniques, and (b) mitigation or prevention of service outages from network failures by applying preventive techniques.
Network Survivability Model - The analytical processes for estimating how well network services will be affected and restored with transparencies to the users as a result of a failure.
Network Terminal Number (NTN) - In the ITU-T International X.121 format, the sets of digits that comprise the complete address of the data terminal end point. Note: For an NTN that is not part of a national integrated numbering format, the NTN is the 10 digits of the ITU-T X.25 14- digit address that follow the Data Network Identification Code (DNIC). When part of a national integrated numbering format, the NTN is the 11 digits of the ITU-T X.25 14-digit address that follow the DNIC.
Network Terminating Interface (NTI) - Synonym for demarcation point. That point at which operational control or ownership of communications facilities changes from one organizational entity to another. Note: The demarcation point is usually the interface point between customer-premises equipment and external network service provider equipment.
Network Termination - Network equipment that provides functions necessary for network operation of ISDN access protocols. Note: Network termination provides functions essential for transmission services.
Network Termination 1 (NT1) - In Integrated Services Digital Networks ( ISDN ), a functional grouping of customer-premises equipment that includes functions that may be regarded as belonging to OSI Layer 1, i.e., functions associated with ISDN electrical and physical terminations on the user premises. Note: The NT1 forms a boundary to the network and may be controlled by the provider of the ISDN services.
Network Termination 2 (NT2) - In Integrated Services Digital Networks ( ISDN ), an intelligent device that may include functionality for OSI Layers 1 through 3 (dependent on individual systems requirements).
Network Topology - The specific physical, i.e., real, or logical, i.e., virtual, arrangement of the elements of a network. Note 1: Two networks have the same topology if the connection configuration is the same, although the networks may differ in physical interconnections, distances between nodes, transmission rates, and/or signal types. Note 2: The common types of network topology are illustrated [refer to the figure on this page] and defined in alphabetical order below:
- bus topology: A network topology in which all nodes, i.e., stations, are connected together by a single bus.
- fully connected topology: A network topology in which there is a direct path (branch) between any two nodes. Note: In a fully connected network with n nodes, there are n(n-1)/2 direct paths, i.e., branches. Synonym fully connected mesh network.
- hybrid topology: A combination of any two or more network topologies. Note 1: Instances can occur where two basic network topologies, when connected together, can still retain the basic network character, and therefore not be a hybrid network. For example, a tree network connected to a tree network is still a tree network. Therefore, a hybrid network accrues only when two basic networks are connected and the resulting network topology fails to meet one of the basic topology definitions. For example, two star networks connected together exhibit hybrid network topologies. Note 2: A hybrid topology always accrues when two different basic network topologies are connected.
- linear topology: See bus topology. A network topology in which all nodes, i.e., stations, are connected together by a single bus.
- mesh topology: A network topology in which there are at least two nodes with two or more paths between them.
- ring topology: A network topology in which every node has exactly two branches connected to it.
- star topology: A network topology in which peripheral nodes are connected to a central node, which rebroadcasts all transmissions received from any peripheral node to all peripheral nodes on the network, including the originating node. Note 1: All peripheral nodes may thus communicate with all others by transmitting to, and receiving from, the central node only. Note 2: The failure of a transmission line, i.e., channel, linking any peripheral node to the central node will result in the isolation of that peripheral node from all others. Note 3: If the star central node is passive, the originating node must be able to tolerate the reception of an echo of its own transmission, delayed by the two-way transmission time, i.e., to and from the central node, plus any delay generated in the central node. An active star network has an active central node that usually has the means to prevent echo-related problems.
- tree topology: A network topology that, from a purely topologic viewpoint, resembles an interconnection of star networks in that individual peripheral nodes are required to transmit to and receive from one other node only, toward a central node, and are not required to act as repeaters or regenerators. Note 1: The function of the central node may be distributed. Note 2: As in the conventional star network, individual nodes may thus still be isolated from the network by a single-point failure of a transmission path to the node. Note 3: A single-point failure of a transmission path within a distributed node will result in partitioning two or more stations from the rest of the network.
Network Trusted Computing Base (NTCB) - The totality of protection mechanisms within a network, including hardware, firmware, and software, the combination of which is responsible for enforcing a security policy.Network Utility - An internetwork administrative signaling mechanism in the call control procedure between packet switching public data networks.
Network Weaving -1. In computer security, a penetration technique in which different communication networks are used to gain access to a data processing system to avoid detection and trace-back. 2. A penetration technique in which different communication networks are linked to access an information system (IS) to avoid detection and trace-back.
Neutral -1. In ac power distribution, the conductor that (a) is intentionally grounded on the supply side of the service disconnect and (b) provides a current return path for ac power currents. 2. In three- phase ac "Y," i.e., wye, power distribution, the low-potential fourth wire that conducts only that current required to achieve electrical balance, i.e., to provide a return path for any current imbalance among the three phases.
Neutral Direct-Current Telegraph System - A telegraph system in which (a) current flows during marking intervals and no current flows during spacing intervals for the transmission of signals over a line, and (b) the direction of current flow is immaterial. Synonyms single-current system, single-current transmission system, single-Morse system.
Neutral Ground - An intentional ground applied to the neutral conductor or neutral point of a circuit, transformer, machine, apparatus, or system.
Neutral Operation - A method of teletypewriter operation in which marking signals are formed by current pulses of one polarity, either positive or negative, and spacing signals are formed by reducing the current to zero or nearly zero.
Neutral Relay - A relay in which the direction of movement of the armature does not depend upon the direction of the current in the circuit controlling the armature.
New Customer Premises Equipment - All customer premises equipment not in service or in the inventory of a regulated telephone utility as of December 31, 1982.
News Client - Synonym newsreader. A local software application ( client program ) that provides access by means of which a user may view one or more forums or newsgroups from one or more news servers. Note: Most newsreaders format and display information from the server in a form suitable to the user.
Newsfeed - Information distributed by a computer , e.g., one operated by an Internet service provider that maintains current articles within selected groups.
Newsgroup - A discussion group in which you can leave messages for others to read on UseNet.
Newsreader - A local software application ( client program ) that provides access by means of which a user may view one or more forums or newsgroups from one or more news servers. Note: Most newsreaders format and display information from the server in a form suitable to the user.Synonym news client.
News Server - A server on a network that stores, organizes, and distributes messages for selected newsgroups.
NF - Abbreviation for noise figure. Of an active device, over the bandwidth of interest, the contribution by the device itself to thermal noise at its output. The noise figure is usually expressed in decibels ( dB ), and is with respect to thermal noise power at the system impedance, at a standard noise temperature (usually 20 o C, 293 K) over the bandwidth of interest. It is determined by (a) measuring (determining) the ratio, usually expressed in dB, of the thermal noise power at the output, to that at the input, and (b) subtracting from that result, the gain, in dB, of the system. Typical noise figures range from 0.5 dB for very low noise devices, to 4 to 8 dB. In some systems, e.g., heterodyne systems, total output noise power includes noise from other than thermal sources, such as spurious contributions from image - frequency transformation, but noise from these sources is not considered in determining the noise figure. In this example, the noise figure is determined only with respect to that noise that appears in the output via the principal frequency transformation of the system, and excludes noise that appears via the image frequency transformation.
NFS - Abbreviation for network file system. 1. A file system that is distributed over a computer network . 2. A file system, on a single computer, that contains the low- level networking files for an entire network.
n -function - A defined action performed by an n -entity. Note: An n -function may be (a) a single action, i.e., a primitive function, or (b) a set of actions.
950 + WXXX - A carrier access code for obtaining switched access to interchange carriers where (a) the calling customer accesses the IC and passes the address information, if any, in two distinct operations; (b) the calling customer usually uses in-band signals to pass the address, if any, to the IC; and (c) the EC does not repeat the address information. Note: The X digits in WXXX are the carrier identification code for the IC, and W is 0 or 1.
Nibble - Part of a byte, usually half of a byte.
NIC -1. Abbreviation for network interface card. A network interface device ( NID ) in the form of a circuit card that is installed in an expansion slot of a computer to provide network access. Note: Examples of NICs are cards that interface a computer with an Ethernet LAN and cards that interface a computer with an FDDI ring network. 2. Abbreviation for network information center. An entity that provides information management, technical support, and administrative services to users of a given network. Note: NICs can form a hierarchy. A specific NIC, designated at the " Internetwork information center" or " InterNIC," has been the authority that assigns the network numbers to the subnetworks that it connects to the Internet.
NID - Network Interface Device - A device used within a local area network, which allows a number of independent devices (computers, modems, etc.) to communicate with one another. Also, a device usually mounted on the outside of the customer's home that connects the customer's inside wiring to the telephone company's wiring and protects the customer's phone equipment from lightning and any large rise or fall in electricity.
NII (National Information Infrastructure) - A proposed, advanced, seamless web of public and private communications networks, interactive services, interoperable hardware and software, computers, databases, and consumer electronics to put vast amounts of information at users' fingertips. Note: NII includes more than just the physical facilities (more than the cameras, scanners, keyboards, telephones, fax machines, computers, switches, compact disks, video and audio tape, cable, wire, satellites, optical fiber transmission lines, microwave nets, switches, televisions, monitors, and printers) used to transmit, store, process, and display voice, data, and images; it encompasses a wide range of interactive functions, user-tailored services, and multimedia databases that are interconnected in a technology-neutral manner that will favor no one industry over any other. Synonym information superhighway.
Nine-Hundred (900) Service - A telephone service via which the caller may access information on a charge-per- call or charge-per- time basis.
NIU - Abbreviation for network interface unit. See network interface device. 1. A device that performs interface functions, such as code conversion, protocol conversion, and buffering, required for communications to and from a network. 2. A device used primarily within a local area network ( LAN ) to allow a number of independent devices, with varying protocols, to communicate with each other. Note 1: An NID converts each device protocol into a common transmission protocol. Note 2: The transmission protocol may be chosen to accommodate directly a number of the devices used within the network without the need for protocol conversion for those devices by the NID.
Nmap - A security -violating, network - scanning tool that can scan a network using a variety of protocols, can operate in stealth mode, and can automatically identify remote operating systems.
NMI - Abbreviation for nautical mile. A unit of distance used in navigation and based on the length of one minute of arc taken along a great circle. Note 1: Because the Earth is not a perfect sphere, various values have been assigned to the nautical mile. The value 1852 meters (6076.1 ft.) has been adopted internationally. Note 2: The nautical mile is frequently confused with the geographical mile, which is equal to 1 min of arc on the Earth's equator (6087.15 ft.).
NNTP - Abbreviation for network news transfer protocol. An application protocol that provides the means to transfer files for computer conferences.
NOC - See Network Operation Center A centralized organization responsible for the operation and maintenance of its network.
No Circuit Double Prime (NC") - An SIT ( special information tone ) classification for call attempts that fail to find an available long distance service provider outgoing trunk.
No Circuit (NC) - A call -disposition category for a call attempt that does not find an available outgoing trunk.
No Circuit Prime (NC') - An SIT ( special information tone ) classification for call attempts that fail to find an available Local Service Provider outgoing trunk.
NOD - Acronym for network outward dialing. An automated PBX service feature that provides for outgoing calls to be dialed directly from the user terminal.
Nodal Clock - The principal clock or alternate clock located at a particular node that provides the timing reference for all major functions at that node.
Nodal Point - Synonym node.
Node - 1. In network topology, a terminal of any branch of a network or an interconnection common to two or more branches of a network. Synonyms junction point, nodal point. 2. In a switched network, one of the switches forming the network backbone. Note: A node may also include patching and control facilities. 3. A technical control facility (TCF). 4. A point in a standing or stationary wave at which the amplitude is a minimum. In this sense, synonym null.
Noise - 1. An undesired disturbance within the frequency band of interest; the summation of unwanted or disturbing energy introduced into a communications system from man-made and natural sources. 2. A disturbance that affects a signal and that may distort the information carried by the signal. 3. Random variations of one or more characteristics of any entity such as voltage, current, or data. 4. A random signal of known statistical properties of amplitude, distribution, and spectral density. 5. Loosely, any disturbance tending to interfere with the normal operation of a device or system.
Noise Current -1. Interfering and unwanted electrical currents in a device or system. 2. In optical communications, the rms component of the optical detector output electrical current with no incoming signal present.
Noise Equivalent Power (NEP) - At a given data - signaling rate or modulation frequency, operating wavelength, and effective noise bandwidth, the radiant power that produces a signal-to-noise ratio of unity at the output of a given optical detector. Note 1: Some manufacturers and authors define NEP as the minimum detectable power per square root bandwidth. When defined this way, NEP has the units of watts per ( hertz ) 1/2 . Therefore, the term is a misnomer, because the units of power are watts. Note 2: Some manufacturers define NEP as the radiant power that produces a signal-to-dark-current noise ratio of unity. The NEP measurement is valid only if the dark-current noise dominates the noise level.
Noise Factor - Synonym noise figure. Of an active device, over the bandwidth of interest, the contribution by the device itself to thermal noise at its output. The noise figure is usually expressed in decibels ( dB ), and is with respect to thermal noise power at the system impedance, at a standard noise temperature (usually 20 o C, 293 K) over the bandwidth of interest. It is determined by (a) measuring (determining) the ratio, usually expressed in dB, of the thermal noise power at the output, to that at the input, and (b) subtracting from that result, the gain, in dB, of the system. Typical noise figures range from 0.5 dB for very low noise devices, to 4 to 8 dB. In some systems, e.g., heterodyne systems, total output noise power includes noise from other than thermal sources, such as spurious contributions from image - frequency transformation, but noise from these sources is not considered in determining the noise figure. In this example, the noise figure is determined only with respect to that noise that appears in the output via the principal frequency transformation of the system, and excludes noise that appears via the image frequency transformation.
Noise Field - An indication of the level of background noise that the terminating end-point may play out in the absence of packets.
Noise Figure (NF) - Of an active device, over the bandwidth of interest, the contribution by the device itself to thermal noise at its output. The noise figure is usually expressed in decibels ( dB ), and is with respect to thermal noise power at the system impedance, at a standard noise temperature (usually 20 o C, 293 K) over the bandwidth of interest. It is determined by (a) measuring (determining) the ratio, usually expressed in dB, of the thermal noise power at the output, to that at the input, and (b) subtracting from that result, the gain, in dB, of the system. Typical noise figures range from 0.5 dB for very low noise devices, to 4 to 8 dB. In some systems, e.g., heterodyne systems, total output noise power includes noise from other than thermal sources, such as spurious contributions from image - frequency transformation, but noise from these sources is not considered in determining the noise figure. In this example, the noise figure is determined only with respect to that noise that appears in the output via the principal frequency transformation of the system, and excludes noise that appears via the image frequency transformation. Synonym noise factor.
Noise Level - The noise power, usually relative to a reference. Note: Noise level is usually measured in dB for relative power or picowatts for absolute power. A suffix is added to denote a particular reference base or specific qualities of the measurement. Examples of noise-level measurement units are dBa, dBa(F1A), dBa(HA1), dBa0, dB, dBm(psoph), dBm0, dBm0P, dBrn, dBrnC, dBrn( f 1 -f 2 ), dBrn(144-line), pW, pWp , and pWp0.
Noise Power - 1. The power generated by a random electromagnetic process. 2. Interfering and unwanted power in an electrical device or system. 3. In the acceptance testing of radio transmitters, the mean power supplied to the antenna transmission line by a radio transmitter when loaded with noise having a Gaussian amplitude-vs.- frequency distribution.
Noise Power Density - The noise power in a bandwidth of 1 Hz, i.e. , the noise power per hertz at a point in a noise spectrum. Note: The noise-power density of the internal noise that is contributed by a receiving system to an incoming signal is expressed as the product of Boltzmann's constant, k, and the equivalent noise temperature, T n . Thus, the noise- power density is often expressed simply as k T . Synonym k T .
Noise Suppression -1. Reduction of the noise power level in electrical circuits. 2. The process of automatically reducing the noise output of a receiver during periods when no carrier is being received.
Noise Temperature - At a pair of terminals, the temperature of a passive system having an available noise power per unit bandwidth at a specified frequency equal to that of the actual terminals of a network. Note: The noise temperature of a simple resistor is the actual temperature of that resistor. The noise temperature of a diode may be many times the actual temperature of the diode.
Noise Voltage -1. Interfering and unwanted voltage in an electronic device or system. 2. In optical communications, the rms component of the optical detector output electrical voltage with no incoming signal present.
Noise Weighting - A specific amplitude-vs.-frequency characteristic that permits a measuring set to give numerical readings that approximate the interfering effects to any listener using a particular class of telephone instrument. Note 1: Noise weighting measurements are made in lines terminated either by the measuring set or the class of instrument. Note 2: The most widely used noise weightings were established by agencies concerned with public telephone service, and are based on characteristics of specific commercial telephone instruments, representing successive stages of technological development. The coding of commercial apparatus appears in the nomenclature of certain weightings. The same weighting nomenclature and units are used in military versions of commercial noise measuring sets.
Noise Window - A notch, i.e., a dip, in the noise frequency spectrum characteristic of a device, such as a transmitter, receiver, channel, or amplifier, from external sources or internal sources. Note: The noise window is usually represented as a band of lower amplitude noise in a wider band of higher amplitude noise.
Noisy Black -1. In facsimile or display systems, such as television, a nonuniformity in the black area of the image, i.e., document or picture, caused by the presence of noise in the received signal. 2. A signal or signal level that is supposed to represent a black area on the object, but has a noise content sufficient to cause the creation of noticeable white spots on the display surface or record medium.
Noisy White -1. In facsimile or display systems, such as television , a nonuniformity in the white area of the image , i.e., , document or picture , caused by the presence of noise in the received signal . 2. A signal or signal level that is supposed to represent a white area on the object, but has a noise content sufficient to cause the creation of noticeable black spots on the display surface or record medium .
No-lone Zone - An Area, room, or space that, when staffed, must be occupied by two or more appropriately cleared individuals who remain within sight of each other.
Nominal Bandwidth - The widest band of frequencies, inclusive of guard bands, assigned to a channel. Note: Nominal bandwidth should not be confused with the terms " necessary bandwidth," " occupied bandwidth," or " rf bandwidth."
Nominal Bit Stuffing Rate - The rate at which stuffing bits are inserted when both the input and output bit rates are at their nominal values.
Nominal Linewidth - In facsimile systems, the average separation between centers of adjacent scanning or recording lines.
Nonassociated Common-Channel Signaling - A form of common-channel signaling where the signaling channel serves one or more trunk groups, at least one of which terminates at a point other than the signal transfer point at which the signaling channel terminates.
Nonassociated Mode Of Signaling - The signaling mode in which messages involving two (nonadjacent) signaling points are communicated between them over two or more signaling links in tandem passing through one or more signaling transfer points other than those which are the origin and destination of the messages.
Nonblocking Switch - A switch that has enough paths across it that an originated call can always reach an available line without encountering a busy condition.
Non-Call Associated Signaling (NCAS) - Signaling that is independent of an end-to-end bearer connection, including support for the functions of registration, authentication, and validation.
Nonce - In cryptography, a time - variant parameter, such as a counter or a time stamp, that is used in key management protocols to prevent message replay and other types of attacks.
Noncentralized Operation - Operation that uses a control discipline for multipoint data communication links in which transmission may be between tributary stations or between the control station and tributary stations.
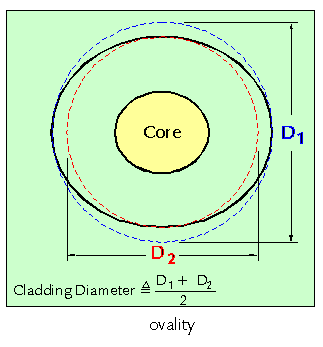
Noncircularity - Synonym ovality. 1. The attribute of an optical fiber, the cross section of the core or cladding of which deviates from a perfect circle. 2. In an optical fiber, the degree of deviation, from perfect circularity, of the cross section of the core or cladding. Note 1: The cross sections of the core and cladding are assumed to first approximation to be elliptical. Quantitatively, the ovality of either the core or cladding is expressed as 2( a - b )/( a + b ), where a is the length of the major axis and b is the length of the minor axis. The dimensionless quantity so obtained may be multiplied by 100 to express ovality as a percentage. Note 2: Alternatively, ovality of the core or cladding may be expressed or specified by a tolerance field consisting of two concentric circles, within which the cross section boundaries must lie.
Noncooperative Remote Rekeying - Synonym automatic remote rekeying. A procedure to rekey a distant crypto-equipment electronically without specific actions by the receiving terminal operator.
Noncritical Technical Load - Of the total technical load at a facility during normal operation, the part that is not required for synchronous operation.
Nonerasable Storage - Synonym read-only memory. A memory in which data, under normal conditions, can only be read.
Non-Fixed Access - In personal communications service ( PCS ), terminal access to a network in which there is no set relationship between a terminal and the access interface. Note: The access interface and the terminal each has its own separate "identifiers." The terminal may be moved from one access interface to another while maintaining the terminal's unique identity.
Nonlinear Distortion - Distortion caused by a deviation from a linear relationship between specified input and output parameters of a system or component.
Nonlinear Scattering - Direct conversion of a photon from one wavelength to one or more other wavelengths. Note 1: In an optical fiber, nonlinear scattering is usually not important below the threshold irradiance for stimulated nonlinear scattering. Note 2: Examples of nonlinear scattering are Raman and Brillouin scattering.
Non-Listed Numbers - Specialized Directory Listings not listed in the phone book but are available through Directory Assistance.
Nonloaded Twisted Pair - A twisted pair that has no intentionally added inductance.
Nonoperational Load - Administrative, support, and housing power requirements.
Non-Published Numbers - Specialized Directory Listings not available in the phone book or through Directory Assistance.
Non-Repeated Video Frame (active frame) - See active video frame identification. The process of comparing each output video frame with its preceding frame(s) in sequence and quantifying the extent of correspondence between each pair; when there is limited correspondence between a pair of frames (such that the differences measured are distinguishable from the measurement noise ), and the corresponding input sequence of frames possesses distinguishable differences, then the current frame is categorized as an active frame.
Nonrepudiation -1. The capability, in security systems, that guarantees that a message or data can be proven to have originated from a specific person. 2. Assurance the sender of data is provided with proof of delivery and the recipient is provided with proof of the sender's identity, so neither can later deny having processed the data.
Nonresonant Antenna - Synonym aperiodic antenna. An antenna designed to have an approximately constant input impedance over a wide range of frequencies. Note: Examples of aperiodic antennas include terminated rhombic antennas and wave antennas.
Non-Return-To-Zero (NRZ) - A code in which "1s" are represented by one significant condition and "0s" are represented by another, with no neutral or rest condition, such as a zero amplitude in amplitude modulation (AM), zero phase shift in phase-shift keying ( PSK ), or mid- frequency in frequency-shift keying ( FSK ). Note: For a given data signaling rate, i.e., bit rate, the NRZ code requires only one-half the bandwidth required by the Manchester code.
Non-Return-To-Zero Change-On-Ones (NRZ1) - A code in which "1s" are represented by a change in a significant condition and "0s" are represented by no change.
Non-Return-To-Zero Mark (NRZ-M) - A binary encoding scheme in which a signal parameter, such as electric current or voltage, undergoes a change in a significant condition or level every time that a "one" occurs, but when a "zero" occurs, it remains the same, i.e. , no transition occurs. Note 1: The transitions could also occur only when "zeros" occur and not when "ones" occur. If the significant condition transition occurs on each "zero," the encoding scheme is called " non-return-to-zero space " ( NRZ -S). Note 2: NRZ-M and NRZ-S signals are technically interchangeable; i.e., one is the logical "NOT" (inverse) of the other. It is necessary for the receiver to have prior knowledge of which scheme is being used. Without such knowledge, it is impossible for the receiver to interpret the data stream correctly; i.e., its output may be the correct data stream or the logical inverse of the correct data stream. Synonyms conditioned baseband representation, differentially encoded baseband, non-return-to-zero one.
Non-Return-To-Zero One (NRZ-1) - Synonym non-return-to-zero mark.
Non-Return-To-Zero Space (NRZ-S) - A binary encoding scheme in which a signal parameter, such as electric current or voltage, undergoes a change in a significant condition or level every time that a "zero" occurs, but when a "one" occurs, it remains the same, i.e. , no transition occurs. Note 1: The transitions could also occur only when "ones" occur and not when "zeros" occur. If the significant condition transition occurs on each "one," the encoding scheme is called "non-return to zero mark " ( NRZ-M ). Note 2: NRZ-S and NRZ-M signals are technically interchangeable; i.e., one is the logical "NOT" (inverse) of the other. It is necessary for the receiver to have prior knowledge of which scheme is being used. Without such knowledge, it is impossible for the receiver to interpret the data stream correctly; i.e., its output may be the correct data stream or the logical inverse of the correct data stream. Synonym non-return-to-zero.
Nonsecret Encryption - Synonym public key cryptography. The type of cryptography in which the encryption process is publicly available and unprotected, but in which a part of the decryption key is protected so that only a party with knowledge of both parts of the decryption process can decrypt the cipher text. Note: Commonly called non-secret encryption in professional cryptologic circles. FIREFLY is an application of public key cryptography. 2. An Encryption system using a linked pair of keys. What one pair of keys encrypts, the other pair decrypts.
Nonshifted Fiber - Synonym dispersion-unshifted fiber. A single-mode optical fiber that has a nominal zero-dispersion wavelength in the 1.3-
m transmission window.
Nonsynchronous Data Transmission Channel - A data transmission channel in which separate timing information is not transferred between the data terminal equipment ( DTE ) and the data circuit terminating equipment ( DCE ).
Nonsynchronous Network - Synonym asynchronous network. A network in which the clocks do not need to be synchronous or mesochronous.
Nonsynchronous System - See asynchronous transmission. Data transmission in which the instant that each character , or block of characters, starts is arbitrary; once started, the time of occurrence of each signal representing a bit within the character, or block, has the same relationship to significant instants of a fixed time frame.
Nonsynchronous Transmission - See asynchronous transmission. Data transmission in which the instant that each character , or block of characters, starts is arbitrary; once started, the time of occurrence of each signal representing a bit within the character, or block, has the same relationship to significant instants of a fixed time frame.
Nontechnical Load - Of the total operational load at a facility during normal operation, the part used for support purposes, such as general lighting, heating, air-conditioning, and ventilating equipment.
Non-Transparent Loopback - A loopback in which the signal transmitted beyond the loopback point (the forward signal ) when the loopback is activated, is not the same as the received signal at the loopback point. The forward signal may be a defined signal or unspecified.
Nontransparent Mode - A mode of operating a data transmission system in which control characters are treated and interpreted as such, rather than simply as data or text bits in a bit.
Normal/Alarm (N/A) State Bit - A bit used in signaling packets to transfer information on alarm status across a permanent virtual circuit in the direction of transmission from the channelized side to the packetized side. The N/A bit set to 0 indicates normal operation. The N/A bit set to 1 indicates the existence of an alarm on the channelized access facility or error condition on the permanent virtual circuit.
Normalized Frequency (V) -1. In an optical fiber, a dimensionless quantity, V, given by
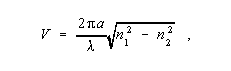
where a is the core radius,
is the wavelength in vacuum, n 1 is the maximum refractive index of the core, and n 2 is the refractive index of the homogeneous cladding. Note 1: In multimode operation of an optical fiber having a power-law refractive index profile, the approximate number of bound modes, i.e., the mode volume, is given by
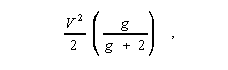
where V is the normalized frequency greater than 5 and g is the profile parameter. Note 2: For a step index fiber, the mode volume is given by V 2/2. For single-mode operation, V < 2.405. Synonym V number. 2. The ratio between an actual frequency and a reference value. 3. The ratio between an actual frequency and its nominal value.
Normal Mode (Application Layer) - The mode of ACSE (association control service element) operation that results in the transfer of ACSE semantics, using the presentation service.
Normal Mode (Presentation Layer) - The mode of operation of the Presentation Layer, which provides the full facilities of the presentation service.
Normal Resolution Still Image - A still image transmitted in the ANSI Tl.314 video stream encoded to the same resolution as the previous motion video ( i.e., QCIF— quarter common intermediate format ). Note: This mode uses a bit 2 "document camera indicator."
Normal Routing - The routing of a given signaling traffic stream under normal conditions (in the absence of failures).
NORM state - A state that exists on a permanent virtual circuit connection when there are no alarm conditions on either the originating or terminating endpoints. The absence of alarms must be satisfied on both the channelized side and the packetized side. During the NORM state, signaling packets have their normal alarm (N/A) bit set to 0.
North American Number Plan (NANP) - A plan for the allocation of unique 10- digit address numbers. The numbers consists of a 3-digit area ( numbering plan area ) code, a 3-digit office code, and a 4-digit line number. The plan also extends to format variations ( e.g., 3-digit and 7-digit address), prefixes ( e.g. , 1, 0, 01, and 011), and special code applications ( e.g., service access codes).
Notarization - A method of changing a key -enciphering key so as to confirm the identities of the originator and the ultimate recipient.
Notch - In a relatively wide band of frequencies, not necessarily of uniform amplitude, a narrow band of frequencies having relatively low amplitudes
Notched Filter - Synonym band-stop filter. - A filter that attenuates, usually to very low levels, all frequencies between two non-zero, finite limits and passes all frequencies not within the limits. Note: A band-stop filter may be designed to stop the specified band of frequencies but usually only attenuates them below some specified level.
Notched Noise - Noise from which a narrow band of frequencies has been removed. Note: Notched noise is usually used for testing devices or circuits.
Not-Ready Condition - At the data terminal equipment / data circuit-terminating equipment ( DTE / DCE ) interface , a steady-state condition that indicates that the DCE is not ready to accept a call -request signal or that the DTE is not ready to accept an incoming call.
Np - Abbreviation for neper. A unit used to express ratios, such as gain, loss, and relative values. Note 1: The neper is analogous to the decibel, except that the Naperian base 2.718281828. . . is used in computing the ratio in nepers. Note 2: The value in nepers, Np , is given by Np = ln( x 1 / x 2 ), where x 1 and x 2 are the values of interest, and ln is the natural logarithm, i.e., logarithm to the base e. Note 3: One neper (Np) = 8.686 dB, where 8.686 = 20/(ln 10). Note 4: The neper is often used to express voltage and current ratios, whereas the decibel is usually used to express power ratios. Note 5: Like the dB, the Np is a dimensionless unit. Note 6: The ITU recognizes both units.
NPA - Abbreviation for numbering plan area. A defined geographic area identified by a unique three- digit code used in the North American Number Plan Area.
NRI - Abbreviation for net radio interface. An interface between a single- channel radio station (usually in a radio net ) and switched communications systems.
NRZ - Abbreviation for non-return-to-zero. A code in which "1s" are represented by one significant condition and "0s" are represented by another, with no neutral or rest condition, such as a zero amplitude in amplitude modulation (AM), zero phase shift in phase-shift keying ( PSK ), or mid- frequency in frequency-shift keying ( FSK ).
NRZ-M - Synonym non-return-to-zero mark. A binary encoding scheme in which a signal parameter, such as electric current or voltage, undergoes a change in a significant condition or level every time that a "one" occurs, but when a "zero" occurs, it remains the same, i.e. , no transition occurs. Note 1: The transitions could also occur only when "zeros" occur and not when "ones" occur. If the significant condition transition occurs on each "zero," the encoding scheme is called " non-return-to-zero space " ( NRZ -S). Note 2: NRZ-M and NRZ-S signals are technically interchangeable; i.e., one is the logical "NOT" (inverse) of the other. It is necessary for the receiver to have prior knowledge of which scheme is being used. Without such knowledge, it is impossible for the receiver to interpret the data stream correctly; i.e., its output may be the correct data stream or the logical inverse of the correct data stream.
NS/EP telecommunications - Abbreviation for National Security or Emergency Preparedness telecommunications. Telecommunications services that are used to maintain a state of readiness or to respond to and manage any event or crisis (local, national, or international) that causes or could cause injury or harm to the population, damage to or loss of property, or degrade or threaten the national security or emergency preparedness posture of the United States.
n-Sequence - A pseudorandom binary sequence of n bits that (a) is the output of a linear shift register and (b) has the property that, if the shift register is set to any nonzero state and then cycled, a pseudorandom binary sequence of a maximum of n = 2 m -1 bits will be generated, where m is the number of stages, i.e. , the number of bit positions in the register, before the shift register returns to its original state and the n -bit output sequence repeats. Note: The register may be used to control the sequence of frequencies for a frequency-hopping spread spectrum transmission system.
NSFnet - The high-speed national network that superseded ARPA Net as the framework of the Internet. Note: NSFnet was created under the auspices of the National Science Foundation.
NTI - Abbreviation for network terminating interface. That point at which operational control or ownership of communications facilities changes from one organizational entity to another. Note: The demarcation point is usually the interface point between customer-premises equipment and external network service provider equipment.
NTIA - Abbreviation for National Telecommunications and Information Administration. The President's principal adviser on telecommunications and information policy issues.
NTN - Abbreviation for network terminal number. In the ITU-T International X.121 format, the sets of digits that comprise the complete address of the data terminal end point. Note: For an NTN that is not part of a national integrated numbering format, the NTN is the 10 digits of the ITU-T X.25 14- digit address that follow the Data Network Identification Code (DNIC). When part of a national integrated numbering format, the NTN is the 11 digits of the ITU-T X.25 14-digit address that follow the DNIC.
NTSC - Abbreviation for National Television Systems Committee. This is the name of the current analog transmission standard used in the U.S., which the committee created in 1953.
NTSC standard - Abbreviation for National Television Standards Committee standard. The North American standard (525-line interlaced raster -scanned video ) for the generation, transmission, and reception of television signals. Note 1: In the NTSC standard, picture information is transmitted in vestigial- sideband AM and sound information is transmitted in FM. Note 2: In addition to North America, the NTSC standard is used in Central America, a number of South American countries, and some Asian countries, including Japan.
NTSC Tuner - A device built in to a TV set that allows reception of analog broadcasting.
Nuclear Hardness -1. An expression of the extent to which the performance of a system, facility, or device is expected to degrade in a given nuclear environment. 2. The physical attributes of a system or component that will allow survival in an environment that includes nuclear radiation and electromagnetic impulses ( EMI ). Note 1: Nuclear hardness may be expressed in terms of either susceptibility or vulnerability. Note 2: The extent of expected performance degradation ( e.g., outage time, data lost, and equipment damage) must be defined or specified. The environment ( e.g., radiation levels, overpressure, peak velocities, energy absorbed, and electrical stress) must be defined or specified. 3. The physical attributes of a system or component that will allow a defined degree of survivability in a given environment created by a nuclear weapon. Note: Nuclear hardness is determined for specified or actual quantified environmental conditions and physical parameters, such as peak radiation levels, overpressure, velocities, energy absorbed, and electrical stress. It is achieved through design specifications and is verified by test and analysis techniques.
Null -1. In an antenna radiation pattern, a zone in which the effective radiated power is at a minimum relative to the maximum effective radiated power of the main beam. Note 1: A null often has a narrow directivity angle compared to that of the main beam. Thus, the null is useful for several purposes, such as radio navigation and suppression of interfering signals in a given direction. Note 2: Because there is reciprocity between the transmitting and receiving characteristics of an antenna, there will be corresponding nulls for both the transmitting and receiving functions. 2. A dummy letter, letter symbol, or code group inserted in an encrypted message to delay or prevent its solution, or to complete encrypted groups for transmission or transmission security purposes. 3. In database management systems, a special value assigned to a row or a column indicating either unknown values or inapplicable usage. 4. Synonym node.
Null Character (NUL) - In transmission systems, a control character (a) that is used to accomplish media-fill stuffing or a time-fill stuffing in storage device or in a data transmission line and (b) that may be inserted and removed from a series of characters without affecting the meaning of the series. Note: The null character may affect the control of equipment or the format of messages.
Numbering Plan Area (NPA) - A defined geographic area identified by a unique three- digit code used in the North American Number Plan Area. Note 1: Defined geographic area could mean the entire area encompassed by the North American Numbering Plan Area (for 800, 888, 877 codes, etc.). Note 2: By virtue of the overlay concept deployed in some states, there may be two (or more) NPAs assigned to the same defined geographic area.
Numerical Aperture (NA) - 1. The sine of the vertex angle of the largest cone of meridional rays that can enter or leave an optical system or element, multiplied by the refractive index of the medium in which the vertex of the cone is located. Note: The NA is generally measured with respect to an object or image point and will vary as that point is moved. 2. For an optical fiber in which the refractive index decreases monotonically from n 1 on the axis to n 2 in the cladding, an expression of the extent of the fiber's ability to accept, in its bound modes, non-normal incident rays, given by NA = (n 1 2-n 2 2)½. Note: In multimode fibers, the term equilibrium numerical aperture is sometimes used. This refers to the numerical aperture with respect to the extreme exit angle of a ray emerging from a fiber in which equilibrium mode distribution has been established. 3. Loosely, the sine of the radiation or acceptance angle of an optical fiber, multiplied by the refractive index of the material in contact with the exit or entrance face. Note: This usage is approximate and imprecise, but is often encountered.
Numerical Aperture Loss - A loss of optical power that occurs at a splice or a pair of mated connectors when the numerical aperture of the "transmitting" fiber exceeds that of the "receiving" fiber, even if the cores are precisely the same diameter and are perfectly aligned. Note 1: The higher numerical aperture of the transmitting fiber means that it emits a larger cone of light than the receiving fiber is capable of accepting, resulting in a coupling loss. Note 2: In the opposite case of numerical aperture mismatch, where the transmitting fiber has the lower numerical aperture, no numerical aperture loss occurs, because the receiving fiber is capable of accepting light from any bound mode of the transmitting fiber.
n -Unit Code - A code in which the signals or groups of digits that represent coded items, such as characters, have the same number of signal elements or digits, namely n elements or digits, where n may be any positive integer. Note: An example of an n -unit code is the 7-unit code (8-unit with parity ) ASCII code. Each character is represented by a pattern of 7 binary digits. The units may also be characters or other special signs.
n -User - In the ISO Open Systems Interconnection--Reference Model ( OSI--RM ), an n +1 entity that uses the services of the n - layer, and below, to communicate with another n +1 entity. Note: If n identifies a specific or a reference level, the n +1 layer is the layer above the n layer and the n -1 layer is the layer below the n layer. Thus, the n +2 layer is two layers above the n layer.
NVIS - Abbreviation for near-vertical-incidence skywave. In radio propagation , a wave that is reflected from the ionosphere at a nearly vertical angle and that is used in short-range communications to reduce the area of the skip zone and thereby improve reception beyond the limits of the ground wave.
NXX Code - In the North American direct distance dialing numbering plan, a central office code of three digits that designates a particular central office or a given 10,000-line unit of subscriber lines; "N" is any number from 2 to 9, and "X" is any number from 0 to 9.
Nyquist Interval - The maximum time interval between equally spaced samples of a signal that will enable the signal waveform to be completely determined. Note 1: The Nyquist interval is equal to the reciprocal of twice the highest frequency component of the sampled signal. Note 2: In practice, when analog signals are sampled for the purpose of digital transmission or other processing, the sampling rate must be more frequent than that defined by Nyquist's theorem, because of quantization erro introduced by the digitizing process. The required sampling rate is determined by the accuracy of the digitizing process.
Nyquist Rate - The reciprocal of the Nyquist interval, i.e., the minimum theoretical sampling rate that fully describes a given signal, i.e., enables its faithful reconstruction from the samples. Note: The actual sampling rate required to reconstruct the original signal will be somewhat higher than the Nyquist rate, because of quantization errors introduced by the sampling process.
Nyquist's Theorem - Synonym Sampling Theorem. A theorem, developed by H. Nyquist, which states that an analog signal waveform may be uniquely reconstructed, without error, from samples taken at equal time intervals. The sampling rate must be equal to, or greater than, twice the highest frequency component in the analog signal.
Fax Switch Products
|
*Note: All prices include shipping and handling in the continental US and most of Canada. We reserve the right to charge up to the actual price of shipping on all orders outside the continental United States. Customer is responsible for any taxes, duties or brokerage charges that may apply. All orders shipped UPS Ground unless specified. For air and express shipments, appropriate charges will be applied to your order.
Need Help?
- Call now for free phone consultation at 1-866-337-0965.
Click here if you want to share 2 devices on 1 line and don't know which device to choose.
Click here if you want to share 3 or more devices on one line and don't know what type to choose.
"Albert Einstein Presents Fax Switch "
"Dancing Bear Fax Switch Presentation"
![]()
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
You didn't find what you need here?
Please visit our sister company, SuperPhoneStore.com for wholesale to the public telephones, phone accessories or the latest electronics. We have over 4500 different products in stock from over 200 premier manufacturers.