
Telecom Dictionary - Definitions of terms
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
S
Safeguarding Statement - [A] statement affixed to a computer output or printout that states the highest classification being processed at the time the product was produced and requires control of the product, at that level, until determination of the true classification by an authorized person. Synonym [in INFOSEC] banner.
Safety Service - Any radiocommunication service used permanently or temporarily for the safeguarding of human life and property.
Sampled Data - Data in which the information content exists only for instantaneous values measured or determined at or for discrete intervals. Note: Sampled data can be analog or digital.
Sampling - See signal sampling. The process of obtaining a sequence of instantaneous values of a particular signal characteristic, usually at regular time intervals.
Sampling Frequency - See sampling rate. The number of samples taken per unit time, i.e., the rate at which signals are sampled for subsequent use, such as for modulation, coding, and quantization.
Sampling Interval - The reciprocal of the sampling rate, i.e. , the interval between corresponding points on two successive sampling pulses of the sampling signal.
Sampling Rate - The number of samples taken per unit time, i.e., the rate at which signals are sampled for subsequent use, such as for modulation, coding, and quantization. Deprecated synonym sampling frequency.
Sampling Theorem - Synonym Nyquist's theorem. A theorem, developed by H. Nyquist, which states that an analog signal waveform may be uniquely reconstructed, without error, from samples taken at equal time intervals. The sampling rate must be equal to, or greater than, twice the highest frequency component in the analog signal.
Sanitize - [In INFOSEC, the] process to remove information from media such that data recovery is not possible. It includes removing all classified labels, markings, and activity logs.
Sanitizing - Of a recording medium, erasing or overwriting all data in such a manner that it cannot be recovered, even by extraordinary, e.g., laboratory, means. Note: Sanitizing is distinguished from simply "deleting" or "erasing" data. For example, a software-based deletion command may simply mark a file or block of data to the effect that it may be overwritten during a subsequent "save" of different data. Until such a save is performed, the deleted data may be recovered, sometimes by the simple expedient of executing a software command. Likewise, digital data, for example, may be "erased," from a magnetic recording medium, but still be recoverable if subjected to laboratory techniques that can identify residual magnetism left after the erasure.
SAP - Abbreviation for service access point. - 1. A physical point at which a circuit may be accessed. 2. In an Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) layer, a point at which a designated service may be obtained.
Satellite - A body which revolves around another body of preponderant mass and which has a motion primarily and permanently determined by the force of attraction of that other body. Note: A parent body and its satellite revolve about their common center of gravity.
Satellite Access - In satellite communications systems, the establishment of contact with a communications satellite space station. Note: An example of satellite access is access at the moment at which an Earth station commences to use a satellite space station as a signal repeater, i.e. , to use its transponder. Each radio frequency (rf) carrier that is relayed by a satellite space station at any time occupies an access channel. Accesses, i.e., channels, are distinguishable by various system parameters, such as frequency, time, or code.
Satellite Communications - A telecommunications service provided via one or more satellite relays and their associated uplinks and downlinks.
Satellite Digital Audio Radio Service (SDARS) - 1. A satellite-based direct-broadcast radio service in which digitally encoded audio entertainment material is broadcast to Earth-based receivers, either directly from an orbiting satellite, or--in cases in which the receiver is in a shielded location--from the satellite to the receiver via a repeater station. 2. A radiocommunication service in which audio programming is digitally transmitted by one or more space stations directly to fixed, mobile, and/or portable stations, and which may involve complementary repeating terrestrial transmitters, telemetry, tracking and control facilities. 3. A radiocommunication service in which compact-disc quality programming is digitally transmitted by one or more space stations.
Satellite Earth Terminal - Synonym Earth terminal. In a satellite link, one of the non-orbiting communications stations that receives, processes, and transmits signals between itself and a satellite. Note: Earth terminals may be at mobile, fixed, airborne, and waterborne Earth terminal complexes.
Satellite Emergency Position-Indicating Radiobeacon - An Earth station in the mobile-satellite service the emissions of which are intended to facilitate search and rescue operations.
Satellite Link - A radio link between a transmitting Earth station and a receiving Earth station through one satellite. A satellite link comprises one uplink and one downlink.
Satellite Network - A satellite system or a part of a satellite system, consisting of only one satellite and the cooperating Earth stations.
Satellite Operation - See satellite PBX. A PBX system that is not equipped with attendant positions, and is associated with an attended main PBX system. Note: The main attendant provides attendant functions for the satellite system.
Satellite PBX - See satellite operation. A PBX system that is not equipped with attendant positions, and is associated with an attended main PBX system. Note: The main attendant provides attendant functions for the satellite system.
Satellite Period - See period (of a satellite). The time elapsing between two consecutive passages of a satellite through a characteristic point on its orbit.
Satellite Relay - An active or passive satellite repeater that relays signals between two Earth terminals.
Satellite System - A space system using one or more artificial Earth satellites.
Saturation - 1. In a communications system, the condition in which a component of the system has reached its maximum traffic handling capacity. Note: Saturation is equivalent to one erlang per circuit. 2. The point at which the output of a linear device, such as a linear amplifier, deviates significantly from being a linear function of the input when the input signal is increased.Note: Modulation often requires that amplifiers operate below saturation.
Scalability - The degree to which video and image formats can be sized in systematic proportions for distribution over communications channels of varying capacities.
Scan - 1. To examine sequentially, part by part. 2. To examine every reference in every entry in a file routinely as part of a retrieval scheme. 3. In radar, one complete rotation of the interrogating antenna. 4. In SONAR, to search 360° or a specific search sector by the use of phased array of transducers. 5. To sweep, i.e., rotate, a beam about a point or about an axis.
Scan Line - The line produced on a recording medium frame by a single sweep of a scanner. In an imaging system, the path traversed by a scanning spot during a single line sweep.
Scanner - A device that examines a spatial pattern, one part after another, and generates analog or digital signals corresponding to the pattern. Note: Scanners are often used in mark sensing, pattern recognition, and character recognition.
Scanning - 1. In telecommunications systems, examination of traffic activity to determine whether further processing is required. Note: Scanning is usually performed periodically. 2. In television, facsimile, and picture transmission, the process of successively analyzing the colors and densities of the object according to a predetermined pattern. 3. The process of tuning a device through a predetermined range of frequencies in prescribed increments and at prescribed times. Note: Scanning may be performed at regular or random increments and intervals. 4. In radar and radio direction-finding, the slewing of an antenna or radiation pattern for the purpose of probing in a different direction. Note 1: In radar, scanning may be mechanical, using a rotary microwave joint to feed the antenna, or electronic, using a phased array of radiators, the radiated pattern (beam) of which depends on the relative phases of the signals fed to the individual radiators. Note 2: In civilian air traffic control radar, scanning usually implies continuous rotation of the antenna or beam about a vertical axis. In military radars, scanning may occur about other than a vertical axis, and may not encompass a full 360°.
Scanning Direction - In facsimile transmitting equipment, the scanning of an object, such as a message surface or the developed plane in the case of a drum, along parallel lines in a specified pattern. Note 1: The scanning direction is equivalent to scanning over a right-hand helix on a drum. Note 2: The orientation of the message on the scanning plane will depend upon its dimensions. Note 3: In facsimile receiving equipment, scanning from right to left and top to bottom, is called "positive" reception and from left to right and top to bottom, is called "negative" reception. Note 4: Scanning direction conventions are included in CCITT Recommendations for phototelegraphic equipment.
Scanning Field - In facsimile systems, the total of the areas that are actually explored by the scanning spot during the scanning of the object by the transmitter or during scanning of the record medium by the receiver.
Scanning Line - In an imaging system, the path traversed by a scanning spot during a single line sweep.
Scanning Line Frequency - In facsimile, the frequency at which a fixed line perpendicular to the direction of scanning is crossed by a scanning spot. Note: The scanning line frequency is equivalent to drum speed in some mechanical systems. Synonym scanning line rate.
Scanning Line Length - In facsimile systems, the total length of a scanning line, equal to the spot speed divided by the scanning line frequency. Note: The scanning line length is usually greater than the length of the available line.
Scanning Line Period - In facsimile systems, the time interval between (a) the instant at which the scanning spot probes or writes to a given spot on one scanning line, and (b) the instant at which the scanning spot probes or writes to the corresponding spot on the next scanning line.
Scanning Line Rate - Synonym scanning line frequency. In facsimile, the frequency at which a fixed line perpendicular to the direction of scanning is crossed by a scanning spot. Note: The scanning line frequency is equivalent to drum speed in some mechanical systems.
Scanning Pitch - The distance between the centers of consecutive scanning lines.
Scanning Rate - In facsimile and television systems, the rate of displacement of the scanning spot along the scanning line.
Scanning Spot - In facsimile systems, the area on the object, i.e., the original, covered instantaneously by the pickup system of the scanner.
Scan-Stop Lockup - In automatic link establishment (ALE) radios, the undesired condition in which the normal process of (a) scanning radio channels, (b) stopping on the desired channel, or (c) returning to scan is terminated by the equipment.
Scatter - See scattering.
Scattering - Of a wave propagating in a material medium, a phenomenon in which the direction, frequency, or polarization of the wave is changed when the wave encounters discontinuities in the medium, or interacts with the material at the atomic or molecular level. Note: Scattering results in a disordered or random change in the incident energy distribution.
Scattering Center - In the microstructure of a transmission medium, a site at which electromagnetic waves are scattered. Note 1: Examples of scattering centers are vacancy defects; interstitial defects; inclusions, such as a gas molecules, hydroxide ions, iron ions, and trapped water molecules; and microcracks or fractures in dielectric waveguides. Note 2: Scattering centers are frozen in the medium when it solidifies and may not necessarily cause Rayleigh scattering, which varies inversely as the fourth power of the wavelength. For example, in glass optical fibers, there is a high attenuation band at 0.95 m, primarily caused by scattering and absorption by OH (hydroxyl) ions.
Scattering Coefficient - The factor that expresses the attenuation caused by scattering, e.g. , of radiant or acoustic energy, during its passage through a medium. Note: The scattering coefficient is usually expressed in units of reciprocal distance.
Scattering Cross Section - The area of an incident wavefront, at a reflecting surface or medium, such as an object in space, through which will pass radiant energy, that, if isotropically scattered from that point, would produce the same power at a given receiver as is actually provided by the entire reflecting surface.
Scattering Loss - The part of the transmission (power) loss that results from scattering within a transmission medium or from roughness of a reflecting surface.
SCC - Abbreviation for specialized common carrier. A common carrier offering a limited type of service or serving a limited market.
Scene - In video, synonymous with clip.
Scene Cut - Video imagery in which consecutive frames are highly uncorrelated.
Scene Cut Response - In video systems, the perceived impairments associated with a scene cut.
Schematic - 1. A diagram, drawing, or sketch that details the elements of a system, such as the elements of an electrical circuit or the elements of a logic diagram for a computer or communications system. 2. Pertaining to a diagram, drawing, or sketch that details the elements of a system, such as the elements of an electrical circuit or the elements of a logic diagram for a computer or communications system.
Scintillation - In electromagnetic wave propagation, a small random fluctuation of the received field strength about its mean value. Note: Scintillation effects become more significant as the frequency of the propagating wave increases.
Scrambler - A device that transposes or inverts signals or otherwise encodes a message at the transmitter to make the message unintelligible at a receiver not equipped with an appropriately set descrambling device. Note: Scramblers usually use a fixed algorithm or mechanism. However, a scrambler provides communications privacy that is inadequate for classified traffic.
Scratch Pad Store (SPS) - Temporary key storage in crypto-equipment.
Scream - Synonym bang. - The exclamation point character (!) used in early addressing schemes to separate the names of individual machines. Note: Scream-style addressing is no longer common.
Screen - 1. In a telecommunications, computing, or data processing system, to examine entities that are being processed to determine their suitability for further processing. 2. A nonferrous metallic mesh used to provide electromagnetic shielding. 3. To reduce undesired electromagnetic signals and noise by enclosing devices in electrostatic or electromagnetic shields. 4. A viewing surface, such as that of a cathode ray tube or liquid crystal display (LCD).
Screen Capture - In computers, the process or act by which the data currently displayed on a monitor, usually representing a single frame of information, are stored or processed in a graphical format. Note: A screen capture thus represents an instantaneous "snapshot" of the state of the display.
Screened-Host Gateway - Synonym bastion host. A host computer that, in a screened subnetwork, performs the functions of a firewall.
Screened Subnetwork - A subnetwork that permits access from both untrusted external networks and from trusted internal networks, but does not permit traffic flow between the two.
Screening Router - A network router capable of discriminating network-based traffic on the protocol type and the value of the protocol fields within the packet.
Script - A relatively short computer program that performs one specific task. Note: A script is normally used to automate complex or advanced features or procedures within a system. Scripts are commonly used to process user information from Web pages (for example, a search engine is a script).
Scripting Language - A programming language supported by and specific to a particular program. Note: A scripting program is normally used to automate complex or advanced features or procedures within the program.
Scroll - In a display device, to move the display window of the screen vertically to view the contents of a stored document. Note: Scrolling may be performed continuously or incrementally.
Scroll-Mode Terminal - A terminal in which the data are displayed (or pass by) a line at a time.
SCSI - Acronym for small computer system interface. An intelligent interface device that expands a microprocessor (CPU) bus to facilitate connections to multiple peripherals (e.g., CD-ROM drives, hard drives, or scanners) and exchange data with those peripherals via a separate communications bus. Note 1: The original SCSI was capable of supporting up to 7 devices at a data rate of 5 Mb/s over an 8-bit parallel bus. Subsequent SCSI versions feature a parallel communications bus having greater width and speed. Note 2: Since SCSI exchanges data with the peripherals over a separate communications bus rather than the processor bus, the CPU can devote the saved processing time to other tasks. Note 3: Pronounced "scuzzy."
SDARS ( Satellite Digital Audio Radio Service) - 1. A satellite-based direct-broadcast radio service in which digitally encoded audio entertainment material is broadcast to Earth-based receivers, either directly from an orbiting satellite, or--in cases in which the receiver is in a shielded location--from the satellite to the receiver via a repeater station. 2. A radiocommunication service in which audio programming is digitally transmitted by one or more space stations directly to fixed, mobile, and/or portable stations, and which may involve complementary repeating terrestrial transmitters, telemetry, tracking and control facilities. 3. A radiocommunication service in which compact-disc quality programming is digitally transmitted by one or more space stations.
SDLC - Abbreviation for synchronous data link control. In a data network, a bit-oriented protocol for the control of synchronous transmission over data links.
SDTV - Abbreviation for Standard Definition TV. A TV with an internal digital tuner. SDTV has the basic digital television format closest to traditional analog TV.
Search Engine - A specialized program that facilitates information retrieval from large segments of the Internet. Note 1: Search engines attempt to help a user locate desired information or resources by seeking matches to user-specified key words. The usual method for finding and isolating this information is to compile and maintain an index of Web resources that can be queried for the key words or concepts entered by the user. The indices are often built from specific resource lists, and may also be created from the output of Web crawlers, wanderers, robots, spiders, or worms. The indices are usually compiled during times of minimum network traffic. Note 2: Different engines are appropriate for different kinds of searches, and most can be optimized for specified results.
Search robot - See bot, droid.
Search Time - In data processing systems, the time interval required to locate a particular data element, record, or file in a storage device.
Search Vehicles - Sources that offer a variety of methods to obtain information on the WWW (e.g. catalogs, directories, search engines, spiders).
SECAM - Acronym for système electronique couleur avec memoire. A television signal standard (625 lines, 50 Hz, 220 V primary power) used in France, eastern European countries, the former USSR, and some African countries.
Second (s) - In the International System of Units (SI), the time interval equal to 9,192,631,770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the cesium-133 atom.
Secondary Channel - In a system in which two channels share a common interface, a channel that has a lower data signaling rate (DSR) capacity than the primary channel.
Secondary Emission - Particles or radiation, such as photons, Compton recoil electrons, delta rays, secondary cosmic rays, and secondary electrons, that are produced by the action of primary radiation on matter.
Secondary Frequency Standard - A frequency standard that does not have inherent accuracy, and therefore must be calibrated against a primary frequency standard. Note: Secondary standards include crystal oscillators and rubidium standards. A crystal oscillator depends for its frequency on its physical dimensions, which vary with fabrication and environmental conditions. A rubidium standard is a secondary standard even though it uses atomic transitions, because it takes the form of a gas cell through which an optical signal is passed. The gas cell has inherent inaccuracies because of gas pressure variations, including those induced by temperature variations. There are also variations in the concentrations of the required buffer gases, which variations cause frequency deviations.
Secondary Radar - A radiodetermination system based on the comparison of reference signals with radio signals retransmitted from the position to be determined. Note: An example of secondary radar is the transponder-based surveillance of aircraft. Synonym secondary surveillance radar.
Secondary Radiation - See secondary emission. Particles or radiation, such as photons, Compton recoil electrons, delta rays, secondary cosmic rays, and secondary electrons, that are produced by the action of primary radiation on matter.
Secondary Service Area - The service area of a broadcast station served by the skywave and not subject to objectionable interference and in which the signal is subject to intermittent variations in strength.
Secondary Station - In a communications network, a station that (a) is responsible for performing unbalanced link-level operations as instructed by the primary station and (b) interprets received commands and generates responses.
Secondary Surveillance Radar - Synonym secondary radar. A radiodetermination system based on the comparison of reference signals with radio signals retransmitted from the position to be determined. Note: An example of secondary radar is the transponder-based surveillance of aircraft.
Secondary Time Standard - A time standard that requires periodic calibration against a primary time standard.
Second Dialtone - 1. Dialtone presented to the call originator after an access code has been dialed for access to a second, outside, telecommunications system or service. 2. Dialtone returned to the call originator after she/he has dialed an access number and has reached a switch providing access to modem, to a fax machine, to another telephone, etc.
Second Window - Of silica-based optical fibers, the transmission window at approximately 1.3
m. Note: The second window is the minimum-dispersion window in silica-based glasses.
SECOR - : Acronym for secure voice cord board . A desk-mounted patch panel that provides the capability for controlling (a) sixteen 50-kb/s wideband or sixteen 2400-b/s narrowband user lines and (b) 5 narrowband trunks to DSN or other narrowband facilities.
SECTEL - Acronym for secure telephone. See STU. A U.S. Government-approved telecommunications terminal that protects the transmission of sensitive or classified information in voice, data, and facsimile systems.
Section Boundary - The boundary that separates a network section from the adjacent circuit section, or separates an access circuit section from the adjacent DTE (data terminal equipment). Synonym boundary
Sector - A predetermined, addressable angular part of a track or band on a magnetic drum or magnetic disk.
Sectoring - In magnetic or optical disk storage media, the division of tracks into a specified number of segments, for the purpose of organizing the data stored thereon.
Secure Communications - Telecommunications deriving security through use of type 1 products and/or protected distribution systems.
Secure Internet Protocols - A set of security rules or standards that determines how computers talk to each other on a network.
Secure Telephone Unit - See STU. A U.S. Government-approved telecommunications terminal that protects the transmission of sensitive or classified information in voice, data, and facsimile systems.
Secure Transmission - 1. In transmission security, see secure communications . 2. In spread-spectrum systems, the transmission of binary coded sequences that represent information that can be recovered only by persons or systems that have the proper key for the spread-spectrum code-sequence generator, i.e., have a synchronized generator that is identical to that used for transmission.
Secure Voice Cord Board - See SECORD. A desk-mounted patch panel that provides the capability for controlling (a) sixteen 50-kb/s wideband or sixteen 2400-b/s narrowband user lines and (b) 5 narrowband trunks to DSN or other narrowband facilities.
Security - 1. A condition that results from the establishment and maintenance of protective measures that ensure a state of inviolability from hostile acts or influences. 2. With respect to classified matter, the condition that prevents unauthorized persons from having access to official information that is safeguarded in the interests of national security. 3. Measures taken by a military unit, an activity or installation to protect itself against all acts designed to, or which may, impair its effectiveness.
Security Filter - 1. In communications security, the hardware, firmware, or software used to prevent access to specified data by unauthorized persons or systems, such as by preventing transmission, preventing forwarding messages over unprotected lines or circuits, or requiring special codes for access to read-only files. 2. [An] AIS trusted subsystem that enforces security policy on the data that passes through it.
Security Kernel - 1. In computer and communications security, the central part of a computer or communications system hardware, firmware, and software that implements the basic security procedures for controlling access to system resources. 2. A self-contained usually small collection of key security-related statements that (a) works as a part of an operating system to prevent unauthorized access to, or use of, the system and (b) contains criteria that must be met before specified programs can be accessed. 3. Hardware, firmware, and software elements of a trusted computing base that implement the reference monitor concept.
Security Management - In network management, the set of functions (a) that protects telecommunications networks and systems from unauthorized access by persons, acts, or influences and (b) that includes many subfunctions, such as creating, deleting, and controlling security services and mechanisms; distributing security-relevant information; reporting security-relevant events; controlling the distribution of cryptographic keying material; and authorizing subscriber access, rights, and privileges.
Seek - To position selectively the access mechanism of a direct access [storage] device.
Seek Time - The time required for the access arm of a direct-access storage device to be positioned on the appropriate track. Synonym positioning time.
Segment - In a distributed queue dual bus (DQDB) network, a protocol data unit (PDU) that (a) consists of 52 octets transferred between DQDB-layer peer entities as the information payload of a slot, (b) contains a header of 4 octets and a payload of 48 octets, and (c) is either a pre-arbitrated segment or a queued arbitrated segment.
Segmented Encoding Law - An encoding law in which an approximation to a curve defined by a smooth encoding law is obtained by a number of linear segments. Synonym piecewise linear encoding law.
Segregation - In a communications system or network, the protection given to information to conceal it from persons having access to the system or network.
Seizing - The temporary dedication of various parts of a communications system to a specific use, usually in response to a user request for service. Note: The parts seized may be automatically connected, such as by direct distance dialing (DDD), or may require operator intervention.
Seizure Signal - In telephone systems, a signal used by the calling end of a trunk or line to indicate a request for service. Note: A seizure signal also locks out the trunk or line to other demands for service.
Selcall - Acronym for selective calling. Calling from one station in which call identification is sent to signal automatically one or more remote stations and to establish links among them. Note 1: Selective calling may be used to un-mute the speakers at designated stations or to initiate a handshake for link establishment. Note 2: Selective calling is specified in CCIR Recommendations for HF and VHF/UHF radio, generally for ship-to-shore, ship-to-ship, aircraft-to-aircraft, and aircraft-to-ground communications.
Selection Position - Synonym decision instant. In the reception of a digital signal, the instant at which a decision is made by a receiving device as to the probable value of a signal condition.
Selective Calling - See selcall. Calling from one station in which call identification is sent to signal automatically one or more remote stations and to establish links among them. Note 1: Selective calling may be used to un-mute the speakers at designated stations or to initiate a handshake for link establishment. Note 2: Selective calling is specified in CCIR Recommendations for HF and VHF/UHF radio, generally for ship-to-shore, ship-to-ship, aircraft-to-aircraft, and aircraft-to-ground communications.
Selective Combiner - A diversity combiner in which (a) the signals from each channel are added together, (b) the gain of each channel is made proportional to the rms signal level and inversely proportional to the mean square noise level in that channel, and (c) the same proportionality constant is used for all channels. Synonyms ratio-squared combiner, post-detection combiner, predetection combining, maximal-ratio combiner.
Selective Fading - Fading in which the components of the received radio signal fluctuate independently.
Selective Jamming - See electronic warfare. Any military action involving the use of electromagnetic and directed energy to control the electromagnetic spectrum or to attack the enemy. The three major subdivisions within electronic warfare are: electronic attack, electronic protection, and electronic warfare support.
Selective Ringing - In a party line, ringing only the desired user instrument. Note: Without selective ringing, all the instruments on the party line will ring at the same time, selection being made by the number of rings.
Selectivity - A measure of the ability of a receiver to discriminate between a wanted signal on one frequency and unwanted signals on other frequencies.
Self-Authentication - 1. A procedure in which a transmitting station, i.e., a calling station, establishes its own validity without the participation of the receiving station, i.e., the called station. Note: The calling station establishes its own authenticity and the called station is not required to challenge the calling station. Self-authentication is usually used only when one-time authentication systems are used to derive the authentication. 2. Implicit authentication, to a predetermined level, of all transmissions on a secure communications system.
Self-Delineating Block - A block in which a bit pattern or a flag identifies the beginning or end of a block.
Self-Synchronizing Code - A code in which the symbol stream formed by a portion of one code word, or by the overlapped portion of any two adjacent code words, is not a valid code word. Note 1: A self-synchronizing code permits the proper framing of transmitted code words provided that no uncorrected errors occur in the symbol stream. Note 2: External synchronization is not required. Note 3: High-level data link control (HDLC) and Advanced Data Communication Control Procedures (ADCCP) frames represent self-synchronizing code words.
Semiautomated Tactical Command and Control System - A machine-aided command and control system in which human intervention is required in varying degrees to operate the system.
Semi-automatic Mode - 1. In telephone systems, an automacic switching system (line sharing device) which routes the call to the intended device only after someone or an electronic device answers the phone call.
Semi-automatic mode is used as a way to use the "Toll Saver" feature on most answering machines or phones with answering machines. When you called in for messages on a long distance call and if you don't have any, you don't have to pay for the long distance call. With an automatic call processor (line sharing device), semi-automatic mode also allows you to use phone company voice mail if you use distinctive ring mode. Also when using a distinctive ring call router ((line sharing device) semi-automatic mode may also allow you to forward only your voice calls to your cell phone and not any other calls sharing the line such as fax or computer conneted calls.
Semiautomatic Switching System - 1. In telephone systems, a switching system in which telephone operators receive call instructions orally from users and complete them by automatic equipment. 2. At tape-relay intermediate stations, the manual routing or rerouting of taped messages without rekeying them.
Semiconductor Laser - Synonym injection laser diode. A laser that uses a forward-biased semiconductor junction as the active medium. Note: Stimulated emission of coherent light occurs at a p-n junction where electrons and holes are driven into the junction. Synonyms diode laser, laser diode.
Semiduplex Operation - 1. A method which is simplex operation at one end of the circuit and duplex operation at the other. Footnote: In general, duplex operation and semiduplex operation require two frequencies in radiocommunication; simplex operation may use either one or two. 2. Operation of a communications network in which a base station operates in a duplex mode with a group of remote stations operating in a half-duplex mode. Note: The terms "half-duplex" and "simplex" are used differently in wire and radio communications.
Sender - A device that accepts address information from a register or routing information from a translator, and then transmits the proper routing information to a trunk or to local equipment. Note: Sender and register functions are often combined in a single unit.
Sending-End Crossfire - In teletypewriter (TTY) systems, interference, in a given channel, caused by transmissions from one or more adjacent TTY channels transmitting from the end at which the crossfire, i.e., interference, is measured.
Sensitive Information - Information, the loss, or misuse, or unauthorized access to or modification of which could adversely affect the national interest or the conduct of federal programs, or the privacy to which individuals are entitled to under 5 U.S.C. Section 552a (the Privacy Act), but that has not been specifically authorized under criteria established by an Executive Order or an Act of Congress to be kept secret in the interest of national defense or foreign policy.
Sensitivity - In an electronic device, e.g., a communications system receiver, or detection device, e.g., PIN diode, the minimum input signal required to produce a specified output signal having a specified signal-to-noise ratio, or other specified criteria. Note 1: The signal input may be expressed as power in dBm or as field strength in microvolts per meter, with input network impedance stipulated. Note 2: "Sensitivity" is sometimes improperly used as a synonym for "responsivity."
Sensor - A device that responds to a physical stimulus, such as thermal energy, electromagnetic energy, acoustic energy, pressure, magnetism, or motion, by producing a signal, usually electrical.
Sentinel - See flag. In data transmission or processing, an indicator, such as a signal, symbol, character, or digit, used for identification. Note: A sentinel may be a byte, word, mark, group mark, or letter that signals the occurrence of some condition or event, such as the end of a word, block, or message.
Separate Channel Signaling - Signaling in which the whole or a part of one or more channels in a multichannel system is used to provide for supervisory and control signals for the message traffic channels. Note: The same channels, such as frequency bands or time slots, that are used for signaling are not used for message traffic. Contrast with common-channel signaling.
Septet - A byte composed of seven binary elements. Synonym seven-bit byte.
Sequence - An arrangement of items according to a specified set of rules, for example, items arranged alphabetically, numerically, or chronologically.
Sequential Access - Synonym serial access. 1. Pertaining to the sequential or consecutive transmission of data into or out of a device, such as a computer, transmission line, or storage device. 2. A process by which data are obtained from a storage device or entered into a storage device in such a way that the process depends on the location of those data and on a reference to data previously accessed.
Sequential Logic Element - A device that has at least one output channel and one or more input channels, all characterized by discrete states, such that the state of each output channel is determined by the previous states of the input channels.
Sequential Transmission - Synonym serial transmission. The sequential transmission of the signal elements of a group representing a character or other entity of data. Note: The characters are transmitted in a sequence over a single line, rather than simultaneously over two or more lines, as in parallel transmission. The sequential elements may be transmitted with or without interruption.
Serial - 1. Pertaining to a process in which all events occur one after the other; for example, the serial transmission of the bits of a character according to the CCITT V.25 protocol. 2. Pertaining to the sequential or consecutive occurrence of two or more related activities in a single device or channel. 3. Pertaining to the sequential processing of the individual parts of a whole, such as the bits of a character or the characters of a word, using the same facilities for successive parts.
Serial Access -: 1. Pertaining to the sequential or consecutive transmission of data into or out of a device, such as a computer, transmission line, or storage device. 2. A process by which data are obtained from a storage device or entered into a storage device in such a way that the process depends on the location of those data and on a reference to data previously accessed. Synonym sequential access.
Serial Computer - 1. A computer that has a single arithmetic and logic unit. 2. A computer, some specified characteristic of which is serial; for example, a computer than manipulates all bits of a word serially.
Serializer - See parallel-to-serial conversion. Conversion of a stream of multiple data elements, received simultaneously, into a stream of data elements transmitted in time sequence, i.e. , one at a time.
Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) - See Dialup Service
Serial Port - A port through which data are passed serially, i.e. , one bit at a time, and that requires only one input channel to handle a set of bits, e.g., all the bits of a byte. Contrast with parallel port.Serial-to-Parallel Conversion - Conversion of a stream of data elements received in time sequence, i.e., one at a time, into a data stream consisting of multiple data elements transmitted simultaneously. Contrast with parallel-to-serial conversion.
Serial Transmission - The sequential transmission of the signal elements of a group representing a character or other entity of data. Note: The characters are transmitted in a sequence over a single line, rather than simultaneously over two or more lines, as in parallel transmission. The sequential elements may be transmitted with or without interruption. Synonym sequential transmission.
Series T Junction - A three-port waveguide junction that has an equivalent circuit in which the impedance of the branch waveguide is predominantly in series with the impedance of the main waveguide at the junction.
Server - A network device that provides service to the network users by managing shared resources. Note 1: The term is often used in the context of a client-server architecture for a local area network (LAN). Note 2: Examples are a printer server and a file server.
Service - In the Open Systems Interconnection--Reference Model (OSI--RM), a capability of a given layer, and the layers below it, that (a) is provided to the entities of the next higher layer and (b) for a given layer, is provided at the interface between the given layer and the next higher layer.
Service Access - In personal communications service (PCS), the ability for the network to provide user access to features and to accept user service requests specifying the type of bearer services or supplementary service that the users want to receive from the PCS network.
Service Access Point (SAP) - 1. A physical point at which a circuit may be accessed. 2. In an Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) layer, a point at which a designated service may be obtained.
Service Bit - A system overhead bit used for providing a network service, such as a request for a repetition or for a numbering sequence. Note: A service bit is not a check bit.
Service Channel - Synonym orderwire circuit. A voice or data circuit used by technical control and maintenance personnel for coordination and control actions relative to activation, deactivation, change, rerouting, reporting, and maintenance of communication systems and services. Synonyms engineering channel, engineering orderwire.
Service Class - See class of service. 1. A designation assigned to describe the service treatment and privileges given to a particular terminal. 2. A subgrouping of telephone users for the purpose of rate distinction. Note: Examples of class of service subgrouping include distinguishing between (a) individual and party lines, (b) Government and non-Government lines, (c) those permitted to make unrestricted international dialed calls and those not so permitted, (d) business, residence, and coin-operated, (e) flat rate and message rate, and (f) restricted and extended area service. 3. A category of data transmission provided by a public data network in which the data signaling rate, the terminal operating mode, and the code structure, are standardized. Note: Class of service is defined in CCITT Recommendation X.1.
Service Data Unit (SDU) - In layered systems, a set of data that is sent by a user of the services of a given layer, and is transmitted to a peer service user semantically unchanged.
Service Feature - In telephony, any of a number of special functions that may be specified initially, or added to, the user's basic service. Note: Modern telephone switches are capable of providing a wide variety of service features, such as call forwarding and call waiting.
Service Identification - The information that uniquely identifies an NS/EP telecommunications service to the service vendor and the service user.
Service Integrity - The degree to which a service is provided without excessive impairment, once obtained.
Service Outage - The state of a service when (a) a network failure impairs or prevents the initiation of new requests for the service, (b) continued use of the service is impaired or not possible, or (c) certain service parameters fall outside prescribed limits.
Service Probability - The probability of obtaining a specified (or higher) grade of service during a given period of time.
Service Profile - Synonym UPT service profile. In universal personal telecommunications service, a record that contains all information related to a UPT user, which information is required to provide that user with UPT service such as subscriptions to basic and supplementing services and call-routing preferences. Note: Each UPT service profile is associated with a single UPT number.
Service Profile Management - Synonym UPT service profile management. In universal personal telecommunications service, authorized access to and manipulation of the UPT service profile. Note: UPT service profile management can be performed by the UPT user, by the UPT customer (subscriber), or by the UPT service provider.
Service Program - Synonym utility program. A computer program that is in general support of the operations and processes of a computer. Note: Examples of utility programs include diagnostic programs, trace programs, input routines, and programs used to perform routine tasks, i.e., perform everyday tasks, such as copying data from one storage location to another. Synonyms service routine, utility routine, utility program.
Service Provider - 1. An organization that provides services for content providers and for users of a computer network. Note: The services may include access to the computer network, content hosting, server of a private message handling system, news server, etc. 2. A company, organization, administration, business, etc., that sells, administers, maintains, charges for, etc., the service. The service provider may or may not be the provider of the network.
Service Routine - Synonym utility program. A computer program that is in general support of the operations and processes of a computer. Note: Examples of utility programs include diagnostic programs, trace programs, input routines, and programs used to perform routine tasks, i.e., perform everyday tasks, such as copying data from one storage location to another. Synonyms service program, utility routine, utility program.
Service Signals - Signals that enable data systems equipment to function correctly, and possibly to provide ancillary facilities. Synonym housekeeping signals.
Service Termination Point - The last point of service rendered by a commercial carrier under applicable tariffs. Note 1: The service termination point is usually on the customer premises. Note 2: The customer is responsible for equipment and operation from the service termination point to user end instruments. Note 3: The service termination point usually corresponds to the demarcation point.
Service User - An individual or organization, including a service vendor, that is provided a telecommunications service for which a priority level has been requested or assigned.
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) - Communication protocol that operates similarly to H.323 but is less complex and more Internet- and Web-friendly. Fully modular and designed from the ground up for functioning over IP networks, it can be tailored more easily than H.323 for Internet applications. SIP and H.323 can and do coexist. See also MGCP.
Session Layer - Layer 5 of the Open Systems Interconnection--Reference Model. . This layer responds to service requests from the Presentation Layer and issues service requests to the Transport Layer. The Session Layer provides the mechanism for managing the dialogue between end-user application processes. It provides for either duplex or half-duplex operation and establishes checkpointing, adjournment, termination, and restart procedures. See Open Systems Interconnection--Reference Model.
Set - 1. A finite or infinite number of objects, entities, or concepts, that have a given property or properties in common. 2 . To configure all or part of a device into a specified state.
Set-Top Box - A stand-alone device that receives and decodes programming so that it may be displayed on a television. Set-top boxes may be used to receive broadcast, cable, and satellite programming.
Seven-Bit Byte - Synonym septet. A byte composed of seven binary elements.
Seven-Hundred (700) Service - A personal telephone service that allows individuals to receive, via a single number, telephone calls in various locations (e.g. , home, office, or car) from call originators using the same common carrier.
Sexadecimal - Synonym hexadecimal. 1. Characterized by a selection, choice or condition that has sixteen possible different values or states. 2. Pertaining to a fixed-radix numeration system in which the radix is sixteen.
Sextet - A byte composed of six binary elements. Synonym six-bit byte.
S-F - Abbreviation for store-and-forward. Pertaining to communications systems in which messages are received at intermediate routing points and recorded i.e., stored, and then transmitted, i.e., forwarded, to the next routing point or to the ultimate recipient.
SF - Abbreviation for single-frequency. See single-frequency signaling. In telephony, signaling in which dial pulses or supervisory signals are conveyed by a single voice-frequency tone in each direction. Note 1: An SF signaling unit converts E & M signaling to a format (characterized by the presence or absence of a single voice-frequency tone), which is suitable for transmission over an ac path, e.g. , a carrier system. The SF tone is present in the idle state and absent during the seized state. In the seized state, dial pulses are conveyed by bursts of SF tone, corresponding to the interruptions in dc continuity created by a rotary dial or other dc dialing mechanism. Note 2: The SF tone may occupy a small portion of the user data channel spectrum, e.g., 1600 Hz or 2600 Hz ("in-band" SF signaling), usually with a notch filter at the precise SF frequency, to prevent the user from inadvertently disconnecting a call if user data has a sufficiently strong spectral content at the SF frequency. The SF tone may also be just outside the user voice band, e.g., 3600 Hz. Note 3: The Defense Data Network (DDN) transmits dc signaling pulses or supervisory signals, or both, over carrier channels or cable pairs on a 4-wire basis using a 2600-Hz signal tone. The conversion into tones, or vice versa, is done by SF signal units.
SFTS - Abbreviation for standard frequency and time signal. See standard time and frequency signal service. In the United States, standard time and frequency signals, broadcast on very precise carrier frequencies by the U.S. Naval Observatory and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), formerly the National Bureau of Standards (NBS). Note: The Radio Regulations (RR) define an identical international service as standard frequency and time signal service
.SGML - Abbreviation for Standard Generalized Mark-up Language. A file format for storage of text and graphics files.
Shadow Loss - 1. The attenuation caused to a radio signal by obstructions in the propagation path. 2. In a reflector antenna, the relative reduction in the effective aperture of the antenna caused by the masking effect of other antenna parts, such as a feed horn or a secondary reflector, which parts obstruct the radiation path.
Shannon (Sh) - The unit of information derived from the occurrence of one of two equiprobable, mutually exclusive, and exhaustive events. Note: A bit may, with perfect formatting and source coding, contain 1 Sh of information. However, the information content of a bit is usually be less than 1 Sh.
Shannon's Law - A statement defining the theoretical maximum rate at which error-free digits can be transmitted over a bandwidth-limited channel in the presence of noise, usually expressed in the form C = W log2(1 + S /N ), where C is the channel capacity in bits per second, W is the bandwidth in hertz, and S /N is the signal-to-noise ratio. Note: Error-correction codes can improve the communications performance relative to uncoded transmission, but no practical error correction coding system exists that can closely approach the theoretical performance limit given by Shannon's law.
Shaping Network - A network inserted in a circuit for the purpose of improving or modifying the waveform of signals.
Sharpness - The informal, subjective evaluation of detail in the clarity or resolution seen in an image. Note: Often sharpness and resolution are assumed to be directly related, because images possessed of greater sharpness are assumed to have greater resolution. An increase in subjective sharpness is usually reported when objects are more clearly delineated from each other and from background having hard, sharply defined edges. A major contribution to subjective sharpness is this high contrast at edge transitions, as is emphasized by both edge enhancement and aperture correction, for example. In many practical systems, increasing the contrast at edge transitions is often accompanied by a reduction in fine detail, and under these conditions sharpness and resolution may describe opposite characteristics.
Sheath - Of a communications or power cable, the outer covering or coverings of tough material, often plastic, that is resistant to environmental hazards such as abrasion, liquid intrusion, solar radiation, etc., and is used to protect cable component(s) such as optical fibers or metallic conductors that transport the signal or power. Note: There may be more than one sheath surrounding a given cable. For example, some cable designs use an inner sheath surrounded by metallic armor, over which is an outer sheath. Synonym jacket.
Sheath Miles - The actual length of cable in route miles.
Shell - In a computer environment, an operating system command interpreter, i.e., a software utility that reads an input specifying an operation, and that may perform, direct, or control the specified operation. Note 1: For example, a shell may permit a user to switch among application programs without terminating any of them. Note 2: A shell may take its input from either a user terminal or from a file.
Shell Access - Basic Dialup Access to the Internet offering e-mail and mail forwarding, telnet, FTP and IRC.
SHF - Abbreviation for super high frequency. See electromagnetic spectrum.
Shield - 1. A housing, screen, sheath, or cover that substantially reduces the coupling of electric, magnetic, or electromagnetic fields into or out of circuits or transmission lines. 2. A protective cover that prevents the accidental contact of objects or persons with parts or components operating at hazardous voltage levels.
Shielded Pair - A 2-wire transmission line surrounded by a sheath of conductive material that protects it from the effects of external fields and confines fields produced within the line.
Shielded Twisted Pair - A transmission line composed of a twisted 2-wire metallic transmission line surrounded by a sheath of conductive material that protects it from the effects of external fields and confines fields produced within the line.
Shielding - See shield. 1. A housing, screen, sheath, or cover that substantially reduces the coupling of electric, magnetic, or electromagnetic fields into or out of circuits or transmission lines. 2. A protective cover that prevents the accidental contact of objects or persons with parts or components operating at hazardous voltage levels.
Shielding Effectiveness - The factor that expresses the attenuation caused by scattering, e.g., of radiant or acoustic energy, during its passage through a medium. Note: The scattering coefficient is usually expressed in units of reciprocal distance.
Shift - 1. The movement of some or all of the characters or bits of a word by the same number of character or bit positions in the direction of a specified end of a word. 2. In radar, the ability to move the origin of a radial display away from the center of the cathode ray tube.
Shift Register - A storage device, usually in a central processing unit (CPU), in which device a serially ordered set of data may be moved, as a unit, into a discrete number of storage locations. Note 1: Shift registers may be configured so that the stored data may be moved in more than one direction. Note 2: Shift registers may be configured so that data may be entered and stored from multiple inputs. Note 3: Shift registers may be grouped into arrays of two or more dimensions in order to perform more complex data operations.
Ship Earth Station - A mobile Earth station in the maritime mobile-satellite service located on board ship.
Ship's Emergency Transmitter - A ship's transmitter to be used exclusively on a distress frequency for distress, urgency or safety purposes.
Ship Station - A mobile station in the maritime mobile service located on board a vessel which is not permanently moored, other than a survival craft station.
Shock Excitation - Synonym impulse excitation. The production of oscillation in a circuit or device by impressing a stimulus (signal) for a period that is extremely short compared to the duration of the oscillation that it produces.
Short Haul Toll Traffic - A general term applied to message toll traffic between nearby points. In common usage, this term is ordinarily applied to message toll traffic between points less than 20 to 50 miles apart.
Shortwave - In radio communications, pertaining to the band of frequencies approximately between 3 MHz and 30 MHz. Note: "Shortwave" is not a term officially recognized by the international community.
Short Wavelength - In optical communication, optical radiation having a wavelength less than approximately 1
m.
Shot Noise - The noise caused by random fluctuations in the motion of charge carriers in a conductor. Note: There is often a minor inconsistency in referring to shot noise in an optical system: many authors refer to shot noise loosely when speaking of the mean square shot noise current (amperes2) rather than noise power (watts).
SI - Abbreviation for International System of Units.
International System of Units (SI)
SI - International System of Units (SI): The modern form of the metric system, which has been adopted by the United States and most other nations. Note: The SI is constructed from seven base units for independent physical quantities. Tables showing these values are included below and are current as of Fall 1995.
SI Prefixes. The common metric prefixes are; Multiplacation Factor Prefix Name Prefix Symbol 1 000 000 000 000 = 1012 tera T 1 000 000 000 = 109 giga G 1 000 000 = 106 mega M 1 000 = 103 kilo k 100 = 102 hecto h 10 = 101 deka da 0.1 = 10-1 deci d 0.01 = 10-2 centi c 0.001 = 10-3 milli m 0.000 001 = 10-6 micro 0.000 000 001 = 10-9 nano n 0.000 000 000 001 = 10-12 pico p
SI Base Units Quantity Unit Name Unit Symbol length meter m mass kilogram kg time second s electric current ampere A thermodynamic temperature kelvin K amount of substance mole mol luminous intensity candela cd
SI derived units. Derived units are formed by combining base units and other derived units according to the algebraic relations linking the corresponding quantities. The symbols for derived units are obtained by means of the mathematical signs for multiplication, division, and use of exponents. For example, the SI unit for velocity is the meter per second (m/s or m•s-1), and that for angular velocity is the radian per second (rad/s or rad•s-1). Some derived SI units have been given special names and symbols, as listed in this table. Quantity Unit Name Unit Symbol Expression in Terms of Other SI Units Absorbed dose, specific energy imparted, kerma, absorbed dose index gray Gy J/kg Activity (of a radionuclide) becquerel Bq 1/s Celsius temperature degree Celsius C
K Dose equivalent sievert Sv J/kg Electric capacitance farad F C/V Electric charge, quantity of electricity coulomb C A•s Electric conductance siemens S A/V Electric inductance henry H Wb/A Electric potential, potential difference, electromotive force volt V W/A Electric resistance ohm V/A Energy, work, quantity of heat joule J N•m Force newton N kg•m/s2 Frequency (of a periodic phenomenon) hertz Hz 1/s Illuminance lux lx lm/m2 Luminous flux lumen lm cd•sr Magnetic flux weber Wb V•s Magnetic flux density tesla T Wb/m2 Plane angle radian rad m/m Power, radiant flux watt W J/s Pressure, stress pascal Pa N/m2 Solid angle steradian sr m2/m2
This HTML version of FS-1037C was last generated on Fri Aug 23 00:22:38 MDT 1996
Sideband - In amplitude modulation (AM), a band of frequencies higher than or lower than the carrier frequency, containing energy as a result of the modulation process. Note: Amplitude modulation results in two sidebands. The frequencies above the carrier frequency constitute what is referred to as the "upper sideband"; those below the carrier frequency, constitute the "lower sideband." In conventional AM transmission, both sidebands are present. Transmission in which one sideband is removed is called " single-sideband transmission."
Sideband Transmission - See single-sideband transmission.
Signal - 1. Detectable transmitted energy that can be used to carry information. 2. A time-dependent variation of a characteristic of a physical phenomenon, used to convey information. 3. As applied to electronics, any transmitted electrical impulse. 4. Operationally, a type of message, the text of which consists of one or more letters, words, characters, signal flags, visual displays, or special sounds, with prearranged meaning and which is conveyed or transmitted by visual, acoustical, or electrical means.
Signal Booster - A device that receives an incoming broadcast signal, amplifies it, and retransmits it on the same frequency. Such devices are used to improve communications in locations within the normal coverage area of a broadcast system where the signal is blocked or shielded due to natural terrain or man-made obstacles.
Signal Compression - 1. In analog (usually audio) systems, reduction of the dynamic range of a signal by controlling it as a function of the inverse relationship of its instantaneous value relative to a specified reference level. Note 1: Signal compression is usually expressed in dB. Note 2: Instantaneous values of the input signal that are low, relative to the reference level, are increased, and those that are high are decreased. Note 3: Signal compression is usually accomplished by separate devices called "compressors." It is used for many purposes, such as (a) improving signal-to-noise ratios prior to digitizing an analog signal for transmission over a digital carrier system, (b) preventing overload of succeeding elements of a system, or (c) matching the dynamic ranges of two devices. Note 4: Signal compression (in dB) may be a linear or nonlinear function of the signal level across the frequency band of interest and may be essentially instantaneous or have fixed or variable delay times. Note 5: Signal compression always introduces distortion, which is usually not objectionable, if the compression is limited to a few dB. Note 6: The original dynamic range of a compressed signal may be restored by a circuit called an " expander." 2. In facsimile systems, a process in which the number of pels scanned on the original is larger than the number of encoded bits of picture information transmitted.
Signaling - 1. The use of signals for controlling communications. 2. In a telecommunications network, the information exchange concerning the establishment and control of a connection and the management of the network, in contrast to user information transfer. 3. The sending of a signal from the transmitting end of a circuit to inform a user at the receiving end that a message is to be sent.
Signaling Message - 1. An assembly of signaling information pertaining to a call that includes, but is not limited to, management transactions, that is transferred (between signaling points) as an entity. 2. An assembly of signaling information that pertains to a call management transaction, and the like and that is transferred as an entity.
Signals Intelligence (SIGINT) - 1. A category of intelligence comprising, either individually or in combination, all communications intelligence, electronics intelligence, and foreign instrumentation signals intelligence, however transmitted. [JP 1-02] 2. Intelligence derived from communications, electronics, and foreign instrumentation signals.
SIGINT - Acronym for signals intelligence. 1. A category of intelligence comprising, either individually or in combination, all communications intelligence, electronics intelligence, and foreign instrumentation signals intelligence, however transmitted. 2. Intelligence derived from communications, electronics, and foreign instrumentation signals.
Signal - 1. Detectable transmitted energy that can be used to carry information. 2. A time-dependent variation of a characteristic of a physical phenomenon, used to convey information. 3. As applied to electronics, any transmitted electrical impulse. 4. Operationally, a type of message, the text of which consists of one or more letters, words, characters, signal flags, visual displays, or special sounds, with prearranged meaning and which is conveyed or transmitted by visual, acoustical, or electrical means.
Signal Center - A combination of signal communication facilities operated by the Army in the field and consisting of a communications center, telephone switching central and appropriate means of signal communications.
Signal Compression - 1. In analog (usually audio) systems, reduction of the dynamic range of a signal by controlling it as a function of the inverse relationship of its instantaneous value relative to a specified reference level. Note 1: Signal compression is usually expressed in dB. Note 2: Instantaneous values of the input signal that are low, relative to the reference level, are increased, and those that are high are decreased. Note 3: Signal compression is usually accomplished by separate devices called "compressors." It is used for many purposes, such as (a) improving signal-to-noise ratios prior to digitizing an analog signal for transmission over a digital carrier system, (b) preventing overload of succeeding elements of a system, or (c) matching the dynamic ranges of two devices. Note 4: Signal compression (in dB) may be a linear or nonlinear function of the signal level across the frequency band of interest and may be essentially instantaneous or have fixed or variable delay times. Note 5: Signal compression always introduces distortion, which is usually not objectionable, if the compression is limited to a few dB. Note 6: The original dynamic range of a compressed signal may be restored by a circuit called an "expander." 2. In facsimile systems, a process in which the number of pels scanned on the original is larger than the number of encoded bits of picture information transmitted.
Signal Contrast - In facsimile, the ratio of the level of the white signal to the level of the black signal. Note: Signal contrast is usually expressed in dB.
Signal Conversion Equipment - Synonym modem. 1. In general, a device that both modulates and demodulates signals. 2. In computer communications, a device used for converting digital, signals into, and recovering them from, quasi-analog signals suitable for transmission over analog communications channels. Note: Many additional functions may be added to a modem to provide for customer service and control features. Synonym signal conversion equipment. 3. In FDM carrier systems, a device that converts the voice band to, and recovers it from, the first level of frequency translation.
Signal Distance - 1. A measure of the difference between a given signal and a reference signal. Note: For analog signals, the signal distance is the root mean square difference between the given signal and a reference signal over a symbol period. 2. Synonym Hamming distance. The number of digit positions in which the corresponding digits of two binary words of the same length are different. Note 1: The Hamming distance between 1011101 and 1001001 is two. Note 2: The concept can be extended to other notation systems. For example, the Hamming distance between 2143896 and 2233796 is three, and between "toned" and "roses" it is also three.
Signal Distortion - See distortion. 1. In a system or device, any departure of the output signal waveform from that which should result from the input signal waveform's being operated on by the system's specified, i.e. , ideal, transfer function. Note: Distortion may result from many mechanisms. Examples include nonlinearities in the transfer function of an active device, such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or operational amplifier. Distortion may also be caused by a passive component such as a coaxial cable or optical fiber, or by inhomogeneities, reflections, etc., in the propagation path. 2. In start-stop teletypewriter signaling, the shifting of the significant instants of the signal pulses from their proper positions relative to the beginning of the start pulse. Note: The magnitude of the distortion is expressed in percent of an ideal unit pulse length.
Signal Droop - In an otherwise essentially flat-topped rectangular pulse, distortion characterized by a decline of the pulse top. See illustration under waveform.
Signal Element - A part of a signal, distinguished by its nature, magnitude, duration, transition, or relative position. Note: Examples of signal elements include signal transitions, significant conditions, significant instants, and binary digits (bits).
Signal Expansion - Restoration of the dynamic range of a compressed signal. Contrast with signal compression.
Signal Frequency Shift - 1. Any change in frequency. 2. Any change in the frequency of a radio transmitter or oscillator. Note: In the radio regime, frequency shift is also called rf shift. 3. See frequency-shift telegraphy. 4. In facsimile, a frequency modulation system where one frequency represents picture black and another frequency represents picture white. Frequencies between these two limits may represent shades of gray. 5. An intentional frequency change used for modulation purposes.
Signaling - 1. The use of signals for controlling communications. 2. In a telecommunications network, the information exchange concerning the establishment and control of a connection and the management of the network, in contrast to user information transfer. 3. The sending of a signal from the transmitting end of a circuit to inform a user at the receiving end that a message is to be sent.
Signaling Channel - A data channel in combination with its associated signaling terminal equipment.
Signaling Connection Control Part (SCCP) - 1. A component part of SS7 protocol that provides additional functions to the message transfer part (MTP) to provide for Connectionless and Connection Oriented network services to transfer signaling information between exchanges and specialized centers in telecommunication networks. The combination of the MTP and the SCCP is called Network Service part. 2. The part of SS7 that provides additional functions to the MTP to cater to both connectionless as well as connection-oriented network services and to achieve an OSI-compatible network service.
Signaling Data Link - A combination of two data channels operating together in a single signaling system.
Signaling Link - A transmission facility that consists of a signaling data link and its transfer control functions, used for reliable transfer of a signaling message.
Signaling Message - 1. An assembly of signaling information pertaining to a call that includes, but is not limited to, management transactions, that is transferred (between signaling points) as an entity. [T1.226-1992] 2. An assembly of signaling information that pertains to a call management transaction, and the like and that is transferred as an entity.
Signaling Path - In a transmission system, a path used for system control, synchronization, checking, signaling, and service signals used in system management and operations rather than for the data, messages, or calls of the users.
Signaling Rate - The aggregate rate at which data pass a point in the transmission path of a data transmission system. Note 1: The DSR is usually expressed in bits per second. Note 2: The data signaling rate is given by
where m is the number of parallel channels, ni is the number of significant conditions of the modulation in the I-th channel, and Ti is the unit interval, expressed in seconds, for the I-th channel. Note 3: For serial transmission in a single channel, the DSR reduces to (1/T )log2n ; with a two-condition modulation, i.e. , n =2, the DSR is 1/T . Note 4: For parallel transmission with equal unit intervals and equal numbers of significant conditions on each channel, the DSR is (m /T )log2 n ; in the case of a two-condition modulation, this reduces to m /T . Note 5: The DSR may be expressed in bauds, in which case, the factor log2ni in the above summation formula should be deleted when calculating bauds. Note 6: In synchronous binary signaling, the DSR in bits per second may be numerically the same as the modulation rate expressed in bauds. Signal processors, such as four-phase modems, cannot change the DSR, but the modulation rate depends on the line modulation scheme, in accordance with Note 4. For example, in a 2400 b/s 4-phase sending modem, the signaling rate is 2400 b/s on the serial input side, but the modulation rate is only 1200 bauds on the 4-phase output side.
Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) - A common-channel signaling system defined by the CCITT in the 1988 Blue Book, in Recommendations Q.771 through Q.774. Note: SS7 is a prerequisite for implementation of an Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN).
Signaling Time Slot - In TDM carrier systems, a time slot starting at a particular phase or instant in each frame and allocated to the transmission of signaling (supervisory and control) data.
Signal Intelligence - 1. A category of intelligence comprising, either individually or in combination, all communications intelligence, electronics intelligence, and foreign instrumentation signals intelligence, however transmitted. 2. Intelligence derived from communications, electronics, and foreign instrumentation signals.
Signal Level - In a communications system, the signal power or intensity at a specified point and with respect to a specified reference level, e.g., 1 mW.
Signal Message - In communications systems, a message, i.e., an assembly of signaling information, that (a) includes associated message alignment and service indications, (b) pertains to a call, and (c) is transferred via the message transfer part.
Signal-Plus-Noise-Plus-Distortion to Noise-Plus-Distortion Ratio - See SINAD. - 1. The ratio of (a) total received power, i.e., the received signal-plus-noise-plus-distortion power to (b) the received noise-plus-distortion power. 2. The ratio of (a) the recovered audio power, i.e., the original modulating audio signal plus noise plus distortion powers from a modulated radio frequency carrier to (b) the residual audio power, i.e., noise-plus-distortion powers remaining after the original modulating audio signal is removed. Note: The SINAD is usually expressed in dB.
Signal-Plus-Noise-to-Noise Ratio ((S +N )/N ) - At a given point in a communications system, the ratio of (a) the power of the desired signal plus the noise to (b) the power of the noise. Note: The (S +N )/N ratio is usually expressed in dB.
Signal Processing - The processing--such as detection, shaping, converting, coding, and time positioning--of signals, that results in their transformation into other forms, such as other waveshapes, power levels, and coding arrangements.
Signal Processing Gain - 1. The ratio of (a) the signal-to-noise ratio of a processed signal to (b) the signal-to-noise ratio of the unprocessed signal. Note: Signal processing gain is usually expressed in dB. 2. In a spread-spectrum communications system, the signal gain, signal-to-noise ratio, signal shape, or other signal improvement obtained by coherent band spreading, remapping, and reconstitution of the desired signal.
Signal Reference Subsystem - The portion of a facility grounding system that (a) provides reference planes, such as ground-return circuits, for all of the signal paths in the facility and (b) is isolated from other circuits, especially isolated from circuits that carry fault, lightning discharge, and power distribution currents.
Signal Regeneration - Signal processing that restores a signal so that it conforms to its original characteristics.
Signal-Return Circuit - A current-carrying return path from a load back to the signal source, i.e., the low side of the closed loop energy transfer circuit between a source-load pair.
Signal Sampling - The process of obtaining a sequence of instantaneous values of a particular signal characteristic, usually at regular time intervals.
Signal Transition - 1. In the modulation of a carrier, a change from one significant condition to another. Note 1: Examples of signal transitions are a change from one electrical current, voltage, or power level to another; a change from one optical power level to another; a phase shift; or a change from one frequency or wavelength to another. Note 2: Signal transitions are used to create signals that represent information, such as "0" and "1" or "mark" and "space." 2. For channel-associated signaling, a change in state of the A bit for 2-state signaling, A and/or B bit in 4-state signaling, or the A, B, C, and/or D bit for 16-state signaling.
Significant Condition - In the modulation of a carrier, one of the values of the signal parameter chosen to represent information. Note 1: Examples of significant conditions are an electrical current, voltage, or power level; an optical power level; a phase value; or a frequency or wavelength chosen to represent a "0" or a "1"; or a "mark" or a "space." Note 2: The duration of a significant condition is the time interval between successive significant instants. Note 3: A change from one significant condition to another is called a " signal transition." Note 4: Signal transitions are used to create signals that represent information, such as "0" and "1" or "mark" and "space." Note 5: Significant conditions are recognized by an appropriate device. Each significant instant is determined when the appropriate device assumes a condition or state usable for performing a specific function, such as recording, processing, or gating.
Significant Instant - In a signal, any instant at which a significant condition of a signal begins or ends. Note: Examples of significant instants include the instant at which a signal crosses the baseline or reaches 10% or 90% of its maximum value.
Silent Interval - Any portion of a ringing cycle during which the ringing signal is not being applied.
Silent Transfer Destination-After activating either Silent Transfer feature, you will want to tell The Stick where to route the call. The "Destination" program feature gives you the option of routing all after-hours calls to either the fax or modem. Factory preset is to the port labeled "FAX".
Silica - Silicon dioxide (SiO2). Note 1: Silica may occur in crystalline or amorphous form, and occurs naturally in impure forms such as quartz and sand. Note 2: Silica is the basic material of which the most common communication-grade optical fibers are presently made.
Silicon Dioxide (SiO2): See silica.
Simulate - To represent certain features of the behavior of a physical or abstract system by the behavior of another system. Note 1: For example, delay lines may be used to simulate propagation delay and phase shift caused by an actual transmission line. Note 2: A simulator may imitate only a few of the operations and functions of the unit it simulates.
SINAD - Abbreviation for signal-plus-noise-plus-distortion to noise-plus-distortion ratio. 1. The ratio of (a) total received power, i.e., the received signal-plus-noise-plus-distortion power to (b) the received noise-plus-distortion power. 2. The ratio of (a) the recovered audio power, i.e., the original modulating audio signal plus noise plus distortion powers from a modulated radio frequency carrier to (b) the residual audio power, i.e., noise-plus-distortion powers remaining after the original modulating audio signal is removed. Note: The SINAD is usually expressed in dB.
Single Bill Fee - Many long distance companies are now adding a fee to the phone bills of customers who are billed for long distance service through their local phone companies. TDS Long Distance does not charge this fee.
Single-Mode Fiber - Synonym single-mode optical fiber.
Single-Mode Optical Fiber - An optical fiber in which only the lowest order bound mode can propagate at the wavelength of interest. Note 1: The lowest order bound mode is ascertained for the wavelength of interest by solving Maxwell's equations for the boundary conditions imposed by the fiber, e.g., core (spot) size and the refractive indices of the core and cladding. Note 2: The solution of Maxwell's equations for the lowest order bound mode will permit a pair of orthogonally polarized fields in the fiber, and this is the usual case in a communication fiber. Note 3: In step-index guides, single-mode operation occurs when the normalized frequency, V, is less than 2.405. For power-law profiles, single-mode operation occurs for a normalized frequency, V, less than approximately
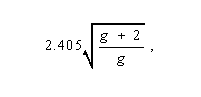
where g is the profile parameter. Note 4: In practice, the orthogonal polarizations may not be associated with degenerate modes. Synonyms monomode optical fiber, single-mode fiber, single-mode optical waveguide, unimode fiber.
Single-Mode Optical Waveguide - Synonym single-mode optical fiber.
Single-Phase Voltage and Frequency - Europe and most other countries in the world use a voltage which is twice that of the US. It is between 220 and 240 volts, whereas in Japan and in most of the Americas the voltage is between 100 and 127 volts.
The system of three-phase alternating current electrical generation and distribution was invented by a nineteenth century creative genius named Nicola Tesla. He made many careful calculations and measurements and found out that 60 Hz (Hertz, cycles per second) was the best frequency for alternating current (AC) power generating. He preferred 240 volts, which put him at odds with Thomas Edison, whose direct current (DC) systems were 110 volts. Perhaps Edison had a useful point in the safety factor of the lower voltage, but DC couldn't provide the power to a distance that AC could.
When the German company AEG built the first European generating facility, its engineers decided to fix the frequency at 50 Hz, because the number 60 didn't fit the metric standard unit sequence (1,2,5). At that time, AEG had a virtual monopoly and their standard spread to the rest of the continent. In Britain, differing frequencies proliferated, and only after World War II the 50-cycle standard was established. A big mistake, however.
Not only is 50 Hz 20% less effective in generation, it is 10-15% less efficient in transmission, it requires up to 30% larger windings and magnetic core materials in transformer construction. Electric motors are much less efficient at the lower frequency, and must also be made more robust to handle the electrical losses and the extra heat generated. Today, only a handful of countries (Antigua, Guyana, Peru, the Philippines, South Korea and the Leeward Islands) follow Tesla’s advice and use the 60 Hz frequency together with a voltage of 220-240 V.
Originally Europe was 110 V too, just like Japan and the US today. It has been deemed necessary to increase voltage to get more power with less losses and voltage drop from the same copper wire diameter. At the time the US also wanted to change but because of the cost involved to replace all electric appliances, they decided not to. At the time (50s-60s) the average US household already had a fridge, a washing-machine, etc., but not in Europe.
The end result is that now, the US seems not to have evolved from the 50s and 60s, and still copes with problems as light bulbs that burn out rather quickly when they are close to the transformer (too high a voltage), or just the other way round: not enough voltage at the end of the line (105 to 127 volt spread !).
Note that currently all new American buildings get in fact 220 volts split in two 110 between neutral and hot wire. Major appliances, such as virtually all drying machines and ovens, are now connected to 220 volts. Americans who have European equipment, can connect it to these outlets.
There are 214 countries listed below.
175 of the countries mentioned use 220-240 volts (50 or 60 Hz).
The 39 other countries use 100-127 volts.
Afghanistan Albania Algeria American Samoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan 220 V 50 Hz Azores Bahamas Bahrain Balearic Islands Bangladesh Barbados Belarus 230 V 50 Hz Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bolivia Bosnia & Herzegovina Botswana Brazil Brunei Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Canary Islands Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Channel Islands (Guernsey & Jersey) Chile China, People's Republic of Colombia Comoros Congo, People's Rep. of Congo, Dem. Rep. of (formerly Zaire) Cook Islands Costa Rica Côte d'Ivoire
(Ivory Coast)Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic East Timor Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faeroe Islands Falkland Islands Fiji Finland France French Guyana Gabon Gambia Gaza Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada (Windward Islands) Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hong Kong Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Ireland (Eire) Isle of Man Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kenya Kazakhstan Kiribati Korea, South Kuwait Kyrgyzstan 220 V 50 Hz Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macau Macedonia Madagascar Madeira Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mexico Micronesia, Federal States of Moldova 230 V 50 Hz Monaco Mongolia Montserrat (Leeward Islands) Morocco Mozambique Myanmar (formerly Burma) Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Réunion Island Romania Russian Federation Rwanda St. Kitts and Nevis (Leeward Islands) St. Lucia (Windward Islands) St. Vincent (Windward Islands) San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia & Montenegro Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Somalia South Africa Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Syria Tahiti Tajikistan Taiwan Tanzania Thailand Togo Tonga Trinidad & Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States of America Uruguay Uzbekistan Venezuela Vietnam Virgin Islands Western Samoa Yemen, Rep. of Zambia Zimbabwe * In Brazil there is no standard voltage. Most states use 127 V electricity (Acre, Amapá, Amazonas, Espírito Santo, Mato Grosso do Sul, Maranhão, Pará, Paraná, Rondônia, Roraima, Sergipe and Minas Gerais). Other – mainly northeastern – states are on 220 V (Alagoas, Brasília, Ceará, Mato Grosso, Goiás, Paraíba, Rio Grande do Norte, Santa Catarina and Tocantins). Although in most parts of the states of Bahia, São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro and Rio Grande do Sul 127 V is used, the cities of Jequié, Jundiaí, São Bernardo do Campo, Novo Friburgo, Bagé, Caxias do Sul and Pelotas run on 220 V. The states of Pernambuco and Piauí use 220 V, except for the cities of Paulista and Teresina (127 V).
** Although the mains voltage in Japan is the same everywhere, the frequency differs from region to region. Eastern Japan uses predominantly 50 Hz (Tokyo, Kawasaki, Sapporo, Yokohoma, Sendai), whereas Western Japan prefers 60 Hz (Osaka, Kyoto, Nagoya, Hiroshima).
*** Saudi Arabia uses 110 V in many parts of the country, such as the Dammam and al-Khobar area (situated in the eastern province of Ash Sharqiyah). 220 V can be commonly found as well, especially in hotels.
Single-Sideband (SSB) Transmission - Sideband transmission in which only one sideband is transmitted. Note: The carrier may be suppressed.
Sink - 1. An absorber of energy. 2. In communications, a device that receives information, control, or other signals from a source. 3. A location at which a specified multiplex structure is terminated through connected equipment removing the frame alignment signal and disassembling the channel time slots.
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) - A method of transferring e-mails between computers on a network.
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol): Communication protocol that operates similarly to H.323 but is less complex and more Internet- and Web-friendly. Fully modular and designed from the ground up for functioning over IP networks, it can be tailored more easily than H.323 for Internet applications. SIP and H.323 can and do coexist. See also MGCP.
Site - 1. The totality of all of the Internet facilities—http, ftp, etc. —offered by an individual or an organization. 2. A Web location where Web pages are found. Synonym (in this sense) Web site. Note: A Web site describes only those resources available through the World Wide Web.
Skew Ray - In a multimode optical fiber, a bound ray that travels in a helical path along the fiber and thus (a) is not parallel to the fiber axis, (b) does not lie in a meridional plane, and (c) does not intersect the fiber axis.
Slamming - When a telephone customer’s long distance service has been switched from one long distance company to another without the customer’s permission. This is illegal.
SLC - Subscriber Line Charge. A monthly fee paid by telephone customers. The money is used to compensate the local telephone company for part of the cost of maintenance and installation of the telephone wire, poles, and other facilities that link a customer’s home to the telephone network.
Slewing - 1. Rotating a directional antenna or transducer rapidly about one or more axes. 2. Changing the frequency or pulse repetition rate of a signal source. 3. Changing the tuning of a receiver, usually by sweeping through many or all frequencies. 4. Redirecting the beam of a fixed antenna array by changing the relative phases of the signals feeding the antenna elements.
SLIP - See Serial Line Internet Protocol or Dialup Access
SLiPPP (Serial Line Internet Point to Point Protocol) - A popular Dialup Access service that comes with a Shell Account, a dedicated IP address, a unique Domain Address and high-speed 28.8 modems.Slit Source - 1. In spectroscopy, an optical source that emits one or more spectrally narrow lines as opposed to a continuous spectrum. 2. In the geometric sense, an optical source having an emitting area in the form of a spatially narrow line, e.g., a slit. Synonym line source.
Smart Bot - Abbreviation for smart robot. See bot.
Smart Robot - See bot.
SMDS - See Switched Multimegabit Data Service
SMTP - See Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
Snell's Law - A law of geometric optics that defines the amount of bending that takes place when a light ray strikes a refractive boundary, e.g., an air-glass interface, at a non-normal angle. Note 1: Snell's law states that
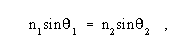
where n1 is the index of refraction of the medium in which the incident ray travels,
1 is the angle, with respect to the normal at the refractive boundary, at which the incident ray strikes the boundary, n2 is the index of refraction of the medium in which the refracted ray travels, and
2 is the angle, with respect to the normal at the refractive boundary, at which the refracted ray travels. The incident ray and refracted ray travel in the same plane, on opposite sides of the normal at the point of incidence. Note 2: If a ray travels from a medium of lower refractive index into a medium of higher refractive index, it is bent toward the normal; if it travels from a medium of higher refractive index to a medium of lower index, it is bent away from the normal. Note 3: If the incident ray travels in a medium of higher refractive index toward a medium of lower refractive index at such an angle that Snell's law would call for the sine of the refracted ray to be greater than unity (a mathematical impossibility); i.e.,
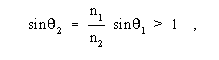
then the "refracted" ray in actuality becomes a reflected ray and is totally reflected back into the medium of higher refractive index, at an angle equal to the incident angle (and thus still "obeys" Snell's Law). This reflection occurs even in the absence of a metallic reflective coating (e.g., aluminum or silver). This phenomenon is called " total internal reflection." The smallest angle of incidence, with respect to the normal at the refractive boundary, which angle will support total internal reflection, is called the " critical angle."
Softphone - A software app that gives you the ability to make and receive calls over the Internet using your PC and a headset or a microphone and speakers. A softphone's interface can look like a traditional phone dial pad or more like an IM client.
Software - 1. A set of computer programs, procedures, and associated documentation concerned with the operation of a data processing system; e.g., compilers, library routines, manuals, and circuit diagrams. 2. Information (generally copyrightable) that may provide instructions for computers; data for documentation; and voice, video, and music for entertainment or education.
Solid State - 1. (electronics). Pertaining to circuits where signals pass through solid semiconductor material such as transistors and diodes as opposed to vacuum tubes where signals pass through a vacuum. The term was introduced to describe the transition from valve-based amplifiers to transistorised amplifiers. Solid-state components last much longer than their thermionic counterparts because of their greater resistance to shock, vibration and mechanical wear.
An electronic component or circuit made of solid materials, such as transistors, chips and bubble memory. There is no mechanical action in a solid state device, although an unbelievable amount of electromagnetic action takes place within.
For data storage, solid state devices are much faster and more reliable than mechanical disks and tapes, but are more expensive. Although solid state costs continually drop, disks, tapes and optical disks also continue to improve their cost/performance ratio.
The first solid state device was the "cat's whisker" of the 1930s. A whisker-like wire was moved around on a solid crystal in order to detect a radio signal.
2. (in physics) - the solid state is one of the three phases of matter (solid, liquid, and gas). Characteristic of or relating to the physical properties of solid materials especially electromagnetic or thermodynamic or structural properties of crystalline solids
SONET - Acronym for synchronous optical network. An interface standard for synchronous optical-fiber transmission, applicable to the Physical Layer of the OSI Reference Model. Note: SONET uses a basic bit rate of 51.840 Mb/s, called OC-1 (optical carrier 1). The SONET hierarchy consists of preset integral multiples of OC-1, i.e., OC-3, OC-12, OC-48, etc.
Sounding - In automated HF radio systems, the broadcasting of a very brief signal, containing the station address, station identifier, or call sign, to permit receiving stations to measure link quality.
Sound Wave - The pattern of disturbance caused by the movement of energy traveling through a medium (such as air, water, or any other liquid or solid matter) as it propagates away from the source of the sound. The source is some object that causes a vibration, such as a ringing telephone, or a person's vocal chords. The vibration disturbs the particles in the surrounding medium; those particles disturb those next to them, and so on. The pattern of the disturbance creates outward movement in a wave pattern, like waves of seawater on the ocean. The wave carries the sound energy through the medium, usually in all directions and less intensely as it moves farther from the source.
The idea that sound moves in waves goes back (at least) to about 240 B.C. The Greek philosopher Chrysippus (c. 240 B.C.), the Roman architect and engineer Vetruvius (c. 25 B.C.), and the Roman philosopher Boethius (A.D. 480-524) each theorized that sound movement might take a wave form.
Source Language - In computing, data processing, and communications systems, a language from which statements are translated. Note: Translators, assemblers, and compilers prepare target language programs, usually machine-language programs, from source language programs, usually high-level language programs written by programmers.
Source User - The user providing the information to be transferred to a destination user during a particular information transfer transaction. Synonym information source.
Space - In telegraphy, one of the two significant conditions of encoding. Note 1: The complementary significant condition is called a " mark." Note 2: In modern digital communications, the two corresponding significant conditions of encoding are called "zero" and "one." Synonyms spacing pulse, spacing signal.
Spam - Slang 1. Unwanted or unsolicited e-mail messages or mailing-list or newsgroup postings. 2. To send an advertisement or solicitation to large numbers of unsolicited recipients, usually via mailing lists or newsgroups.
Spare - An individual part, subassembly, or assembly supplied for the maintenance or repair of systems or equipment.
Speckle Noise - Synonym modal noise. - Noise generated in an optical fiber system by the combination of mode-dependent optical losses and fluctuation in the distribution of optical energy among the guided modes or in the relative phases of the guided modes.
Spectral Density - For a specified bandwidth of radiation consisting of a continuous frequency spectrum, the total power in the specified bandwidth divided by the specified bandwidth. Note: Spectral density is usually expressed in watts per hertz.
Spectral Width - The wavelength interval over which the magnitude of all spectral components is equal to or greater than a specified fraction of the magnitude of the component having the maximum value. Note 1: In optical communications applications, the usual method of specifying spectral width is the full width at half maximum. This method may be difficult to apply when the spectrum has a complex shape. Another method of specifying spectral width is a special case of root-mean-square deviation where the independent variable is wavelength,
, and f (
) is a suitable radiometric quantity. Note 2: The relative spectral width ,
/
, is frequently used where
is obtained according to note 1, and
is the center wavelength.
Spectrum - 1. Federal government designation of a range of frequencies for a category of use or uses. For example, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) allocated the 1900 MHz band for personal communications services. Allocation, typically accomplished in years-long FCC proceedings, tracks new technology development. However, the FCC can shift existing allocations to accommodate changes in spectrum demand. As an example, some UHF television channels were recently reallocated to public safety. 2. A range of electromagnetic radio frequencies used in the transmission of radio, data, and video.
Speech Digit Signaling - Synonym bit robbing. - In digital carrier systems, the practice or technique of preempting, at regular intervals and for the purpose of transmitting signaling information, one digit time slot that (a) is associated with the given user channel for which signaling is required, and (b) is used primarily for transporting encoded speech via that channel. Note 1: Bit robbing is an option in networks compatible with T-carrier, e.g., an ISDN. Note 2: In conventional T-carrier systems, bit robbing uses, in every sixth frame, the time slot associated with the least significant bit.
Speed Dialing - 1. Synonym abbreviated dialing. 2. Dialing at a speed greater than the normal ten pulses per second.
Speed Dialing 8 - Allows you to use preprogrammed one digit dialing to complete calls (local, regional toll, or long distance). Up to eight numbers may be stored in memory. This feature is compatible with Speed Dial 30, which would then give you up to 38 storable numbers. Allows you to program up to eight frequently called phone numbers for dialing with a single-digit code.
To activate dial 74# and wait for the dial tone. Enter the one-digit code you’ve selected followed by the corresponding phone number (up to 15 digits). Several short tones will confirm your entry. Repeat this procedure for up to seven more numbers. To call a speed-dial number wait for the dial tone and press the one-digit code of the number you wish to call followed by #.
Speed Dialing 30 - Allows you to use preprogrammed one, or two, digit dialing to complete calls (local, regional toll or long distance). Up to 30 numbers may be stored in memory. This feature is compatible with Speed Dial 8, which would then give you up to 38 storable numbers. Allows you to program up to 30 frequently called phone numbers for dialing with a two-digit code.
To activate dial 74# and wait for the dial tone. Enter the one-digit code you’ve selected followed by the corresponding phone number (up to 15 digits). Several short tones will confirm your entry. Repeat this procedure for up to seven more numbers. To call a speed-dial number wait for the dial tone and press the one-digit code of the number you wish to call followed by #.
Splice - 1. To join, permanently, physical media that conduct or transmit power or a communication signal. 2. A device that so joins conducting or transmitting media. 3. The completed joint.
Splice Organizer - In optical communication, a device that facilitates the splicing or breaking out of fiber optic cables. Note: The organizer provides means to separate and secure individual buffer tubes, fibers, and/or pigtails. It also provides means to secure mechanical splices or protective sleeves used in connection with fusion splices, and has means to contain the slack fiber that remains after the splicing process is completed.
Splitter - See directional coupler, T-coupler, tee coupler. - A transmission coupling device for separately sampling (through a known coupling loss) either the forward (incident) or the backward (reflected) wave in a transmission line. Note: A directional coupler may be used to sample either a forward or backward wave in a transmission line. A unidirectional coupler has available terminals or connections for sampling only one direction of transmission; a bidirectional coupler has available terminals for sampling both directions.
Spontaneous Emission - Radiation emitted when the internal energy of a quantum mechanical system drops from an excited level to a lower level without regard to the simultaneous presence of similar radiation. Note: Examples of spontaneous emission include radiation from an LED, and radiation from an injection laser below the lasing threshold.
Spoofing - 1. [The] interception, alteration, and retransmission of a cipher signal or data in such a way as to mislead the recipient.2. [An] attempt to gain access to an AIS by posing as an authorized user. 3. Unauthorized use of legitimate Identification and Authentication (I&A) data, however it was obtained, to mimic a subject different from the attacker. Impersonating, masquerading, piggybacking, and mimicking are forms of spoofing.
Spot Speed - In facsimile systems, the speed of the scanning or recording spot along the available line. Note: The spot speed is usually measured on the object or on the recorded copy.
SS7 - Abbreviation for Signaling System No. 7. - A common-channel signaling system defined by the CCITT in the 1988 Blue Book, in Recommendations Q.771 through Q.774. Note: SS7 is a prerequisite for implementation of an Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN).
SR-3 Distinctive Ring Auto Call Processor - The Multi-Link SR-3 Selective Ring Auto Call Processor routes distinctive ring numbers to up to 3 devices on 1 line. Use for Voice, Answering machine, Modem or Fax Switch use.
SSL - The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a common protocol for managing the security of data transmission over the Internet. You can tell if a Web page is encrypted by looking for the "lock" graphic within your browser window. Sites that need to transfer sensitive information such as passwords and credit card information from the browser to the server must have SSL enabled. TDS uses SSL for your protection.
Standard - 1. Guideline documentation that reflects agreements on products, practices, or operations by nationally or internationally recognized industrial, professional, trade associations or governmental bodies. Note: This concept applies to formal, approved standards, as contrasted to de facto standards and proprietary standards, which are exceptions to this concept. 2. An exact value, a physical entity, or an abstract concept, established and defined by authority, custom, or common consent to serve as a reference, model, or rule in measuring quantities or qualities, establishing practices or procedures, or evaluating results. A fixed quantity or quality.
Standby - 1. In computer and communications systems operations, pertaining to a power-saving condition or status of operation of equipment that is ready for use but not in use. Note: An example of a standby condition is a radio station operating condition in which the operator can receive but is not transmitting. 2. Pertaining to a dormant operating condition or state of a system or equipment that permits complete resumption of operation in a stable state within a short time. 3. Pertaining to spare equipment that is placed in operation only when other, in-use equipment becomes inoperative. Note: Standby equipment is usually classified as (a) hot standby equipment, which is warmed up, i.e., powered and ready for immediate service, and which may be switched into service automatically upon detection of a failure in the regular equipment, or (b) cold standby equipment, which is turned off or not connected to a primary power source, and which must be placed into service manually.
Star Network - See network topology. An active star network has an active central node that usually has the means to prevent echo-related problems.
Star Topology - See network topology. A network topology in which peripheral nodes are connected to a central node, which rebroadcasts all transmissions received from any peripheral node to all peripheral nodes on the network, including the originating node. Note 1: All peripheral nodes may thus communicate with all others by transmitting to, and receiving from, the central node only. Note 2: The failure of a transmission line, i.e., channel, linking any peripheral node to the central node will result in the isolation of that peripheral node from all others. Note 3: If the star central node is passive, the originating node must be able to tolerate the reception of an echo of its own transmission, delayed by the two-way transmission time, i.e., to and from the central node, plus any delay generated in the central node. An active star network has an active central node that usually has the means to prevent echo-related problems.
Start Signal - 1. A signal that prepares a device to receive data or to perform a function. 2. In start-stop transmission, a signal at the beginning of a character that prepares the receiving device for the reception of the code elements. Note: A start signal is limited to one signal element usually having the duration of a unit interval.
Start-Stop Transmission - 1. Asynchronous transmission in which a start pulse and a stop pulse are used for each symbol. 2. Signaling in which each group of code elements corresponding to an alphanumeric character is (a) preceded by a start signal that serves to prepare the receiving mechanism for the reception and registration of a character and (b) followed by a stop signal that serves to bring the receiving mechanism to rest in preparation for the reception of the next character.
Statement - 1. In programming languages, a language construct that represents a set of declarations or a step in a sequence of actions. 2. In computer programming, a symbol string or other arrangement of symbols. 3. In computer programming, a meaningful expression or generalized instruction, represented in a source language.
Stimulated Emission - In a quantum mechanical system, the radiation emitted when the internal energy of the system drops from an excited level (induced by the presence of radiant energy at the same frequency) to a lower level. Note: An example of stimulated emission is the radiation from an injection laser diode operated above the lasing threshold.
Stop Signal - 1. In start-stop transmission, a signal at the end of a character that prepares the receiving device for the reception of a subsequent character. A stop signal is usually limited to one signal element having any duration equal to or greater than a specified minimum value. 2. A signal to a receiving mechanism to wait for the next signal.
Storage - (1) The capacity of a device to hold and retain data. (2) Short for mass storage.
Store-and-Forward (S-F) - Pertaining to communications systems in which messages are received at intermediate routing points and recorded i.e., stored, and then transmitted, i.e., forwarded, to the next routing point or to the ultimate recipient.
Start Message - Synonym go-ahead notice. - In a tape-relay communications system, a service message, usually sent to a relay station or to a tributary station, that contains a request to the operator to resume transmitting over a specified channel or channels. Synonyms go-ahead message, start notice.
Start Notice - Synonym go-ahead notice. - In a tape-relay communications system, a service message, usually sent to a relay station or to a tributary station, that contains a request to the operator to resume transmitting over a specified channel or channels. Synonyms go-ahead message, start message .
State Subscriber Line Charge - A charge mandated by some state public service or utility commissions to compensate the local phone company for part of the cost of providing local telephone lines associated with state services, i.e. intrastate long distance and local exchange services.
Station - 1. A telephone set attached to a multi-line Key system or PBX. An automatic call processor will work on a PBX station extension, but WILL NOT work on a Key system station extension. 2. One or more transmitters or receivers or a combination of transmitters and receivers, including the accessory equipment, necessary at one location for carrying on a radiocommunication service, or the radio astronomy service. Each station shall be classified by the service in which it operates permanently or temporarily.
Step-Index Profile - For an optical fiber, a refractive index profile characterized by a uniform refractive index within the core and a sharp decrease in refractive index at the core-cladding interface. Note 1: The step-index profile corresponds to a power-law index profile with the profile parameter approaching infinity. Note 2: The step-index profile is used in most single-mode fibers and some multimode fibers.
Steradian (sr) - The metric unit of solid angle. See International System of Units.
Stick - Business quality Single Line Automatic Call Processor. Line sharing device for small or home business as well large corporations and organizations. Automatically routes calls to the assigned device. The Stick allows up to three telecommunication devices plus an answering machine to share one single phone line. This is Higgins International's popular fax switch. Click here to find out more.
Pages for the Stick:
- The Stick - Saving Money For Small & Large Businesses
- The Stick: Fax, Phone, Voice Device
- The Stick Fax Switch from Multi-Link - Higgins International
- The Stick - Automatic Call Processor for phones, fax, & modems
- The Stick - Phone/Fax/Modem Switch from Multi-Link, Inc.
- The Stick - The most popular fax switch in the world.
Stimulated Emission - In a quantum mechanical system, the radiation emitted when the internal energy of the system drops from an excited level (induced by the presence of radiant energy at the same frequency) to a lower level. Note: An example of stimulated emission is the radiation from an injection laser diode operated above the lasing threshold.
Storage - 1. The retention of data in any form, usually for the purpose of orderly retrieval and documentation. 2. A device consisting of electronic, electrostatic, electrical, hardware, or other elements into which data may be entered, and from which data may be obtained, as desired.
Store - To copy data from a CPU to memory, or from memory to a mass storage device.
Store-and-Forward (S-F) - Pertaining to communications systems in which messages are received at intermediate routing points and recorded i.e., stored, and then transmitted, i.e., forwarded, to the next routing point or to the ultimate recipient.
Strength Member - Any component of a communication cable, metallic or optical, the function of which is to protect the transport medium, i.e., conductor or fiber, from excessive tensile and bending stresses during installation and while in service.
Stratum - The number of a clock (in a hierarchical synchronization distribution system) that defines the quality of the clock by specifying parameters such as frequency accuracy, pull-in range, and noise performance. Note: Only stratum 1 clocks may operate independently; other clocks are slaved directly or indirectly to a stratum 1 clock.
String - A sequence of data elements, such as bits or characters, considered as a whole.
Stuffing - See bit stuffing, de-stuffing. is the insertion of one or more bits into a transmission unit as a way to provide signaling information to a receiver. The receiver knows how to detect and remove or disregard the stuffed bits.
Subassembly - A major subdivision of an assembly consisting of a package of parts, elements, and circuits that perform a specific function.
Subcarrier - A carrier used to modulate another carrier. Note: The modulated carrier can be used to modulate another carrier, and so on, so that there can be several levels of subcarriers, i.e., several intermediate carriers.
Subscriber - The party identified in the account records of a common carrier as responsible for payment of the telephone bill. (1.) Any adult person authorized by such party to change telecommunications services or to charge services to the accounts; or (2.) any person contractually or otherwise lawfully authorized to represent such party.
Successful Block Transfer - The transfer of a correct, nonduplicate, user information block between the source user and intended destination user. Note: Successful block transfer occurs when the last bit of the transferred block crosses the functional interface between the telecommunications system and the intended destination user. Successful block transfer can only occur within a defined maximum block transfer time after initiation of a block transfer attempt.
Successful Disengagement - The termination of user information transfer between a source user and a destination user in response to a disengagement request. Note: Successful disengagement occurs at the earliest moment at which either user is able to initiate a new information transfer transaction.
Sunspot - In the photosphere, i.e., visible disk of the Sun, a dark marking that manifests a magnetic anomaly that is associated with interference with radio communications on Earth. Note: Sunspot activity, i.e., the number of sunspots occurring at a given time or on a given day, is cyclic. The period of a cycle, from maximum through minimum and back to maximum sunspot count, is approximately 11 years.
Supergroup - See group, multiplex hierarchy.
Superluminescent LED - A light-emitting diode in which there is stimulated emission with amplification but insufficient feedback for oscillations to build up to achieve lasing action.
Surface Wave - A wave that is guided along the interface between two different media or by a refractive index gradient. Note 1: The field components of the wave diminish with distance from the interface. Note 2: Optical energy is not converted from the surface wave field to another form of energy and the wave does not have a component directed normal to the interface surface. Note 3: In optical fiber transmission, evanescent waves are surface waves. Note 4: In radio transmission, ground waves are surface waves that propagate close to the surface of the Earth, the Earth having one refractive index and the atmosphere another, thus constituting an interface surface.
Surge Protector - See Surge Suppressor
Surge Suppressor - A surge suppressor (sometimes optimistically called a "surge protector") is a device inserted in the alternating current (AC) utility line and/or telephone line to prevent damage to electronic equipment from voltage "spikes" called transients. A more accurate term for this type of device is "transient suppressor." A typical surge suppressor is a small box with several utility outlets, a power switch, and a 3-wire cord for plugging into a wall outlet.
In most countries where electronic equipment is used, the effective AC utility voltage is 110 to 120 volts; the peak voltage is on the order of plus-or-minus 160 to 170 volts at a frequency of 60 hertz. But transients, which arise from various causes, commonly reach peak levels of several hundred volts. These pulses are of short duration, measured in microseconds (units of 10-6 second), but in that time, they can cause hardware to malfunction. The worst type of transient occurs when lightning strikes in the vicinity (it is not necessary for a power line to be directly hit). Such a "spike" can peak at thousands of volts and cause permanent damage to equipment.
A surge suppressor prevents the peak AC voltage from going above a certain threshold such as plus-or-minus 200 volts. semiconductor devices are used for this purpose. The power line is effectively short-circuited to electrical ground for transient pulses exceeding the threshold, while the flow of normal 60-Hz current is unaffected. For the suppressor to work, a 3-wire AC power connection must be used. "Cheater" adapters, which allow 3-wire appliances to be used with 2-wire outlets or extension cords, defeat the electrical ground connection and render most surge suppressors ineffective.
Surge suppressors should be used as a matter of habit with all semiconductor-based electronic and computer hardware, including peripherals such as printers, monitors, external disk drives, and modems. But the suppressor should not be relied upon to provide protection against lightning-induced transients. The safest procedure, inconvenient though it be, is to ensure that all susceptible hardware is plugged into the suppressor box, and to unplug the suppressor's main power cord when the equipment is not in use if you live in a thunderstorm-prone area.
Surveillance - 1. The use of (usually) electronic means, passive or active, to obtain information about the nature, position, or movement of, e.g., aircraft (cooperative or non-cooperative, friendly or unfriendly), sources of electromagnetic emissions, etc. 2. Nonintrusive monitoring of digital signals in real time to recognize performance degradations and failures and system intrusion attempts.
SVGA - Abbreviation for Super Video Graphics Array. This is a display mode with a resolution of 800 x 600 pixels.
Switch - A device that opens or closes circuits, completes or breaks an electrical path.
Switched Circuit - In a communications network , a circuit that may be temporarily established at the request of one or more of the connected stations.
Switched Multimegabit Data Service (SMDS) - A new standard for extremely high-speed data transfer (up to 34 Mbps).
Switching - The controlling or routing of signals in circuits to execute logical or arithmetic operations or to transmit data between specific points in a network. Note: Switching may be performed by electronic, optical, or electromechanical devices.
Switching Center - In communications systems, a facility in which switches are used to interconnect communications circuits on a circuit-, message-, or packet-switching basis. Synonyms, in telephony, central office, switching exchange, switching facility. Deprecated synonym switch.
Switching Exchange - Synonym switching center.
Switching System - 1. A communications system consisting of switching centers and their interconnecting media. 2. Part of a communication system organized to temporarily associate functional units, transmission channels or telecommunication circuits for the purpose of providing a desired telecommunication facility. Note: Examples of NATO-owned switching systems are IVSN and TARE.
Symmetry - The attribute describing the relationship of information flow between two (or more) access points or reference points involved in a communication. Symmetry characterizes the structure associated with a telecommunication service or a connection. Values associated with this attribute are unidirectional, bidirectional symmetric, and bidirectional asymmetric.
Synchronism - 1. The state of being synchronous. 2. For repetitive events with the same, multiple, or submultiple repetition rates, a relationship among the events such that a significant instant of one event bears a fixed time relationship to a corresponding instant in another event. Note: Synchronism is maintained when there is a fixed, i.e. , constant, phase relationship among the group of repetitive events. 3. The simultaneous occurrence of two or more events at the same instant on the same coordinated time scale.
Synchronization -1. The attaining of synchronism between the frequencies or between the frequencies and phases of two or more signals. 2. The obtaining of a desired fixed relationship among corresponding significant instants of two or more signals. 3. A state of simultaneous occurrences of significant instants among two or more signals.
Synchronous - 1. Pertaining to the relationship of two or more repetitive signals that have simultaneous occurrences of significant instants. Note: " Isochronous " and " anisochronous " pertain to characteristics. " Synchronous " and " asynchronous " pertain to relationships. 2. Pertaining to synchronism.
Synchronous Optical Network - See SONET.
System - 1. Any organized assembly of resources and procedures united and regulated by interaction or interdependence to accomplish a set of specific functions. 2. A combination of two or more interrelated equipment (sets) arranged in a functional package to perform an operational function or to satisfy a requirement. 3. A collection of personnel, equipment, and methods organized to accomplish a set of specific functions.
System Overhead Information - See overhead information. - Digital information transferred across the functional interface between a user and a telecommunications system, or between functional units within a telecommunications system, for the purpose of directing or controlling the transfer of user information or the detection and correction of errors. Note: Overhead information originated by the user is not considered to be system overhead information. Overhead information generated within the communications system and not delivered to the user is system overhead information. Thus, the user throughput is reduced by both overheads while system throughput is reduced only by system overhead.
Fax Switch Products
|
*Note: All prices include shipping and handling in the continental US and most of Canada. We reserve the right to charge up to the actual price of shipping on all orders outside the continental United States. Customer is responsible for any taxes, duties or brokerage charges that may apply. All orders shipped UPS Ground unless specified. For air and express shipments, appropriate charges will be applied to your order.
Need Help?
- Call now for free phone consultation at 1-866-337-0965.
Click here if you want to share 2 devices on 1 line and don't know which device to choose.
Click here if you want to share 3 or more devices on one line and don't know what type to choose.
"Albert Einstein Presents Fax Switch "
"Dancing Bear Fax Switch Presentation"
![]()
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
You didn't find what you need here?
Please visit our sister company, SuperPhoneStore.com for wholesale to the public telephones, phone accessories or the latest electronics. We have over 4500 different products in stock from over 200 premier manufacturers. Check it out!