
Telecom Dictionary - Definitions of terms
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
F
Facet Erosion - In laser diodes, a phenomenon in which a high field intensity of stimulated optical radiation causes degradation of the facets, i.e., those forming the cavity mirrors, decreasing reflectivity and resulting in a decrease of the internal quantum efficiency and an increase in the threshold current.
Facility - 1. A fixed, mobile, or transportable structure, including (a) all installed electrical and electronic wiring, cabling, and equipment and (b) all supporting structures, such as utility, ground network, and electrical supporting structures. 2. A network-provided service to users or the network operating administration. 3. A transmission pathway and associated equipment. 4. In a protocol applicable to a data unit, such as a block or frame, an additional item of information or a constraint encoded within the protocol to provide the required control. 5. A real property entity consisting of one or more of the following: a building, a structure, a utility system, pavement, and underlying land.
Facility Assembly - A group of interconnected equipment and transmission media uniquely identified and dedicated to a specific type of service.
Facility Code - A two- digit code (FC) used in the exchange - carrier -to- interexchange carrier (EC-to- IC ) facility / service selective signaling protocol and the IC-to-EC facility/service selective signaling protocol that identifies the type of facility requested.
Facility Grounding System - The electrically interconnected system of conductors and conductive elements that (a) provides multiple current paths to the earth electrode subsystem, and (b) consists of the earth electrode subsystem, the lightning protection subsystem, and the fault protection subsystem.
Facility Group - The particular group of facilities to route the call.
Facility Group Member - The specific member of a trunk group or a multi-line hunt group.
Facsimile - (FACSimile) Originally called "telecopying," it is the communication of a printed page between remote locations. Fax machines scan a paper form and transmit a coded image over the telephone system. The receiving machine prints a facsimile of the original. A fax machine is made up of a scanner, printer and modem with fax signaling. (see Fax)
Fax standards were developed starting in 1968 and are classified by Groups. Groups 1 and 2, used until the late 1980s, transmitted a page in six and three minutes respectively. Group 3 transmits at less than one minute per page and uses data compression at 9,600 bps. The Group 3 speed increase led to the extraordinary rise in usage in the late 1980s. Group 3 resolution is 203x98 dpi in standard mode, 203x196 in fine mode and 203x392 in super fine mode.
Group 3 is still the standard today, but Group 4 machines can transmit a page in just a few seconds and provide up to 400x400 resolution. Group 4 requires 56 to 64 Kbps bandwidth and needs ISDN or Switched 56 circuits. See fax/modem and e-mail.Facsimile Converter - 1. In a facsimile receiver, a device that changes the signal modulation from frequency-shift keying (FSK) to amplitude modulation (AM). 2. In a facsimile transmitter, a device that changes the signal modulation from amplitude modulation (AM) to frequency-shift keying (FSK).
Facsimile Frequency Shift - At any point in a frequency-shift facsimile system, the numerical difference between the frequency that corresponds to a white signal and the frequency that corresponds to a black signal.
Facsimile Picture Signal - In facsimile systems, the baseband signal that results from the scanning process.
Facsimile Receiver - In a facsimile system, the equipment that converts the facsimile picture signal into a recorded copy.
Facsimile Recorder - In a facsimile receiver, the device that performs the final conversion of the facsimile picture signal to an image of the object, i.e., makes the recorded copy.
Facsimile Signal Level - In a facsimile system, the signal level at any point in the system. Note 1: The facsimile signal level is used to establish the operating levels. Note 2: The facsimile signal level is usually expressed in dB with respect to some standard value, such as 1 mW (milliwatt), i.e., 0 dBm.
Facsimile Transceiver - In a facsimile system, the equipment that sends and receives facsimile signals. Note: Full-duplex facsimile transceivers can send and receive at the same time; half-duplex facsimile transceivers cannot.
Facsimile Transmitter - In a facsimile system, the equipment that converts the baseband picture signals, i.e., the baseband signals resulting from scanning the object, into signals suitable for transmission by a communications system.
Fade - 1. In signal propagation, see fading. 2. In video, the act of dissolving a video picture to either a color, pattern, or titles. Note: Fading a video image is often used as an artistic tool in video productions, usually seen as a fade to black. 3. In audio, a decrease in the sound level until it is no longer audible.
Fade Margin - 1. A design allowance that provides for sufficient system gain or sensitivity to accommodate expected fading, for the purpose of ensuring that the required quality of service is maintained. 2. The amount by which a received signal level may be reduced without causing system performance to fall below a specified threshold value. Synonym fading margin.
Fading - In a received signal, the variation (with time ) of the amplitude or relative phase, or both, of one or more of the frequency components of the signal. Note: Fading is caused by changes in the characteristics of the propagation path with time.
Fading Distribution - The probability distribution that signal fading will exceed a given value relative to a specified reference level. Note 1: In the case of phase interference fading, the time distribution of the instantaneous field strength usually approximates a Rayleigh distribution when several signal components of equal amplitude are present. Note 2: The field strength is usually measured in volts per meter. Note 3: The fading distribution may also be measured in terms of power level, where the unit of measure is usually watts per square meter and the expression is in dB.
Fading Margin - Synonym fade margin. 1. A design allowance that provides for sufficient system gain or sensitivity to accommodate expected fading, for the purpose of ensuring that the required quality of service is maintained. 2. The amount by which a received signal level may be reduced without causing system performance to fall below a specified threshold value.
Fail - See failure, graceful degradation. The temporary or permanent termination of the ability of an entity to perform its required function.
Fail Safe - 1. Of a device, the capability to fail without detriment to other devices or danger to personnel. 2. Pertaining to the automatic protection of programs and/or processing systems to maintain safety when a hardware or software failure is detected in a system. 3. The automatic protection of programs and/or processing systems when hardware or software failure is detected. 4. Pertaining to the structuring of a system such that either it cannot fail to accomplish its assigned mission regardless of environmental factors or that the probability of such failure is extremely low
Fail-Safe Operation - 1. Operation that ensures that a failure of equipment, process, or system does not propagate beyond the immediate environs of the failing entity. 2. A control operation or function that prevents improper system functioning or catastrophic degradation in the event of circuit malfunction or operator error.
Fail Soft - The selective termination of affected nonessential processing, when hardware or software failure is determined to be imminent.
Failure - The temporary or permanent termination of the ability of an entity to perform its required function.
Failure Access - An Unauthorized access to data resulting from a hardware or software failure.
Failure Control - The methods used to detect imminent hardware or software failure and provide fail safe or fail soft recovery.
Fair Queuing - The controlling of congestion in gateways by restricting every host to an equal share of gateway bandwidth. Note: Fair queuing does not distinguish between small and large hosts or between hosts with few active connections and those with many.
Fake Sector - In information assurance, a sector consisting of a header but no data, used in large numbers on a diskette to cause an unauthorized copying program to fail to copy the diskette.
Fall Time - The time required for the amplitude of a pulse to decrease (fall) from a specified value (usually 90 percent of the peak value exclusive of overshoot or undershoot ) to another specified value (usually 10 percent of the peak value exclusive of overshoot or undershoot). Note: Limits on undershoot and oscillation, i.e., hunting, may need to be specified when specifying fall time limits. Synonym pulse decay time.
False Character - See illegal character. A character, or a combination of bits, that is not valid in a given system according to specified criteria, such as with respect to a specified alphabet, a particular pattern of bits, a rule of formation, or a check code.
False Clock - A condition where a phase-locked loop controlling a clock locks on a frequency other than the correct frequency. Note 1: False clock can occur when there is excessive phase shift, as a function of frequency, in the loop. Note 2: False clock often occurs where the false frequency is a harmonic of the correct frequency.
False Lock - A condition where a phase-locked loop locks to a frequency other than the correct one, or to an improper phase.
Fan-Beam Antenna - A directional antenna producing a main beam having a large ratio of major to minor dimension at any transverse cross section.
Fan Out - Synonym break out. To separate the individual fibers or buffer tubes of a fiber-optic cable for the purpose of splicing or installing optical connectors.
Fanout Cable - Synonym breakout cable. A multifiber fiber -optic cable design in which individual fibers, usually tight-buffered, are surrounded by separate strength members and jackets, which are in turn enveloped by a common jacket. Note 1: The breakout cable facilitates easy installation of fiber-optic connectors. All that need be done to prepare the ends of the cable to receive connectors is to remove the outer jacket, exposing what are essentially individual single-fiber cables. Note 2: Because it tends to induce bends in the fibers, the breakout cable design usually results in slightly higher transmission losses, for a given fiber, than loose- buffer designs.
FAQ - An acronym for Frequently Asked Questions. FAQs are online documents that list and answer the most common questions on a particular subject.
FAQ File - Abbreviation for Frequently Asked Questions file. An online file that contains frequently asked questions with answers provided to assist new users and avoid repetitive offline inquiries. Note: An FAQ file is usually created for Internet news groups, but is also used in other applications.
Faraday Effect - A magneto-optic effect in which the polarization plane of an electromagnetic wave is rotated under the influence of a magnetic field parallel to the direction of propagation. Note: The Faraday effect may be used to modulate a lightwave.
Far-End Block Error (FEBE) - An indication returned to a transmitting node (source) that an errored block has been detected at the receiving node (sink).
Far-End Crosstalk - Crosstalk that is propagated in a disturbed channel in the same direction as the propagation of a signal in the disturbing channel. Note: The terminals of the disturbed channel, at which the far-end crosstalk is present, and the energized terminals of the disturbing channel, are usually remote from each other.
Far-End Customer Interface - An associated, loop signaling, customer installation located at the far end of the network transmission path from the network interface (NI) described in the designated document.
Far-End receive Failure (FERF) - An indication returned to a transmitting link terminating equipment (LTE) upon receipt of a line AIS ( alarm indication signal ) code or detection of an incoming line failure at the receiving LTE.
Far Field - Synonym far-field region. The region where the angular field distribution is essentially independent of distance from the source. Note 1: If the source has a maximum overall dimension D that is large compared to the wavelength, the far-field region is commonly taken to exist at distances greater than 2D 2/
from the source,
being the wavelength. Note 2: For a beam focused at infinity, the far-field region is sometimes referred to as the Fraunhofer region. Synonyms far field, far zone, Fraunhofer region, radiation field.
Far-Field Region - The region where the angular field distribution is essentially independent of distance from the source. Note 1: If the source has a maximum overall dimension D that is large compared to the wavelength, the far-field region is commonly taken to exist at distances greater than 2D 2/
from the source,
being the wavelength. Note 2: For a beam focused at infinity, the far-field region is sometimes referred to as the Fraunhofer region. Synonyms far field, far zone, Fraunhofer region, radiation field.
Far-Field Diffraction Pattern - The diffraction pattern of a source (such as an LED, ILD, or the output end of an optical fiber ) observed at an infinite distance from the source. Note 1: A far- field pattern exists at distances that are large compared with s 2 /
, where s is a characteristic dimension of the source and
is the wavelength. For example, if the source is a uniformly illuminated circle, then s is the radius of the circle. Note 2: The far-field diffraction pattern of a source may be observed at infinity or (except for scale) in the focal plane of a well-corrected lens. The far-field pattern of a diffracting screen illuminated by a point source may be observed in the image plane of the source. Synonym Fraunhofer diffraction pattern.
Far-Field Radiation Pattern - A radiation pattern measured at the far field of an antenna or other emitter.
Far-Field Region - The region where the angular field distribution is essentially independent of distance from the source. Note 1: If the source has a maximum overall dimension D that is large compared to the wavelength, the far-field region is commonly taken to exist at distances greater than 2D 2/
from the source,
being the wavelength. Note 2: For a beam focused at infinity, the far-field region is sometimes referred to as the Fraunhofer region. Synonyms far field, far zone, Fraunhofer region, radiation field.
Far Zone - Synonym far-field region. - The region where the angular field distribution is essentially independent of distance from the source. Note 1: If the source has a maximum overall dimension D that is large compared to the wavelength, the far-field region is commonly taken to exist at distances greater than 2D 2/
from the source,
being the wavelength. Note 2: For a beam focused at infinity, the far-field region is sometimes referred to as the Fraunhofer region. Synonyms far field, far zone, Fraunhofer region, radiation field.
Fast Packet Switching - A packet switching technique that increases the throughput by eliminating overhead. Note 1: Overhead reduction is accomplished by allocating flow control and error correction functions to either the user applications or the network nodes that interface with the user. Note 2: Cell relay and frame relay are two implementations of fast packet switching.
Fast Select - An optional user facility in the virtual call service of CCITT X.25 protocol (now, ITU-T X.25 protocol) that allows the inclusion of user data in the call request/connected and clear indication packets. Note: Fast select is an essential feature of the CCITT X.25 (1984) protocol.
Fat Client - A client -centric computing model where software must be installed on each client in a network . This often requires that each client computer be upgraded to the same level.
Fault - 1. An accidental condition that causes a functional unit to fail to perform its required function. 2. A defect that causes a reproducible or catastrophic malfunction. Note: A malfunction is considered reproducible if it occurs consistently under the same circumstances. 3. In power systems, an unintentional short-circuit, or partial short-circuit, between energized conductors or between an energized conductor and ground.
Fault Management - In network management, the set of functions that (a) detect, isolate, and correct malfunctions in a telecommunications network, (b) compensate for environmental changes, and (c) include maintaining and examining error logs, accepting and acting on error detection notifications, tracing and identifying faults, carrying out sequences of diagnostics tests, correcting faults, reporting error conditions, and localizing and tracing faults by examining and manipulating database information.
Fault Protection Subsystem - In a facility power distribution system, the subsystem that provides a direct path from each power sink to the earth electrode subsystem . Note: The fault protection subsystem is usually referred to as a "green wire."
Fault Tolerance - The extent to which a functional unit will continue to operate at a defined performance level even though one or more of its components are malfunctioning.
FaxSwitches.info -FaxSwitches.info is the first and only comparison engine specifically for fax switches. Choose the best line sharing technology for your particular needs and application. We offer all of the major brands and models here in one store. We make it easy to find exactly the right fax switch for your business.
- Fax Switches - All Products
- Long Range Systems
- Multi-Link, Inc.
- Viking Electronics
- About FaxSwitches.info
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Contact Us
- My Account
- Site Map
Fax Tone Detection -This feature, when activated, tells fax switch to detect the presence of CNG/fax tones which may be transmitted by a calling fax machine or PC Fax card. All calls accompanied by CNG tones, whether they be from a fax machine or PC Fax card, are routed through to equipment connected to the device port labeled FAX. If no fax-type equipment is used on fax switch, simply deactivate this feature.
Fax (Telecopying) - The telephonic transmission of scanned-in printed material (text or images), usually to a telephone number associated with a printer or other output device. The original document is scanned with a fax machine, which treats the contents (text or images) as a single fixed graphic image, converting it into a bitmap. In this digital form, the information is transmitted as electrical signals through the telephone system. The receiving fax machine reconverts the coded image and prints a paper copy of the document.
Almost all modems manufactured today are capable of sending and receiving fax data. Fax/modem software generates fax signals directly from disk files or the screen. Even if a document is text only, it is treated by the computer as a scanned image and is transmitted to the receiver as a bitmap. Faxing a message online works well if the recipient wants only to read the message. However, if the document requires editing, it must be converted into ASCII text by an OCR (optical character recognition) program, or it must be retyped manually into the computer. A more efficient method of sending documents that require modification is through the e-mail system. E-mail files are already ASCII text so they can be edited immediately in any text editor or word processing program.
The Internet now provides a new and cheaper way to send faxes in some cases. A number of free and commercial companies provide arrangements for using the Internet rather than the public telephone system for most or part of the path to the fax point. Some services also provide the ability to broadcast a fax to multiple addresses. Acronym for facsimile.
Fax Board - Fax capability built onto a printed circuit board. Today, most fax boards are fax/modems, which also provide data transmission. See fax/modem.
Fax Group - An encoding format used for fax transmission. There are two types: Fax Group 3, also known as G3, and Fax Group 4, also known as G4. Fax Group 3 and 4 are two of the encoding formats for Tagged Image File Format (TIFF) files. The more commonly used format, Fax Group 3, is Recommendation T.4 of the
CCIT , now known as the ITU-T (for Telecommunication Standardization Sector of the International Telecommunications Union). Fax Group 3 supports one-dimensional image compression of black and white images, On a standard fax machine, Fax Group 3 uses redundancy reduction to enhance speed and is able to transmit a page in one minute or less. Fax Group 3 can achieve compression ratios of 10:1 for office documents and 15:1 for engineering drawings with a resolution of 200 dots per inch (dpi).Less frequently used, Fax Group 4 (G4) is ITU-T Recommendation T.6 and supports two-dimensional image compression, compressing the line width as well as the line length. Fax Group 4 can achieve compression ratios of 15:1 for office documents and 20:1 for engineering drawings with a resolution of 400 dpi. Unlike Fax Group 3, Fax Group 4 can use Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) for transmission.
Fax Logger - Automatically storing copies of incoming and outgoing faxes onto some storage medium.
Fax Machine (Facsimile) - A device that attaches to your telephone line and is capable of scanning a document, electronically transmitting and receiving the image, and printing the image(sometimes called "TELEFAX" or "TELECOPIER")Fax/Modem - A combination fax board and data modem available as an external unit that plugs into the serial port of the computer or as an expansion board for internal installation. It includes a switch that routes the call to the fax or data modem. Incoming faxes are printed on the computer's printer. Most all modems today are fax/modems.
A fax/modem requires software that generates the fax transmission from typed-in text, a disk file or from a screen image. Fax/modems often transmit a sharper image than a fax machine, which obtains its source material by scanning the page.
Group 3 fax/modems provide various levels of processing based upon their service class. Class 1 devices perform basic handshaking and data conversion and are the most flexible, because much of the work is done by the computer's CPU. Class 2 devices establish and end the call and perform error checking. There are a variety of de facto Class 2 implementations and one Class 2.0 standard. As PCs have become more powerful, future service classes with more features are unlikely.Fax Modem Switch - A device that allows a single phone line to be shared for a fax machine and a modem. When a call comes in and it is a fax call, the call is automatically routed to the fax machine or fax.modem. If the call is a modem call, it is routed to the correct modem.. Some devices handle voice, fax and data modem switching. May require a security access code (SAC) in the dialing string to automatically switch to the modem.
Fax over Internet Protocol (FoIP) - The fax counterpart to VoIP, available from some providers either free or at additional cost. FoIP is actually more reliable than VoIP because of its tolerance for poor latency.
Fax Phone Switch - A device that tests a phone line for a fax signal and routes the call to the fax machine. When a fax machine dials a number and the line answers, it emits an 1100Hz signal (CNG tone) to identify itself. Tone Detection Fax Phone Switches listen for this signal and if present, automatically routes the call to a fax machine, fax modem or fax printer. Calls without the fax tones are automatically routes to phones or phone system. Some devices handle voice, fax and data modem switching and may require keying in a security access code (SAC) to switch to the modem. Distinctive Ring Fax Phone Switches use a phone company feature called distinctive ring to route the calls instead of using tones. See CNG tone. Synonyms Automatic Fax Switch , Fax Switch , Phone Fax Switch , Fax Modem Switch. For more info see Fax Switch.
Fax Server - A computer in a network that provides a bank of fax/modems, allowing users to fax out and remote users to fax in over the next available modem. The fax server may be a dedicated machine or implemented on a file server that is providing other services.
A fax server (or faxserver) is a system installed in a local area network (LAN) server that allows computer users who are attached to the LAN to send and receive fax messages. Fax messages can be stored as printable word processing, graphics, database, or spreadsheet files. Scanned documents can be sent as fax messages, allowing a computer and scanner to effectively emulate a dedicated fax machine.
A fax server is composed of a computer with a fax program, a
fax modem (a modem capable of sending and receiving fax signals as well as conventional Internet data), a connection to the Internet or a telephone line, and connections to the LAN users.There are several advantages to a fax server when compared with an ordinary fax machine. A single fax server can emulate multiple fax machines (one for each network user), thereby reducing overhead. Some functions can be automated. For example, a business fax server can automatically send invoices and purchase orders to customers and suppliers at specified times. Received faxes can be automatically stored as files on the server, and retrieved later by network users. In addition, a fax server can function without paper, reducing clutter and eliminating the need to continually check paper trays.
The term "fax server" is sometimes used to describe a program that enables a computer to send and receive fax messages.
Fax Switch - A device that analyses incoming phone calls for a fax signal and routes the call to the fax machine. When a fax machine dials a number and the line answers, it emits an 1100Hz signal (CNG tone) to identify itself. A tone detection fax switch listens for these CNG tones and if present, routes the call to the fax device. Another type of fax switch is a distinctive ring fax switch, which is a device that tests a phone line for a distinctive ring signal and routes the call to a specific device (example: phone, phone system, answering machine, fax machine. fax modem). For more info see Distinctive Ring Definition and Use. Some devices handle voice, fax and data modem switching and may require keying in a security access code (SAC) to switch to the modem. See CNG tone. For more info see Fax Switch.
Fax Switches - Fax Switches test a phone line for a fax signal and routes the call to the fax machine. When a fax machine dials a number and the line answers, it emits an 1100Hz signal (CNG tone) to identify itself. Some devices handle voice, fax and data modem switching and may require keying in a security access code (SAC) to switch to the modem. See CNG tone. For more info see Fax Switches.
Fax Tone Detection-This feature, when activated, tells automatic call processors and fax switches to detect the presence of CNG/fax tones which may be transmitted by a calling fax machine or PC Fax card. All calls accompanied by CNG tones, whether they be from a fax machine or PC Fax card, are routed through to equipment connected to the device port labeled FAX. If no fax-type equipment is used on the line sharing device, simply deactivate this feature. Typically with most line sharing equipment the factory preset is "on".
FC - Abbreviation for functional component. - In intelligent networks, an elemental call -processing component that directs internal network resources to perform specific actions, such as collecting dialed digits. Note: An FC is unique to the intelligent-network-IN/2 architecture.
FCC - Federal Communications Commission. The U.S. Government board made up of five presidential appointees that has the authority to regulate all non-Federal Government interstate telecommunications (including radio and television broadcasting) as well as all international communications that originate or terminate in the United States. Note: Similar authority for regulation of Federal Government telecommunications is vested in the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA).
The FCC is the regulator of telephone and telecommunications services in the United States. It's not yet known the full extent to which the FCC will regulate VoIP communications. Part of the complication lies with determining the regulation of communications that begin or end on an FCC-regulated system, such as the standard telephone service.
FCC Registration Program - The Federal Communications Commission program and associated directives intended to assure that all connected terminal equipment and protective circuitry will not harm the public switched telephone network or certain private line services. Note 1: The FCC registration program requires the registering of terminal equipment and protective circuitry in accordance with Subpart C of part 68, Title 47 of the Code of Federal Regulations. This includes the assignment of identification numbers to the equipment and the testing of the equipment. Note 2: The FCC registration program contains no requirement that accepted terminal equipment be compatible with, or function with, the network.
FCS - Abbreviation for frame check sequence. See cyclic redundancy check. 1. An error - detection scheme that (a) uses parity bits generated by polynomial encoding of digital signals, (b) appends those parity bits to the digital signal, and (c) uses decoding algorithms that detect errors in the received digital signal. Note: Error correction, if required, may be accomplished through the use of an automatic repeat-request ( ARQ ) system. 2. An error checking mechanism that checks data integrity by computing a polynomial algorithm based checksum.
FDDI - Abbreviation for fiber distributed data interface. A concept, defined in ANSI standards, for an optical- fiber -based token-ring network, featuring (a) dual counter-rotating logical rings, each with a data transmission capacity of 100 Mb/s, (b) reliable data transfer , (c) active link monitoring, (d) station management, and (e) survivability features. Note 1: The four standards are (a) ANSI X3T9.5, containing Physical Media Dependent (PMD) specifications, (b) ANSI X3T9.5, containing the Physical (PHY) specifications, (c) ANSI X3.139, containing Media Access Control ( MAC ) specifications, and (d) ANSI X39.5, containing the Station Management (SMT) specifications. Note 2: The data rate of an FDDI ring may be doubled to 200 Mb/s, with loss of redundancy. Note 3: FDDI-2 , a second- generation FDDI network standard, is under development.
FDDI-2: See fiber distributed data interface. FDDI-2, a second-generation FDDI network standard, is under development.
FDHM - See full width at half maximum. An expression of the extent of a function, given by the difference between the two extreme values of the independent variable at which the dependent variable is equal to half of its maximum value. Note 1: FWHM is applied to such phenomena as the duration of pulse waveforms and the spectral width of sources used for optical communications . Note 2: The term full duration at half maximum ( FDHM ) is preferred when the independent variable is time.
FDM - Abbreviation for frequency-division multiplexing. The deriving of two or more simultaneous, continuous channels from a transmission medium by assigning a separate portion of the available frequency spectrum to each of the individual channels.
FDMA - Abbreviation for frequency-division multiple access. The use of frequency division to provide multiple and simultaneous transmissions to a single transponder.
FDX - Abbreviation for full duplex. See full-duplex (FDX) circuit, full-duplex (FDX) operation. A circuit that permits simultaneous transmission in both directions.
Feature Code - A code (or codes) used to select/activate a service feature (e.g., forwarding, using two- or three-digit codes preceded by * or 1 1 or #, and which may precede subsequent digit selection).
FEC - Abbreviation for forward error correction. A system of error control for data transmission wherein the receiving device has the capability to detect and correct any character or code block that contains fewer than a predetermined number of symbols in error. Note: FEC is accomplished by adding bits to each transmitted character or code block, using a predetermined algorithm.
Federal Communications Commission - See FCC. The U.S. Government board made up of five presidential appointees that has the authority to regulate all non-Federal Government interstate telecommunications (including radio and television broadcasting) as well as all international communications that originate or terminate in the United States. Note: Similar authority for regulation of Federal Government telecommunications is vested in the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA).
Federal Excise Tax - A 3% tax mandated by the federal government imposed on all telecommunications services including local, long distance and wireless bills.
Federal Networking Council (FNC) - The body responsible for coordinating networking needs among U.S. Federal agencies.
Federal Subscriber Line Charge - This is a charge paid by consumers implemented by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). It is intended to recover some of the costs associated with a customer's local telephone line to access the interstate long distance network. It helps keep interstate long distance rates low. You pay this charge whether or not you actually make long distance calls.
Federal Telecommunications System (FTS) - A switched long-distance telecommunications service formerly provided for official Federal Government use. Note: FTS has been replaced by Federal Telecommunications Service 2000 (FTS2000).
Federal Telecommunications System 2000 Service - See FTS2000. The designation for a defunct Federal telecommunications contract replaced by the contract designated by the title "FTS2001."
Federal Universal Service Charge – See "Universal Service Fund Surcharge"
Feed - 1. To supply a signal to the input of a system, subsystem, equipment, or component, such as a transmission line or antenna. 2. A coupling device between an antenna and its transmission line. Note: A feed may consist of a distribution network or a primary radiator. 3. A transmission facility between (a) the point of origin of a signal, such as is generated in a radio or television studio, and (b) the head-end of a distribution facility, such as a broadcasting station in a network. 4. Pertaining to the function of inserting one thing into another, such as in a feed horn, paper feed, card feed, and line feed.
Feedback - 1. The return of a portion of the output, or processed portion of the output, of a (usually active) device to the input. Note 1: The feedback signal will have a certain magnitude and phase relationship relative to the output signal or the input signal. This relationship can be used to influence the behavior, such as the gain and stability, of the overall circuit. Note 2: If the feedback is regenerative (additive), it is called "positive feedback," which increases gain and distortion, and decreases linearity and stability. Note 3: If the feedback is degenerative (subtractive), it is called "negative feedback," which reduces the gain and distortion, and increases linearity and stability. Note 4: Feedback may occur inadvertently, and be detrimental. 2. Information returned as a response to an originating source.
Feedback Path - The signal path from the input of the bit-masking block to the output of the adaptive predictor.
Feeder Echo Noise - Signal distortion resulting from reflected waves in a transmission line that is many wavelengths long and mismatched at both the generator and the load ends.
Feeder Link - A radio link from an Earth station at a given location to a space station, or vice versa, conveying information for a space radiocommunication service other than for the fixed-satellite service. The given location may be at a specified fixed point, or at any fixed point within specified areas.
Feed-Forward Path - In the encoder, the signal path from the input of the PCM-to-uniform-PCM converter to the output of the adaptive quantizer. In the decoder, the feed-forward path is the signal path from the input of the feed-forward inverse adaptive quantizer to the output of the synchronous coding adjustment block.
FEP - Abbreviation for front-end processor. A programmed-logic or stored-program device that interfaces data communication equipment with an input / output bus or memory of a data processing computer.
Fermat's Principle - A principle stating that a ray of light follows the path that requires the least time to travel from one point to another, including reflections and refractions that may occur. Synonym least-time principle.
Fetch Protection - 1. [An] AIS-provided restriction to prevent a program from accessing data in another user's segment of storage. 2. [An] information-system (IS) hardware-provided restriction to prevent a program from accessing data in another user's segment of storage.
FET photodetector: A photodetector using photogeneration of carriers in the channel region of a field-effect transistor structure to provide photodetection with current gain.
Fiber - See optical fiber. A filament of transparent dielectric material, usually glass or plastic, and usually circular in cross section, that guides light. Note 1: An optical fiber usually has a cylindrical core surrounded by, and in intimate contact with, a cladding of similar geometry. Note 2: The refractive index of the core must be slightly higher than that of the cladding for the light to be guided by the fiber.
Fiber Amplifier - A device that amplifies an optical signal directly, without the need to convert it to an electrical signal, amplify it electrically, and reconvert it to an optical signal. Note 1: One type of fiber amplifier uses a doped fiber (e.g., a fiber doped with erbium), which bears the communication signal, and which is optically pumped with a laser having a high-powered continuous output at an optical frequency slightly higher than that of the communication signal. The signal is intensified by Raman amplification. Note 2: Because neither optical-electrical conversion nor electrical amplification takes place, this type of amplifier is well suited for a wide variety of applications, both digital and analog. Note 3: Because this type of amplifier does not require extraordinary frequency (wavelength) control of the pumping laser, it is relatively simple.
Fiber Axis - The longitudinal center of symmetry of an optical fiber, i.e., the locus of points that are determined by the centers of mechanical symmetry of the outside diameters of fiber cross sections sampled continuously along the length of the fiber.
Fiber Bandwidth - See bandwidth (of an optical fiber).
Fiber Buffer - See buffer. In a fiber optic communication cable, one type of component used to encapsulate one or more optical fibers for the purpose of providing such functions as mechanical isolation, protection from physical damage and fiber identification. Note: The buffer may take the form of a miniature conduit, contained within the cable and called a loose buffer, or loose buffer tube, in which one or more fibers may be enclosed, often with a lubricating gel. A tight buffer consists of a polymer coating in intimate contact with the primary coating applied to the fiber during manufacture.
Fiber Cable - See fiber optic cable. A telecommunications cable in which one or more optical fibers are used as the propagation medium. Note 1: The optical fibers are surrounded by buffers, strength members, and jackets for protection, stiffness, and strength. Note 2: A fiber-optic cable may be an all-fiber cable, or contain both optical fibers and metallic conductors. One possible use for the metallic conductors is the transmission of electric power for repeaters. Synonyms optical cable, optical fiber cable.
Fiber Cutoff Wavelength (
cf): See cutoff wavelength. 1. The wavelength corresponding to the cutoff frequency. 2. In an uncabled single-mode optical fiber, the wavelength greater than which a particular waveguide mode ceases to be a bound mode. Note 1: The cutoff wavelength is usually taken to be the wavelength at which the normalized frequency is equal to 2.405. Note 2: The cabled cutoff wavelength is usually considered to be a more functional parameter because it takes into consideration the effects of cabling the fiber.
Fiber Dispersion - See dispersion. In optical fiber communications, the incorrect terms " multimode dispersion " and " intermodal dispersion " should not be used as synonyms for the correct term " multimode distortion." Note: In classical optics, "dispersion" is used to denote the wavelength dependence of refractive index in matter, (dn/d
, where n is the refractive index and
is the wavelength) caused by interaction between the matter and light. "Dispersion," as used in fiber optic communications, should not be confused with "dispersion" as used by optical lens designers. Note 5: Three types of dispersion, relating to optical fibers, are defined as follows:
- material dispersion: In optical fiber communication, the wavelength dependence of the velocity of propagation (of the optical signal) on the bulk material of which the fiber is made. Note 1: Because every optical signal has a finite spectral width, material dispersion results in spreading of the signal. Note 2: Use of the redundant term " chromatic dispersion " is discouraged. Note 3: In pure silica, the basic material from which the most common telecommunication-grade fibers are made, material dispersion is minimum at wavelengths in the vicinity of 1.27
m (slightly longer in practical fibers).
- profile dispersion: In an optical fiber, that dispersion attributable to the variation of refractive index contrast with wavelength. Profile dispersion is a function of the profile dispersion parameter.
- waveguide dispersion: Dispersion, of importance only in single-mode fibers, caused by the dependence of the phase and group velocities on core radius, numerical aperture, and wavelength. Note 1: For circular waveguides, the dependence is on the ratio, a /
, where a is the core radius and
is the wavelength. Note 2: Practical single-mode fibers are designed so that material dispersion and waveguide dispersion cancel one another at the wavelength of interest.
Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) - A concept, defined in ANSI standards, for an optical-fiber-based token-ring network, featuring (a) dual counter-rotating logical rings, each with a data transmission capacity of 100 Mb/s, (b) reliable data transfer, (c) active link monitoring, (d) station management, and (e) survivability features. Note 1: The four standards are (a) ANSI X3T9.5, containing Physical Media Dependent (PMD) specifications, (b) ANSI X3T9.5, containing the Physical (PHY) specifications, (c) ANSI X3.139, containing Media Access Control (MAC) specifications, and (d) ANSI X39.5, containing the Station Management (SMT) specifications. Note 2: The data rate of an FDDI ring may be doubled to 200 Mb/s, with loss of redundancy. Note 3: FDDI-2, a second-generation FDDI network standard, is under development.
Fiber Optic (or "optical fiber") - Refers to the medium and the technology associated with the transmission of information as light impulses along a glass or plastic wire or fiber. Fiber optic wire carries much more information than conventional copper wire and is far less subject to electromagnetic interference. Most telephone company long-distance lines are now fiber optic.
Transmission on fiber optic wire requires repeating at distance intervals. The glass fiber requires more protection within an outer cable than copper. For these reasons and because the installation of any new wiring is labor-intensive, few communities yet have fiber optic wires or cables from the phone company's branch office to local customers (known as local loop).
Fiber Optic Bus - See bus. One or more optical fibers that serve as a common connection for a group of related devices.
Fiber Optic Cable - A telecommunications cable in which one or more optical fibers are used as the propagation medium. Note 1: The optical fibers are surrounded by buffers, strength members, and jackets for protection, stiffness, and strength. Note 2: A fiber-optic cable may be an all-fiber cable, or contain both optical fibers and metallic conductors. One possible use for the metallic conductors is the transmission of electric power for repeaters. Synonyms optical cable, optical fiber cable.
Fiber Optic Isolator - See optical isolator. A device that uses a short optical transmission path to accomplish electrical isolation between elements of a circuit. Note 1: The optical path may be air or a dielectric waveguide. Note 2: The transmitting and receiving elements of a fiber optic isolator may be contained within a single compact module, for mounting, e.g., on a circuit board.
Fiber Optic Link - A communications link that transmits signals by means of modulated light propagated in an optical fiber.
Fiber Optics (FO): The branch of optical technology concerned with the transmission of light through fibers made of transparent materials such as glasses and plastics. Note 1: Telecommunications applications of fiber optics use flexible low-loss fibers, using a single fiber per optical path. Present-day plastic fibers have losses that are too high for telecommunications applications. Note 2: Various industrial and medical applications of fiber optics, such as endoscopes, use flexible fiber bundles in which individual fibers are spatially aligned, permitting optical relay of an image. Note 3: Some specialized industrial applications use rigid (fused) aligned fiber bundles for image transfer; such as in the fiber optics faceplates used on some cathode ray rubes (CRTs) to "flatten" the image.
Fiber Pigtail - See pigtail. A short length of optical fiber that is permanently affixed to an active device, e.g., LED or laser diode, and is used to couple the device, using a splice or connector, to a longer fiber. 2. A short length of single-fiber cable, usually tight-buffered, that has an optical connector on one end and a length of exposed fiber at the other end. Note: The exposed fiber of the pigtail is then spliced to one fiber of a multifiber trunk, i.e., arterial, cable, to enable the multifiber cable to be "broken out" into individual single-fiber cables that may be connected to a patch panel or an input or output port of an optical receiver or transmitter. 3. A short length of electrical conductor permanently affixed to a component, used to connect the component to another conductor.
Fidelity - The degree to which a system, or a portion of a system, accurately reproduces, at its output, the essential characteristics of the signal impressed upon its input or the result of a prescribed operation on the signal impressed upon its input.
FidoNet - A network designed for e-mail distribution through individual bulletin board systems rather than through Internet servers.
Field - 1. The volume of influence of a physical phenomenon, expressed vectorially. 2. On a data medium or in storage, a specified area used for a particular class of data, e.g. , a group of character positions used to enter or display wage rates on a screen. 3. Defined logical data that are part of a record. 4. The elementary unit of a record that may contain a data item, a data aggregate, a pointer, or a link. 5. In an interlaced, raster -scanned video display, a partial frame, consisting of every nth scanning line of a complete frame, where n is an integer equal to the number of fields (usually two) in a complete frame. Note 1: For example, in the National Television Standards Committee (NTSC) television specification used in the United States, a single frame is composed of two fields, each of which has half the number of scanning lines in a complete frame. The scanning lines of a field are separated by twice the space between the scanning lines in the full frame. The two fields are interlaced, i.e. , a complete frame consists of the following traces, which are listed in the order of their appearance in the complete frame, but not the order in which scanning occurs: the first line of the first field, the first line of the second field, the second line of the first field, the second line of the second field, the third line of the first field, the third line of the second field, etc. , until completion of the full frame. The fields are scanned alternately, one complete field at a time. Thus, the flicker rate of the display is perceived by the eye to be twice as fast as that which would result if the complete frame were to be scanned in line-by-line order. Note 2: Not all scanning lines are necessarily applied to user information, i.e. , the graphic display. Certain scanning lines, not seen under ordinary viewing conditions, are often used for transmitting test signals that indicate the quality of the displayed video.
Field-Disturbance Sensor - A restricted radiation device which establishes a radio frequency field in its vicinity and detects changes in that field resulting from the movement of persons or objects within the radio frequency field. Examples: microwave intrusion sensors; devices that use rf energy for production line counting and sensing.
Field Intensity - The irradiance of an electromagnetic wave under specified conditions. Note: Field intensity is usually expressed in watts per square meter
Field Strength - 1. The magnitude of an electric, magnetic, or electromagnetic field at a given point. Note: The field strength of an electromagnetic wave is usually expressed as the rms value of the electric field, in volts per meter. The field strength of a magnetic field is usually expressed in amperes per meter Synonym radio field intensity. 2. The electric field strength in the horizontal plane.
Field Tag - Synonym flag. In data transmission or processing, an indicator, such as a signal, symbol, character, or digit, used for identification. Note: A flag may be a byte, word, mark, group mark, or letter that signals the occurrence of some condition or event, such as the end of a word, block, or message.
Field Wire - A flexible insulated wire used in field telephone and telegraph systems. Note 1: WD-1 and WF-16 are types of field wire. Note 2: Field wire usually contains conductors and high-tensile-strength strands serving as strength members.
FIFO - Abbreviation for first-in first-out. A queuing discipline in which entities in a queue leave the queue in the same order in which they arrive. Note 1: Service, when available, is offered to the entity that has been in the FIFO queue the longest. Note 2: FIFO techniques are used in message switching.
File - 1. The largest unit of storage structure that consists of a named collection of all occurrences in a database of records of a particular record type. 2. A set of related records treated as a unit, for example, in stock control, a file could consist of a set of invoices.
File Archive - Synonym FTP archive. A collection of files that are available by using file transfer protocol (FTP). Synonym file site.
File Name Extension - 1. A suffix that is preceded by a decimal (".") and that is appended to a computer file name. Note: Common filename extensions with their meanings are:
.wpd = a type of word-processing document
.doc = a type of word-processing document
.exe = executable code or a self-extracting archive file.
.gif = a graphical interchange format (graphics file)
.txt = a text file.
2. Proprietary HTML tags that are recognized by a single Web browser or by those Web browsers developed by a single company.
File-Oriented Applications - Applications concerned with the storage, manipulation, and exchange of information between application processes in the form of files.
File Protection - 1. The execution of appropriate administrative, technical, or physical means to guard against the unauthorized access to, modification of, or deletion of a file. [After 2382-8] 2. [The] aggregate of processes and procedures designed to inhibit unauthorized access, contamination, elimination, modification, or destruction of a file or any of its contents.
File Security - [A] means by which access to computer files is limited to authorized users only.
File Server - 1. A high-capacity disk storage device or a computer that each computer on a network can use or access and retrieve files that can be shared among attached computers. 2. A program, running on a computer, that allows different programs, running on other computers, to access the files of that computer.
File Site - Synonym FTP archive. A collection of files that are available by using file transfer protocol (FTP).
File Transfer - In networking, a service to move a part or the whole of a file's content over a computer network.
File Transfer, Access, and Management (FTAM) - An application's service and protocol based on the concept of virtual file store. Note: FTAM allows remote access to various levels in a file structure and provides a comprehensive set of file management capabilities.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) - A common method for sending and/or receiving files between Internet sites using a login system. Publicly accessed FTP sites are often called anonymous FTPs.
Fill - See bit stuffing. The insertion of noninformation bits into data. Note 1: Stuffed bits should not be confused with overhead bits. Note 2: In data transmission, bit stuffing is used for various purposes, such as for synchronizing bit streams that do not necessarily have the same or rationally related bit rates, or to fill buffers or frames. The location of the stuffing bits is communicated to the receiving end of the data link, where these extra bits are removed to return the bit streams to their original bit rates or form. Bit stuffing may be used to synchronize several channels before multiplexing or to rate-match two single channels to each other. Synonym positive justification.
Fill Bit - See bit stuffing. The insertion of noninformation bits into data. Note 1: Stuffed bits should not be confused with overhead bits. Note 2: In data transmission, bit stuffing is used for various purposes, such as for synchronizing bit streams that do not necessarily have the same or rationally related bit rates, or to fill buffers or frames. The location of the stuffing bits is communicated to the receiving end of the data link, where these extra bits are removed to return the bit streams to their original bit rates or form. Bit stuffing may be used to synchronize several channels before multiplexing or to rate-match two single channels to each other.
Fill Device - [A] COMSEC item used to transfer or store key in electronic form or to insert key into a crypto-equipment.
Filled Cable - A cable that has a nonhygroscopic material, usually a gel, inside the jacket or sheath. Note 1: The nonhygroscopic material fills the spaces between the interior parts of the cable, preventing moisture from entering minor leaks in the sheath and migrating inside the cable. Note 2: A metallic cable, such as a coaxial cable or a metal waveguide, filled with a dielectric material, is not considered as a filled cable.
Fill-in Area - The area where the coverage contour of an FM translator or booster station is within the protected contour of the associated primary station (i.e., predicted 0.5 mV/m contour for commercial Class B stations, predicted 0.7 mV/m contour for commercial Class B1 stations, and predicted 1 mV/m contour for all other classes of stations).
Fill-in Signal Unit (FISU) - A signal unit that is transmitted when there are no message signal units or link status signal units to be transmitted. It contains only error control and delimitation information.
FILO - Abbreviation for first-in last-out. A queuing discipline in which entities in a queue leave the queue in the reverse order from that in which they arrived. Note: An understanding of FILO techniques is important in the understanding of store-and-forward capabilities in packing switching.
Filter - In electronics, a device which transmits only part of the incident energy and may thereby change the spectral distribution of energy:
- (a) high pass filters transmit energy above a certain frequency;
- (b) low pass filters transmit energy below a certain frequency;
- (c) band pass filters transmit energy of a certain bandwidth;
- (d) band stop filters transmit energy outside a specific frequency band
Filtered Symmetric Differential Phase-Shift Keying (FSDPSK) - A method of encoding information for digital transmission in which (a) a binary 0 is encoded as a +90° change in the carrier phase and a binary 1 is encoded as a -90° change in the carrier phase, and (b) abrupt phase transitions are smoothed by filtering or other functionally equivalent pulse shaping techniques.
Final Trunk Group - A last-choice trunk group that receives overflow traffic, may receive first-route traffic and for which there is no alternate route. There are various types of final trunk groups, differentiated by the type of traffic that they carry.
Finger - A computer-operating-system command for accessing limited network-user-account information. Note: Finger is limited to providing information such as the full name of the account holder and address information, intentionally made public by the account holder. Finger is also used to establish the existence of an address and to discover whether or not the account is currently logged on.
Finished Call - 1. In an information transaction, a call in which the call originator or call receiver terminates the communication and goes on hook, i.e., hangs up. 2. In an information transfer transaction, the termination of the information transfer phase.
FIP - Acronym for Federal Information Processing.
FIP Equipment - In the Federal government, any equipment or interconnected system or subsystems of equipment (as defined in 41CFR) used in the automatic acquisition, storage, manipulation, management, movement, control, display, switching, interchange, transmission, or reception of data or information.
FIP System - In the Federal government, any organized combination of FIP equipment, software, services, support services, or related supplies.
FIREFLY - [A] key management protocol based on public key cryptography.
Firewall - 1. A computer that (a) acts as an interface between two networks ( e.g., the Internet and an private network, respectively), and (b) regulates traffic between those networks for the purpose of protecting the internal network from electronic attacks originating from the external network. The firewall is capable of handling the following tasks: (a) isolating internal and external traffic (a bridge service ); (b) making internal addresses invisible and directly unaccessible from outside and passing through authorized traffic after proper checking (a proxy service); (c) facilitating protected (encrypted) connections to cooperative parties over public networks (a tunneling service); (d) filtering outgoing traffic for security and network usage rules (filtering or monitoring service); (e) filtering incoming traffic for rogue data (viruses, spam, inappropriate data (filtering), or improper actions ( port scanning, overload prevention, etc. ; (f) blocking forbidden external services or addresses (blocking, "network nanny"-functions); (g) providing log -in services for authorized outside users and simulating the approved outside user as an inside user (proxy, log-in server ); (h) caching network traffic (cache service); (i) converting between different network protocols on different protocol levels (bridge when handling lower level protocols, gateway when handling higher level protocols); (j) traffic diverting ( e.g., for cost optimizing, accounting, network planning, monitoring); (k)providing consistent, open entry to the internal network ( portal service) and facilitating public network address and connection sharing (proxy service). 2. A system designed to defend against unauthorized access to or from a private network. Firewalls can be implemented in both hardware and software, or a combination of both.
Firmware - 1. Software that is embedded in a hardware device that allows reading and executing the software, but does not allow modification, e.g., writing or deleting data by an end user. Note 1: An example of firmware is a computer program in a read-only memory ( ROM ) integrated circuit chip. A hardware configuration is usually used to represent the software. Note 2: Another example of firmware is a program embedded in an erasable programmable read-only memory (EPROM) chip, which program may be modified by special external hardware, but not by an application program. 2. A program recorded in permanent or semipermanent computer memory.
First-In First-Out (FIFO) - A queuing discipline in which entities in a queue leave the queue in the same order in which they arrive. Note 1: Service, when available, is offered to the entity that has been in the FIFO queue the longest. Note 2: FIFO techniques are used in message switching.
First-In Last-Out (FILO) - A queuing discipline in which entities in a queue leave the queue in the reverse order from that in which they arrived. Note: An understanding of FILO techniques is important in the understanding of store-and-forward capabilities in packing switching.
First-Route Traffic - Traffic that has not been route-advanced at any switching system.
First Window - Of silica-based optical fibers, the transmission window at approximately 830 to 850 nm.
FISINT - Acronym for foreign instrumentation signals intelligence. - 1. Intelligence information derived from electromagnetic emissions associated with the testing and operational deployment of foreign aerospace, surface, and subsurface systems. 2. Technical information and intelligence information derived from the intercept of foreign instrumentation signals by other than the intended recipients. Foreign instrumentation signals intelligence is a category of signals intelligence. Note: Foreign instrumentation signals include but are not limited to signals from telemetry, beaconry, electronic interrogators, tracking/fusing/ arming/firing command systems, and video data links.
Five-Hundred (500) Service - A telephone service that allows individuals to receive, via a single number, telephone calls in various locations (e.g., home, office, or car phone) from call originators not necessarily using the same common carrier.
Fixed Access - In personal communications service ( PCS ), terminal access to a network in which there is a set relationship between a terminal and the access interface. Note: A single " identifier " serves for both the access interface and the terminal. If the terminal moves to another access interface, that terminal assumes the identity of the new interface.
Fixed Attenuator - See pad. A network, of fixed resistors, that attenuates signals by a fixed amount with negligible distortion. Note: The resistive network is called an attenuator if the resistance is adjustable.
Fixed Loop - A service feature that permits an attendant on an assisted call to retain connection through the attendant position for the duration of the call. Note: The attendant will usually receive a disconnect signal when the call is terminated.
Fixed Microwave Auxiliary Station - A fixed station used in connection with (a) the alignment of microwave transmitting and receiving antenna systems and equipment, (b) coordination of microwave radio survey operations, and (c) cue and contact control of television pickup station operations.
Fixed-Reference Modulation - Modulation in which the significant condition for any signal element is based on a fixed reference.
Fixed-Satellite Service -1. A radiocommunication service between Earth stations at given positions when one or more satellites are used; the given position may be a specified fixed point or any fixed point within specified areas; in some cases this service includes satellite -to-satellite links, which may also be effected in the inter-satellite service, the fixed-satellite service may also include feeder links for other space radiocommunication services. 2. A radiocommunication service between Earth stations at given positions when one or more satellites are used; the given position may be a specified fixed point or any fixed point within specified areas; in some cases this service includes satellite-to-satellite links, which may also be operated in the inter-satellite service; the fixed-satellite service may also include feeder links of other space radiocommunication services.
Fixed Service (FX) - A radiocommunication service between specified fixed points.
Fixed Station 1. A station in the fixed service. 2. The term "fixed station" in the fixed public or fixed public press service includes all apparatus used in rendering the authorized service at a particular location under a single instrument of authorization.
Fixed Storage - Synonym read-only storage. A storage device in which the contents cannot be modified, except by a particular user, or when operating under particular conditions, e.g. , a storage device in which writing is prevented by a lockout.
Fixed-Tolerance-Band Compaction - Data compaction accomplished by storing or transmitting data only when the data fall outside prescribed limits. Note: An example of fixed- tolerance - band compaction in a telemetering system is the transmission of the temperature only when the temperature is above or below preestablished threshold limits. Thus, the recipient of the transmission is to assume that the value is in the prescribed range unless a signal to the contrary occurs.
Flag: In data transmission or processing, an indicator, such as a signal, symbol, character, or digit, used for identification. Note: A flag may be a byte, word, mark, group mark, or letter that signals the occurrence of some condition or event, such as the end of a word, block, or message. Synonym field tag.
Flag Sequence - In data transmission or processing, a sequence of bits used to delimit, i.e. mark, the beginning and end of a frame. Note 1: An 8-bit sequence is usually used as the flag sequence; for example, the 8-bit flag sequence 01111110. Note 2: Flag sequences are used in bit-oriented protocols, such as Advanced Data Communication Control Procedures ( ADCCP ), Synchronous Data Link Control ( SDLC ), and High-Level Data Link Control ( HDLC ).
Flame - To send nasty or insulting messages, usually in response to someone's having broken the rules of Internet etiquette (called netiquette ).
Flash -1. A signal generated by the momentary depression of the telephone switchhook or other device. Note: A flash may be used to request additional services. 2. An on-hook signal of a defined duration, used to activate network features.
Flash Card - In computer -based equipment (such as MP3 players, digital cameras, and palm-held computers), a type of memory storage device approximately the size of a matchbook, capable of recording several megabytes of (usually compressed) digitized audio files or data files. Synonym flash memory card.
Flash Feature - A supplementary calling feature provided by the near-end customer interface (CI) that is activated or controlled through the use of one or more flash signals.
Flash Memory Card - Synonym flash card. In computer -based equipment (such as MP3 players, digital cameras, and palm-held computers), a type of memory storage device approximately the size of a matchbook, capable of recording several megabytes of (usually compressed) digitized audio files or data files.
FLASH Message - A category of precedence reserved for initial enemy contact messages or operational combat messages of extreme urgency. Brevity is mandatory.
Flash Signal: A loop -open signal of 300 to 1000 ms at the network interface (NI) that is generated by the network, typically under the control of the far-end customer interface (CI), to control supplementary calling features when such features are provided by the near-end CI.
Flat Fading - Fading in which all frequency components of a received radio signal vary in the same proportion simultaneously.
Flat Panel TV Sets - Thin, lightweight TV sets that can be hung on a wall. Current flat panels (also called “flat screens”) use LCD or Plasma screen technology.
Flat Rate Service - Telephone service in which a single payment permits an unlimited number of local calls to be made without further charge for a specified period of time.
Flat Weighting - In a noise-measuring set, a noise weighting based on an amplitude-frequency characteristic that is flat over a frequency range that must be stated. Note 1: Flat noise power is expressed in dBrn (f1- f2) or in dBm (f1- f2). Note 2: "3-kHz flat weighting" and "15-kHz flat weighting" are based on amplitude-frequency characteristics that are flat between 30 Hz and the frequency indicated.
Flaw - 1. In computer security, an error of commission, an omission, or an oversight that allows protection mechanisms to be bypassed or disabled. 2. An error of commission, omission, or oversight in an information system (IS) that may allow protection mechanisms to be bypassed. Synonym loophole.
Flaw Hypothesis Methodology - System analysis and penetration technique in which the specification and documentation for an information system (IS) are analyzed to produce a list of hypothetical flaws. This list is prioritized on the basis of the estimated probability that a flaw exists, on the ease of exploiting it, and on the extent of control or compromise it would provide. The prioritized list is used to perform penetration testing of a system.
F layer - See F region. That portion of the ionosphere existing between approximately 160 and 400 km above the surface of the Earth, consisting of layers of increased free-electron density caused by the ionizing effect of solar radiation. Note 1: The F region reflects normal- incident frequencies at or below the critical frequency (approximately 10 MHz ) and partially absorbs waves of higher frequency. Note 2: The F 1 layer exists from about 160 to 250 km above the surface of the Earth and only during daylight hours. Though fairly regular in its characteristics, it is not observable everywhere or on all days. The principal reflecting layer during the summer for paths of 2,000 to 3,500 km is the F 1 layer. The F 1 layer has approximately 5 × 10 5 e/cm 3 (free electrons per cubic centimeter) at noontime and minimum sunspot activity, and increases to roughly 2 × 10 6 e/cm 3 during maximum sunspot activity. The density falls off to below 10 4 e/cm 3 at night. Note 3: The F 1 layer merges into the F 2 layer at night. Note 4: The F 2 layer exists from about 250 to 400 km above the surface of the Earth. The F 2 layer is the principal reflecting layer for HF communications during both day and night. The horizon-limited distance for one- hop F 2 propagation is usually around 4,000 km. The F 2 layer has about 10 6 e/cm 3 . However, variations are usually large, irregular, and particularly pronounced during magnetic storms.
Fleming's Rule - A rule stating that if the thumb of the right hand points in the direction of an electric current, then the curled fingers point in the direction of the magnetic field that encircles the current; and further, if the curled fingers of the right hand describe the electric current in a solenoid, then the thumb points in the direction of the magnetic field inside the solenoid. Synonym right-hand rule.
Flexible Disk - Synonym diskette. In computer technology, a small disk of flexible plastic, coated with a magnetizable material and enclosed in a protective jacket, used to store digital data. Note: A diskette is distinguished from a hard disk by virtue of the fact that it is flexible, and unlike most hard disks, is removable from its drive.
Flicker - In video, any of several visual artifacts similar to ( i.e., manifested as) a stroboscopic effect ( jerkiness ), sometimes caused by or related to vertical synchronization characteristics or video field display rates.
Flip-Flop - A device that may assume either one of two reversible, stable states. Note 1: The flip-flop is used as a basic control element in computer and communications systems. Note 2: In a flip-flop, the transition from one stable state to the other is unstable, i.e., for the very short period during which the transition takes place, both outputs may assume the same state, which state may be unpredictable. Synonyms bistable circuit, bistable multivibrator, bistable trigger circuit.
Floating - See conference floating. In conference calling, the state in which the conference is active but without a controller. This state is possible when two or more conferees exist on an active conference and the controller successfully disconnects himself/herself.
Floating Head - A magnetic head floating on a layer of air away from the recording surface. Synonyms air-floating head, flying head.
Floating-Point Coding Compaction - Data compaction accomplished by using coefficients, a base, and exponents to specify the scale, range, or magnitude of numbers. Note: An example of floating -point coding compaction is using 119.8 × 10 6 , 119.8(6), or 119.86 to represent 119,800,000. If the number is rounded to 120,000,000, it might be written as 1206 or 127 in which the last digit is the number of zeros to be appended to the preceding digits. Thus, only three positions are required instead of nine to represent the number in storage or in a message, which is only 33% of the original space and time requirement.
Float Operation - Operation of a dc system with the battery, rectifier, and load all connected in parallel. The battery charger supplies the normal dc load plus any battery self-discharge current or recharge current required after a discharge.
Flooding - Insertion of a large volume of data resulting in denial of service. Synonyms [in e-mail and forum postings] mail bombing, spamming; [in radio and wireline communications] flood-search routing, pilot-make-busy.
Flooding Compound - A substance surrounding the buffer tubes of a fiber -optic cable, to prevent water intrusion into the interstices in the event of a breach of the jacket.
Flood Projection - In facsimile , the optical method of scanning in which the object is floodlighted and the scanning spot is defined by a masked portion of the illuminated area.
Flood Search Routing - In a telephone network, nondeterministic routing in which a dialed number received at a switch is transmitted to all switches, i.e., flooded, in the area code directly connected to that switch; if the dialed number is not an affiliated subscriber at that switch, the number is then retransmitted to all directly connected switches, and then routed through the switch that has the dialed number corresponding to the particular user end instrument affiliated with it. Note 1: All digits of the numbering plan are used to identify a particular subscriber. Note 2: Flood search routing allows subscribers to have telephone numbers independent of switch codes. Note 3: Flood search routing provides the highest probability that a call will go through even though a number of switches and links fail.
floppy disk - Synonym diskette. In computer technology, a small disk of flexible plastic, coated with a magnetizable material and enclosed in a protective jacket, used to store digital data. Note: A diskette is distinguished from a hard disk by virtue of the fact that it is flexible, and unlike most hard disks, is removable from its drive.
flops - Acronym for floating -point operations per second. Note: For example, 15 Mflops equals 15 million floating-point arithmetic operations per second.
Flowchart - A graphical representation in which symbols are used to represent such things as operations, data , flow direction, and equipment, for the definition, analysis, or solution of a problem. Synonym flow diagram.
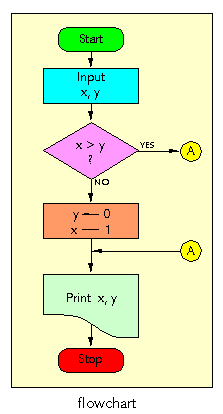
Flow Control - See transmit flow control. In data communications systems, control of the rate at which data are transmitted from a terminal so that the data can be received by another terminal. Note 1: Transmit flow control may occur between data terminal equipment ( DTE ) and a switching center, via data circuit-terminating equipment ( DCE ), or between two DTEs. The transmission rate may be controlled because of network or DTE requirements. Note 2: Transmit flow control can occur independently in the two directions of data transfer, thus permitting the transfer rates in one direction to be different from the transfer rates in the other direction.
Flow Control Procedure - A procedure for controlling the rate of transfer of data among elements of a network, e.g. , between a DTE ( data terminal equipment ) and a data switching exchange network, to prevent overload.
Flow Diagram - Synonym flowchart. A graphical representation in which symbols are used to represent such things as operations, data , flow direction, and equipment, for the definition, analysis, or solution of a problem.
Flowline - On a flowchart, a line that (a) has an indicated direction, (b) represents a connection between other symbols, and (c) indicates the sequence of operations or the transfer of control.
Flutter - Rapid variation of signal parameters, such as amplitude, phase, and frequency. Note: Examples of flutter are (a) rapid variations in received signal levels, such as variations that may be caused by atmospheric disturbances, antenna movements in a high wind, or interaction with other signals, (b) in radio propagation, a phenomenon in which nearly all radio signals that are usually reflected by ionospheric layers in or above the E-region experience partial or complete absorption, (c) in radio transmission, rapidly changing signal levels, together with variable multipath time delays, caused by reflection and possible partial absorption of the signal by aircraft flying through the radio beam or common scatter volume, (d) the variation in the transmission characteristics of a loaded telephone circuit caused by the action of telegraph direct currents on the loading coils, (e) in recording and reproducing equipment, the deviation of frequency caused by irregular mechanical motion, e.g., that of capstan angular velocity in a tape transport mechanism, during operation. Synonym [loosely] frequency flutter .
Flux - 1. The lines of force of a magnetic field. 2. Obsolete synonym for radiant power.
Flying Head - Synonym floating head. A magnetic head floating on a layer of air away from the recording surface.
Flywheel Effect - In an oscillator, the continuation of oscillations after removal of the control stimulus. Note 1: The flywheel effect is usually caused by interacting inductive and capacitive circuits in the oscillator. Note 2: The flywheel effect may be desirable, such as in phase -locked loops used in synchronous systems, or undesirable, such as in voltage-controlled oscillators. Synonym flywheeling.
Flywheeling - Synonym flywheel effect. In an oscillator, the continuation of oscillations after removal of the control stimulus. Note 1: The flywheel effect is usually caused by interacting inductive and capacitive circuits in the oscillator. Note 2: The flywheel effect may be desirable, such as in phase -locked loops used in synchronous systems, or undesirable, such as in voltage-controlled oscillators.
FM - Abbreviation for frequency modulation. Modulation in which the instantaneous frequency of a sine wave carrier is caused to depart from the center frequency by an amount proportional to the instantaneous value of the modulating signal. Note 1: In FM, the carrier frequency is called the center frequency. Note 2: FM is a form of angle modulation. Note 3: In optical communications, even if the electrical baseband signal is used to frequency-modulate an electrical carrier (an "FM" optical communications system), it is still the intensity of the lightwave that is varied (modulated) by the electrical FM carrier. In this case, the "information," as far as the lightwave is concerned, is the electrical FM carrier. The lightwave is varied in intensity at an instantaneous rate corresponding to the instantaneous frequency of the electrical FM carrier.
FM Blanketing - That form of interference to the reception of other broadcast stations, which is caused by the presence of an FM broadcast signal of 115 dB
(562 mV/m) or greater signal strength in the area adjacent to the antenna of the transmitting station. The 115-dB
contour is referred to as the " blanketing area."
FM Broadcast Translator - See translator. A device that converts information from one system of representation into equivalent information in another system of representation. Note: An example of a translator in telephony is the device that converts dialed digits into call - routing information. 2. A computer program that translates from one languag into another language and in particular from one programming language into another programming language. 3. In FM and TV broadcasting, a repeater station that receives a primary station 's signal , amplifies it, shifts it in frequency, and rebroadcasts it. 4. A device that converts one frequency to another.
FM Capture Effect - Synonym capture effect. A phenomenon, associated with FM reception, in which only the stronger of two signals at or near the same frequency will be demodulated. Note 1: The complete suppression of the weaker signal occurs at the receiver limiter, where it is treated as noise and rejected. Note 2: When both signals are nearly equal in strength, or are fading independently, the receiver may switch from one to the other.
FM Capture Ratio - See capture effect. A phenomenon, associated with FM reception, in which only the stronger of two signals at or near the same frequency will be demodulated. Note 1: The complete suppression of the weaker signal occurs at the receiver limiter, where it is treated as noise and rejected. Note 2: When both signals are nearly equal in strength, or are fading independently, the receiver may switch from one to the other.
FM Improvement Factor - The quotient obtained by dividing the signal-to-noise ratio ( SNR ) at the output of an FM receiver by the carrier-to-noise ratio ( CNR ) at the input of the receiver. Note: When the FM improvement factor is greater than unity, the improvement in the SNR is always obtained at the expense of an increased bandwidth in the receiver and the transmission path.
FM Improvement Threshold - The point in an FM receiver at which the peaks in the rf signal equal the peaks of the thermal noise generated in the receiver. Note: A baseband signal-to-noise ratio of about 30 dB is typical at the improvement threshold, and this ratio improves 1 dB for each decibel of increase in the signal above the threshold.
FM Threshold Effect - In an FM receiver, the effect produced when the desired- signal gain begins to limit the desired signal, and thus noise limiting (suppression). Note: FM threshold effect occurs at (and above) the point at which the FM signal-to-noise improvement is measured.
FM Threshold Extension - A change in the value of the FM threshold of a receiver. Note: FM threshold extension may be obtained by decreasing the operational bandwidth, thus decreasing the received noise power and allowing the threshold of the desired signal to occur at a lower signal input level.
FO - Abbreviation for fiber optics. The branch of optical technology concerned with the transmission of light through fibers made of transparent materials such as glasses and plastics. Note 1: Telecommunications applications of fiber optics use flexible low- loss fibers, using a single fiber per optical path. Present-day plastic fibers have losses that are too high for telecommunications applications. Note 2: Various industrial and medical applications of fiber optics, such as endoscopes, use flexible fiber bundles in which individual fibers are spatially aligned, permitting optical relay of an image. Note 3: Some specialized industrial applications use rigid (fused) aligned fiber bundles for image transfer; such as in the fiber optics faceplates used on some cathode ray rubes (CRTs) to "flatten" the image.
FoIP (Fax over Internet Protocol) - The fax counterpart to VoIP, available from some providers either free or at additional cost. FoIP is actually more reliable than VoIP because of its tolerance for poor latency.
Followup - Synonym thread. In computer conferencing, a set of sequential messages containing closely related information.
Footprint - In satellite communications, that portion of the Earth's surface over which a satellite antenna delivers a specified amount of signal power under specified conditions. Note: The limiting case of footprint area is somewhat less than one-half the Earth's surface, and depends on the altitude of the satellite.
Forbidden Character - Synonym illegal character. A character, or a combination of bits, that is not valid in a given system according to specified criteria, such as with respect to a specified alphabet, a particular pattern of bits, a rule of formation, or a check code.
Forced Rerouting - A procedure of transferring signaling traffic from one signaling route to another, when the signaling route in use fails or is required to be cleared of traffic.
Foreign Exchange (FX) Service - A network -provided service in which a telephone in a given local exchange area is connected, via a private line, to a central office in another, i.e., "foreign", exchange, rather than the local exchange area 's central office. Note: To call originators, it appears that the subscriber having the FX service is located in the foreign exchange area.
Foreign Instrumentation Signals Intelligence (FISINT) - 1. Intelligence information derived from electromagnetic emissions associated with the testing and operational deployment of foreign aerospace, surface, and subsurface systems. 2. Technical information and intelligence information derived from the intercept of foreign instrumentation signals by other than the intended recipients. Foreign instrumentation signals intelligence is a category of signals intelligence. Note: Foreign instrumentation signals include but are not limited to signals from telemetry, beaconry, electronic interrogators, tracking/fusing/ arming/firing command systems, and video data links.
Form - An HTML-based, interactive, ease-of-use Web site feature, containing checkboxes, option lists, text boxes, and buttons that allow users to submit pre-formatted requests or queries or to respond to pre-formatted questions.
Format - 1. The arrangement of bits or characters within a group, such as a word, message, or language. 2. The shape, size, and general makeup of a document.
Format Converter -1. In video and television technology, a device that allows the reformatting of a digital data stream originating from one sampling structure (lines per frame, pixels per line) into a digital data stream of another sampling structure for the purposes of recording or passing the original data stream through distribution devices designed to accommodate the latter structure. Note: Since, in format conversion, the data still represent the original sampling structure, this process is not the same as standards conversion (from PAL to NTSC, for instance). A format converter can, for instance, accept a signal introduced in a proposed format, and convert it for recording on, and subsequent reproduction from, a high-definition television digital recorder designed for the 1125/60/2:1 format. 2. In television technology, a system that converts display information from the familiar 3 x 4 aspect ratio to the newer 9 x 16 aspect ratio.
Format Structure - A combination of two or more data elements grouped in a prescribed sequence.
Fortran - See language processor. A program that performs tasks, such as translating and interpreting, required for processing a specified programming language. Note: Examples of language processors include a Fortran processor and a COBOL processor.
Fortuitous Conductor - Any conductor that may provide an unintended path for signals. Note: Examples of fortuitous conductors are water pipes, wires, cables, and metal building and equipment structural members.
Fortuitous Distortion - Distortion resulting from causes generally subject to laws concerning random occurrences.
Forum - A computer conference devoted to a specific subject, having an initiator, members, readers, and possibly moderators. Synonyms chat group, discussion group, discussion list, discussion thread, follow up, interest group, library, newsgroup, thread.
Forward Busying - In a telecommunications system, a feature in which supervisory signals are forwarded in advance of address signals in order to seize assets of the system before attempting to establish a connection.
Forward Channel - The channel of a data circuit that transmits data from the originating user to the destination user. Note: The forward channel carries message traffic and some control information.
Forward Echo - In a transmission line, an echo propagating in the same direction as the original wave and consisting of energy reflected back by one discontinuity and then forward again by another discontinuity. Note: Forward echoes can be supported by reflections caused by splices or other discontinuities in the transmission medium ( e.g. , optical fiber, twisted pair, or coaxial tube). In metallic lines, they may be supported by impedance mismatches between the source or load and the characteristic impedance of the transmission medium.
Forward Error Correction (FEC) - A system of error control for data transmission wherein the receiving device has the capability to detect and correct any character or code block that contains fewer than a predetermined number of symbols in error. Note: FEC is accomplished by adding bits to each transmitted character or code block, using a predetermined algorithm.
Forward Indicator Bit (FIB) - A bit in a signal unit which indicates the start of a retransmission cycle.
Forward Propagation Ionospheric Scatter (FPIS) - Synonym ionospheric scatter. The propagation of radio waves by scattering as a result of irregularities or discontinuities in the ionization of the ionosphere.
Forward Recovery - The data reconstitution of a later version of data by using an earlier version and data recorded in a journal.
Forward Scatter - The deflection --by diffraction, nonhomogeneous refraction, or nonspecular reflection by particulate matter of dimensions that are large with respect to the wavelength in question but small with respect to the beam diameter --of a portion of an incident electromagnetic wave, in such a manner that the energy so deflected propagates in a direction that is within 90° of the direction of propagation of the incident wave. Note: The scattering process may be polarization -sensitive, i.e. , incident waves that are identical in every respect but their polarization may be scattered differently.
Forward Secrecy - The confidence that the compromise of a long-term private key does not compromise any earlier session keys.
Forward Sequence Number (FSN) - A field in a signal unit used to identify the transmitted message signal units.
Forward Signal: A signal sent in the direction from the calling to the called station, i.e. , from the original data source to the original data sink. Note: The forward signal is transmitted in the forward channel.
FOT - Abbreviation for frequency of optimum transmission. In the transmission of radio waves via ionospheric reflection, the highest effective, i.e., working, frequency that is predicted to be usable for a specified path and time for 90% of the days of the month. Note 1: The FOT is normally just below the value of the maximum usable frequency (MUF). In the prediction of usable frequencies, the FOT is commonly taken as 15% below the monthly median value of the MUF for the specified time and path. Note 2: The FOT is usually the most effective frequency for ionospheric reflection of radio waves between two specified points on Earth. Synonyms frequency of optimum traffic, optimum traffic frequency, optimum transmission frequency, optimum working frequency.
Fourier Analysis - The definition of a periodic waveform of arbitrary shape as a summation of sine waves having specific amplitudes and phases, and having frequencies corresponding to the harmonics of the waveform being defined. Note: A Fourier analysis is particularly well suited for communications equipment design and for predicting the performance of a given design.
Four-Wire Circuit - A two-way circuit using two paths so arranged that the respective signals are transmitted in one direction only by one path and in the other direction by the other path. Note: The four-wire circuit gets its name from the fact that, historically, two conductors were used in each of two directions for full-duplex operation. The name may still be applied, e.g., to a communications link supported by optical fibers, even though only one fiber is required for transmission in each direction.
Four-Wire Repeater - A repeater, consisting of two amplifiers, one associated with each direction, used in a four-wire circuit.
Four-Wire Terminating Set - A balanced transformer used to perform a conversion between 4-wire and 2-wire operation. Note 1: For example, a 4-wire circuit may, by means of a 4-wire terminating set, be connected to a 2-wire telephone set. Also, a pair of 4-wire terminating sets may be used to introduce an intermediate 4-wire loop into a 2-wire circuit, in which loop repeaters may be situated to amplify signals in each direction without positive feedback and oscillation. Note 2: Four-wire terminating sets have been largely supplanted by resistance hybrids.
Fox Message - A standard test message that includes all the alphanumerics on a teletypewriter and also function characteristics ( space, figures shift, letters shift). Note: An example of a fox message is "THE QUICK BROWN FOX JUMPED OVER THE LAZY DOG'S BACK 1234567890."
FPIS - Abbreviation for forward propagation ionospheric scatter. See ionospheric scatter.
FPS - Abbreviation for frames per second. In video and television, the number of images contained in a single second of a moving picture. Note: Thirty fps is considered full- motion video in NTSC systems, while 25 fps is considered full-motion in PAL and SECAM systems. Many proprietary video technologies produce 15 fps video; 24 fps is considered full-motion in motion-picture technology.
Fractal - A mathematical formula or algorithm that constitutes or defines an efficient way of formulating computer graphics. Fractal graphics translate the natural curves of an object into mathematical formulas, from which the entire image can later be constructed. Fractals are self-similar in that any piece of the fractal design contains a miniature of the entire design. A fractal is completely described by (a) one piece ( layer ) of the design, and (b) a sublayer of the design, which sublayer shows how contiguous pieces (layers) fit together. For this reason, fractal patterns (designs) require very little computer storage space. An example of a fractal is a fern leaf design.
Fractional Frequency Deviation - Synonym fractional frequency offset . A measure of the deviation of the frequency of a signal from a reference, expressed as a ratio. The ratio is dimensionless but typically expressed as parts per million, ppm. For example, 4.6 ppm = 4.6/106. Fractional frequency offset = [(f-fr) / fr] where: f = the actual frequency output of the signal in question, and fr = the reference frequency.
Fractional Frequency Fluctuation - The deviation of the frequency of an oscillator from its nominal constant frequency, normalized to the nominal frequency.
Fractional Frequency Offset - A measure of the deviation of the frequency of a signal from a reference, expressed as a ratio. The ratio is dimensionless but typically expressed as parts per million, ppm. For example, 4.6 ppm = 4.6/106. Fractional frequency offset = [(f-fr) / fr] where: f = the actual frequency output of the signal in question, and fr = the reference frequency. Synonym fractional frequency deviation.
Fractional T1 - A fractional T1 or T3 line is a T1 or T3 digital phone line in the North American T-carrier system that is leased to a customer at a fraction of its data-carrying capacity and at a correspondingly lower cost. A T1 line contains 24 channels, each with a data transfer capacity of 64 Kbps. The customer can rent some number of the 24 channels. The transmission method and speed of transfer remain the same. Overhead bits and
framing are still used, but the unrented channels simply contain no data.In telecommunications a fractional T1 is a portion of the 1.544 Mb/s (T1-aggregate) bit stream; the available fractions being determined by the type of multiplexer used to achieve the T1 aggregate bit stream.
T3 lines (which offer 672 64 Kbps channels) are also sometimes offered as a fractional service. T1 and fractional T1 service are sometimes advertised as "point-to-point" service (from the customer to the service provider).
Fragmentation -1. The process in which an IP ( Internet protocol ) datagram is broken into smaller pieces to fit the requirements of a given physical network; the reverse process of reassembly. 2. The physical separation of portions of a file on a computer disk.
Frame -1. In data transmission, the sequence of contiguous bits delimited by, and including, beginning and ending flag sequences. Note 1: A frame usually consists of a specified number of bits between flag sequences and usually includes an address field, a control field, and a frame check sequence. Note 2: Frames usually consist of a representation of the original data to be transmitted, together with other bits which may be used for error detection or control. Additional bits may be used for routing, synchronization, or overhead information not directly associated with the original data. 2. In the multiplex structure of pulse-code modulation ( PCM ) systems, a set of consecutive time slots in which the position of each digit can be identified by reference to a frame-alignment signal. Note: The frame-alignment signal does not necessarily occur, in whole or in part, in each frame. 3. In a time-division multiplexing ( TDM ) system, a repetitive group of signals resulting from a single sampling of all channels, including any required system information, such as additional synchronizing signals. Note: "In-frame" is the condition that exists when there is a channel -to-channel and bit-to-bit correspondence, exclusive of transmission errors, between all inputs of a time-division multiplexer and the output of its associated demultiplexer. 4. In ISDN, a block of variable length, labeled at the Data Link Layer of the Open Systems Interconnection--Reference Model. 5. In video display, the set of all picture elements that represent one complete image. Note: In NTSC and other television standards used throughout the world, a frame consists of two interlaced fields, each of which has half the number of scanning lines, and consequently, half the number of pixels, of one frame. 6. In video display, one complete scanned image from a series of video images. Note: A video frame is usually composed of two interlaced fields. 7. In computer screen displays of HTML documents, a portion (usually rectangular) of the screen where one usually finds the same types of fields/information displayed, in the same manner as one usually finds the same or similar information displayed in the same segment of different copies of a printed form. 8. An HTML feature that allows multiple Web pages to be viewed simultaneously (by means of scrolling or re-sizing) through a browser window.
Frame Alignment - 1. In the reception of framed digital data, the extent to which a received frame is correctly aligned with respect to the clock at the receiver. 2. The state in which the frame of the receiving equipment is synchronized with that of the received signal.
Frame-Alignment Recovery Time - Synonym reframing time. The time interval between the instant at which a valid frame-alignment signal is available at the receiving data terminal equipment and the instant at which frame alignment is established. Note: The reframing time includes the time required for replicated verification of the validity of the frame-alignment signal.
Frame-Alignment Signal - In the transmission of data frames, a distinctive sequence of bits used to accomplish frame alignment. Note: A frame-alignment signal may also contain additional bits for status, control, and error detection.
Frame-Alignment Time Slot - A time slot occupying the same relative position in every frame and used to transmit the frame alignment signal.
Frame Check Sequence (FCS) - 1. An error-detection scheme that (a) uses parity bits generated by polynomial encoding of digital signals, (b) appends those parity bits to the digital signal, and (c) uses decoding algorithms that detect errors in the received digital signal. Note: Error correction, if required, may be accomplished through the use of an automatic repeat-request (ARQ) system. 2. [An] error checking mechanism that checks data integrity by computing a polynomial algorithm based checksum.
Framed Interface - An interface through which information flow is partitioned into physical, periodic frames consisting of overhead information and an information payload.
Frame Duration - The time between the beginning of a frame and the end of that frame. Note: For fixed-length frames, at a fixed data rate, frame duration is constant.
Frame Frequency - Synonym frame rate. The number of frames transmitted or received per unit time. Note 1: The frame rate is usually expressed in frames per second. Note 2: In television transmission, the frame rate must be distinguished from the field rate, which in the NTSC and other systems, is twice the frame rate.
Frame Grabber - A device that can seize and record a single frame of video information out of a sequence of many frames.
Frame Matching - The process of comparing one sequence of frames with another sequence of frames in order to determine the correspondence between frames in each sequence and the correspondence of individual frames. Note: One means to test the correspondence between two video frames is to compare their digital representations on a pixel by pixel basis, and summarizing over all pixels as the mean-square of the differences (usually called "mean square error ").
Frame Overhead - Bits ( binary digits) that are added at regular intervals to a digital signal at the sending end of a digital link and used to provide network functions such as framing, operations, administration, and maintenance.
Frame Pitch - The distance, time, or number of bits between corresponding points, i.e., significant instants, in two consecutive frames.
Frame Rate - The number of frames transmitted or received per unit time. Note 1: The frame rate is usually expressed in frames per second. Note 2: In television transmission, the frame rate must be distinguished from the field rate, which in the NTSC and other systems, is twice the frame rate.Synonym frame frequency.
Frame-Rate Conversion - With respect to television or other video display technologies, the process of transforming from one standard frame rate to another, using an algorithm. Note: Standard display rates of 24, 25, 29.97, 30, and 60 fps (frames per second) presently exist.
Frame Relay - An interface protocol for statistically multiplexed packet -switched data communications in which (a) variable-sized packets (frames) are used that completely enclose the user packets they transport, and (b) transmission rates are usually between 56 kb/s and 1.544 Mb/s (the T-1 rate). Note 1: In frame relay, (a) there is neither flow-control nor an error -correction capability, (b) there is information -content independence, (c) there is a correspondence only to the ISO Open systems Interconnection--Reference Model Layers 1 and 2, (d) variable-sized user packets are enclosed in larger packets (frames) that add addressing and verification information, (e) frames may vary in length up to a design limit, usually 1 kilobyte or more, (f) one frame relay packet transports one user packet, (g) implementation of fast-packet technology is used for connection -oriented frame relay services, and (h) there is a capability to handle time - delay insensitive traffic, such as LAN interworking and image transfer. Note 2: Frame relay is referred to as the local management interface (LMI) standard and is specified in ANSI T1.617.
Frame Relaying Protocol Data Unit (FPDU) - A data unit exchanged at the user-network interface and having a format based on that defined in CCITT Recommendation Q.921 (1988) ( ANSI T1.602).
Frame Relaying Service Data Unit (FSDU) - The data unit exchanged at the functional boundary between the core function of Q.921 and the end-to-end protocol implemented above the core functions of Q.921.
Frame Size - The number of octets after the address field and before the frame check sequence ( FCS ) field in a frame. The octet count is done either before zero-bit insertion or after zero-bit extraction.
Frame Slip - In the reception of framed data, the loss of synchronization between a received frame and the receiver clock, causing a frame misalignment event, and resulting in the loss of the data contained in the received frame. Note: A frame slip should not be confused with a dropped frame where synchronization is not lost, e.g. , in the case of buffer overflow.
Frame Synchronization - Of a received stream of framed data, the process by which incoming frame alignment signals, i.e. , distinctive bit sequences, are identified, i.e. , distinguished from data bits, permitting the data bits within the frame to be extracted for decoding or retransmission. Note: The usual practice is to insert, in a dedicated time slot within the frame, a noninformation bit that is used for the actual synchronization of the incoming data with the receiver. Synonym framing.
Frame Synchronization Pattern - In digital communications, a prescribed recurring pattern of bits transmitted to enable the receiver to achieve frame synchronization.
Framing -1. In time-division multiplexing reception, synonym frame synchronization. 2. In video reception, the process of adjusting the timing of the receiver to coincide with the received video synchronization pulse. 3. In facsimile, the adjustment of the facsimile picture to a desired position in the direction of line progression.
Framing Bit -1. A bit used for frame synchronization. 2. In a bit stream, a bit used in determining the beginning or end of a frame. Note 1: The framing bit occurs at a specific position in the frame. Note 2: In a bit stream, framing bits are noninformation bits. Note 3: Framing in a digital signal is usually repetitive.
Framing Signal - See frame-alignment signal, framing bit. In the transmission of data frames, a distinctive sequence of bits used to accomplish frame alignment. Note: A frame-alignment signal may also contain additional bits for status, control, and error detection.
Fraunhofer Diffraction Pattern - Synonym far-field diffraction pattern. The diffraction pattern of a source (such as an LED, ILD, or the output end of an optical fiber ) observed at an infinite distance from the source. Note 1: A far- field pattern exists at distances that are large compared with s 2 /
, where s is a characteristic dimension of the source and
is the wavelength. For example, if the source is a uniformly illuminated circle, then s is the radius of the circle. Note 2: The far-field diffraction pattern of a source may be observed at infinity or (except for scale) in the focal plane of a well-corrected lens. The far-field pattern of a diffracting screen illuminated by a point source may be observed in the image plane of the source. Synonym Fraunhofer diffraction pattern.
Fraunhofer Region - Synonym far-field region. The region where the angular field distribution is essentially independent of distance from the source. Note 1: If the source has a maximum overall dimension D that is large compared to the wavelength, the far-field region is commonly taken to exist at distances greater than 2D 2/
from the source,
being the wavelength. Note 2: For a beam focused at infinity, the far-field region is sometimes referred to as the Fraunhofer region.
Free Net - A radio net in which any station may communicate with any other station in the net without first obtaining the permission of the net- control station. Note: Permission to operate as a free net is granted by the net-control station until such time as a directed net is established by the net-control station. See [for Internet systems] freenet.
Freenet - A system of computer networks (usually funded by individuals or organizations) consisting of community-based bulletin board systems with, e.g., e-mail, information services, interactive communications, and conferencing, and that are available to the user free of charge, or for a small membership fee. See [for radio communications] free net.
Freephone - In the U.K., Freephone is a type of Number Translation Service (NTS) that allows a phone user to call a non-geographic number beginning with 0800 or 0500 without incurring a charge. All charges and associated costs are charged to the organization that receives the call. Businesses and non-profit help lines often offer Freephone numbers. Freephone is similar to 1-800 numbers used in the U.S.
Free Routing - The routing of messages in such a manner that they are forwarded toward their destination or addressee over any available channel without dependence upon predetermined routing.
Free-Running Capability - In a synchronized oscillator, the capability to operate in the absence of a synchronizing signal.
Free Space - A theoretical concept of space devoid of all matter. Note: Free space also implies remoteness from material objects that could influence the propagation of electromagnetic waves.
Free-Space Coupling - Coupling of magnetic, electric, or electromagnetic fields that are not confined to a conductor. Note: Coupling by the deliberate introduction of capacitors and inductors is not considered free-space coupling.
Free-Space Loss - The signal attenuation that would result if all absorbing, diffracting, obstructing, refracting, scattering, and reflecting influences were sufficiently removed so as to have no effect on propagation. Note: Free-space loss is primarily caused by beam divergence, i.e. , signal energy spreading over larger areas at increased distances from the source.
Freeware - Software that is developed usually by individuals or small companies and distributed, usually via FTP, at essentially no cost to the recipient. Note: Often the developer or another party retains the copyright to the software product; therefore, freeware is not necessarily in the public domain, and its distribution may be controlled by the copyright owner.
Freeze Frame - A frame of visual information that is selected from a set of motion video frames, and is held in a buffer.
Freeze Frame Television - Television in which fixed ("still") images are transmitted sequentially at a rate far too slow to be perceived as continuous motion by human vision. Note: Transmission of an image is usually performed periodically by a processing unit that contains memory in which data representing the image are stored. For an image of specified quality, e.g., resolution and color fidelity, freeze- frame television has a lower bandwidth requirement than that of full-motion operation.
Freeze-Out - The condition that occurs when an earlier nonactive speaker on an input transmission trunk channel becomes active and cannot immediately be assigned to a bearer channel, due to lack of free instantaneous transmission capacity.
Freeze-Out Fraction - The ratio of the total time that the individual channels experience the freeze-out condition to the total time of the active intervals, and their corresponding hangover times and front end delays, for all transmission trunks over a fixed interval of time, e.g., 1 minute.
F region - That portion of the ionosphere existing between approximately 160 and 400 km above the surface of the Earth, consisting of layers of increased free-electron density caused by the ionizing effect of solar radiation. Note 1: The F region reflects normal-incident frequencies at or below the critical frequency (approximately 10 MHz) and partially absorbs waves of higher frequency. Note 2: The F1 layer exists from about 160 to 250 km above the surface of the Earth and only during daylight hours. Though fairly regular in its characteristics, it is not observable everywhere or on all days. The principal reflecting layer during the summer for paths of 2,000 to 3,500 km is the F1 layer. The F1 layer has approximately 5 × 105 e/cm3(free electrons per cubic centimeter) at noontime and minimum sunspot activity, and increases to roughly 2 × 106 e/cm3 during maximum sunspot activity. The density falls off to below 104 e/cm3 at night. Note 3: The F1 layer merges into the F2 layer at night. Note 4: The F2 layer exists from about 250 to 400 km above the surface of the Earth. The F2 layer is the principal reflecting layer for HF communications during both day and night. The horizon-limited distance for one-hop F2 propagation is usually around 4,000 km. The F2 layer has about 106 e/cm3. However, variations are usually large, irregular, and particularly pronounced during magnetic storms.
French Telephone Jack - Below is an image of a typical telephone jack in France. You will notice that a French telephone jack is much bigger than what you would find in the US.
The adapter is type F-010 as is the jack.
Interestingly enough the telephone connector pin is the same as in the US. That is RJ11, but there is a large adapter that the phone connector pin plugs into and then the adapter is plugged into the phone jack.
This all means that if you have a DSL line you will have two adapters sticking out of your wall. The first will be for your DSL modem and the second will be for your telephone. Your French ISP will send you the adapter (sometimes two) that the modem will plug into. Normally you will get the adapters when you receive your modem, but if need be you can buy DSL adapters in most supermarkets.
French Telephone Adaptor - Adapter
This is a typical French adapter (type F-010) that plugs into the phone wall jack. At the bottom of the adapter is the plug for a RJ11 phone line.

French F-010 - F-010 is a type of telephone plug and matching socket. The F-010 standard originated in France and is used there and in other countries, including Algeria, Andorra, Bhutan, Burkina Faso, Chad, Comoros, Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, French Guiana, Gabon, Grenadines, Guadeloupe, Ivory Coast, Madagascar, Mali, Martinique, Mauritania, Mauritius, Monaco, Morocco, New Caledonia, Niger, Polynesia, Rwanda, St. Martin, Somalia, Tahiti, Togo and Tunisia.
French Adapters Plugged into each other

This is an example of two French telephone adapters sticking out of a wall.
The first adapter is for the DSL modem and the second is for the telephone.Frequency - A certain "size" of radio wave: The rate at which the electric and magnetic fields of a radio wave vibrate per second. 1. For a periodic function, the number of cycles or events per unit time. 2. The number of cycles occurring per second of an electrical or electromagnetic wave; a number representing a specific point in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Frequency Accuracy - The degree of conformity to a specified value of a frequency.
Frequency Aging - Of an oscillator, the change in frequency, over time, caused by internal changes in oscillator parameters even when external factors, such as environment and power supply characteristics, are constant.
Frequency Allocation - See allocation (of a frequency band).
Frequency Allotment - See allotment (of a radio frequency or radio frequency channel ).
Frequency-Analysis Compaction - Data compaction accomplished by using an expression composed of a number of different frequencies of different magnitudes to represent a particular curve. Note: An example of frequency -analysis compaction is the use of a Fourier analysis to represent an arbitrary curve, a periodic function, an aperiodic function, or a wave shape. Thus, the fundamental frequency, the amplitude of the fundamental frequency, and the amplitudes and frequencies of the harmonics are all that are needed to reconstitute the function or wave shape. The shape can thus be readily stored and transmitted in this compacted form.
Frequency Assignment -1. Authorization, given by an Administration, for a radio station to use a radio frequency or radio frequency channel under specified conditions 2. The process of authorizing a specific frequency, group of frequencies, or frequency band to be used at a certain location under specified conditions, such as bandwidth, power, azimuth, duty cycle, or modulation. Synonym radio frequency channel assignment.
Frequency Assignment Authority - The power granted an Administration, or its designated or delegated leader or agency via treaty or law, to specify frequencies, or frequency bands, in the electromagnetic spectrum for use in systems or equipment. Note: Primary frequency assignment authority for the United States is exercised by the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) for the Federal Government and by the Federal Communications Commission ( FCC ) for non-Federal Government organizations. International frequency assignment authority is vested in the International Frequency Registration Board of the International Telecommunication Union.
Frequency Averaging -1. The process by which the relative phases of precision clocks are compared for the purpose of defining a single time standard. 2. A process in which network synchronization is achieved by use, at all nodes, of oscillators that adjust their frequencies to the average frequency of the digital bit streams received from connected nodes. Note: In frequency averaging, all oscillators are assigned equal weight in determining the ultimate network frequency.
Frequency Band - See electromagnetic spectrum. The range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation from zero to infinity. Note: The electromagnetic spectrum was, by custom and practice, formerly divided into 26 alphabetically designated bands. This usage still prevails to some degree. However, the ITU formally recognizes 12 bands, from 30 Hz to 3000 GHz. New bands, from 3 THz to 3000 THz, are under active consideration for recognition.
Frequency Band Allocation - See allocation (of a frequency band ). 1. Entry in the Table of Frequency Allocations of a given frequency band for the purpose of its use by one or more (terrestrial or space) radiocommunication services or the radio astronomy service under specified conditions. This term shall also be applied to the frequency band concerned. 2. The process of designating radio-frequency bands for use by specific radio services.
Frequency-Change Signaling - A signaling method in which one or more discrete frequencies correspond to each desired significant condition of a code. Note 1: The transition from one set of frequencies to the other may be a continuous or a discontinuous change in frequency or in phase. Note 2: Frequency-change signaling may be used in both supervisory signaling and data transmission.
Frequency Coherence - See phase coherence. The state in which two signals maintain a fixed phase relationship with each other or with a third signal that can serve as a reference for each.
Frequency Compatibility -1. Of an electronic device, the extent to which it will operate at its designed performance level in its intended operational environment (including the presence of interference ) without causing interference to other devices. 2. The degree to which an electrical or electronic device or devices operating on or responding to a specified frequency or frequencies is capable of functioning with other such devices.
Frequency Departure -1. The difference between the instantaneous frequency of a digital signal and the long-term average frequency of that signal. 2. An unintentional deviation from the nominal frequency value.
Frequency-Derived Channel - A channel derived by dividing an allocated or available bandwidth over a medium into two or more portions, each usable separately. Note: A frequency -derived channel is continuously available and may be further divided on either a frequency or time basis.
Frequency Deviation -1. The amount by which a frequency differs from a prescribed value, such as the amount an oscillator frequency drifts from its nominal frequency. 2. In frequency modulation, the absolute difference between (a) the maximum permissible instantaneous frequency of the modulated wave or the minimum permissible instantaneous frequency of the modulated wave and (b) the carrier frequency. 3. In frequency modulation, the maximum absolute difference, during a specified period, between the instantaneous frequency of the modulated wave and the carrier frequency.
Frequency Dispersal - An electronic counter- countermeasure ( ECCM ) in which communications nets ' operating frequencies are widely separated from each other, causing a requirement to spread jamming power over wider frequency bands and thus compelling a reduction of available jamming power on any single channel or frequency, or causing a requirement for more jamming power or more jamming equipment.
Frequency Displacement - The end-to-end shift in frequency that may result from independent frequency translation errors in a circuit.
Frequency Distortion - Synonym amplitude-vs.-frequency distortion. Distortion in a transmission system caused by nonuniform attenuation, or gain, in the system with respect to frequency under specified operating conditions.
Frequency Diversity - Transmission and reception in which the same information signal is transmitted and received simultaneously on two or more independently fading carrier frequencies.
Frequency-Division Multiple Access (FDMA) - The use of frequency division to provide multiple and simultaneous transmissions to a single transponder.
Frequency-Division Multiplexing (FDM) - A scheme in which numerous signals are combined for transmission on a single communications line or channel. Each signal is assigned a different frequency (subchannel) within the main channel.
A typical analog Internet connection via a twisted pair telephone line requires approximately three kilohertz (3 kHz) of bandwidth for accurate and reliable data transfer. Twisted-pair lines are common in households and small businesses. But major telephone cables, operating between large businesses, government agencies, and municipalities, are capable of much larger bandwidths.
Suppose a long-distance cable is available with a bandwidth allotment of three megahertz (3
MHz ). This is 3,000 kHz, so in theory, it is possible to place 1,000 signals, each 3 kHz wide, into the long-distance channel. The circuit that does this is known as amultiplexer . It accepts the input from each individual end user, and generates a signal on a different frequency for each of the inputs. This results in a high-bandwidth, complex signal containing data from all the end users. At the other end of the long-distance cable, the individual signals are separated out by means of a circuit called a demultiplexer, and routed to the proper end users. A two-way communications circuit requires a multiplexer/demultiplexer at each end of the long-distance, high-bandwidth cable.When FDM is used in a communications network, each input signal is sent and received at maximum speed at all times. This is its chief asset. However, if many signals must be sent along a single long-distance line, the necessary bandwidth is large, and careful engineering is required to ensure that the system will perform properly. In some systems, a different scheme, known as time-division multiplexing, is used instead.
Frequency Drift - An undesired progressive change in frequency with time. Note 1: Causes of frequency drift include component aging and environmental changes. Note 2: Frequency drift may be in either direction and is not necessarily linear.
Frequency-Exchange Signaling - Frequency-change signaling in which the change from one significant condition to another is accompanied by decay in amplitude of one or more frequencies and by buildup in amplitude of one or more other frequencies. Note: Frequency-exchange signaling applies to supervisory signaling and user - information transmission. Synonym two-source frequency keying.
Frequency Fluctuation - A short-term variation, with respect to time, of the frequency of an oscillator. Note: Frequency fluctuation, f ( t ), is given by
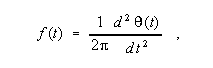
where
( t ) is the phase angle of the sinusoidal wave with respect to time, t .
Frequency Flutter - A deviation of frequency that generally results from irregular motion of the recording medium during the recording, duplication, or reproduction. Synonym [loosely] flutter.
Frequency Frogging -1. The interchanging of the frequencies of carrier channels to accomplish specific purposes, such as to prevent feedback and oscillation, to reduce crosstalk, and to correct for a high frequency-response slope in the transmission line. Note: Frequency frogging is accomplished by having modulators, which are integrated into specially designed repeaters, translate a low-frequency group to a high-frequency group, and vice versa. A channel will appear in the low group for one repeater section and will then be translated to the high group for the next section because of frequency frogging. This results in nearly constant attenuation with frequency over two successive repeater sections, and eliminates the need for large slope equalization and adjustments. Singing and crosstalk are minimized because the high- level output of a repeater is at a different frequency than the low-level input to other repeaters. 2. In microwave systems, the alternate use of two frequencies at repeater sites to prevent feedback and oscillation.
Frequency Guard Band - A frequency band deliberately left vacant between two channels to provide a margin of safety against mutual interference.
Frequency Hopping - The repeated switching of frequencies during radio transmission according to a specified algorithm, to minimize unauthorized interception or jamming of telecommunications. Note: The overall bandwidth required for frequency hopping is much wider than that required to transmit the same information using only one carrier frequency.
Frequency-Hopping Spread Spectrum - A signal structuring technique employing automatic switching of the transmitted frequency. Selection of the frequency to be transmitted is typically made in a pseudo-random manner from a set of frequencies covering a band wider than the information bandwidth. The intended receiver would frequency- hop in synchronization with the code of the transmitter in order to retrieve the desired information. Note: In many cases, used as an electronic counter- countermeasure ( ECCM ) technique.
Frequency Hour - One frequency used for one hour regardless of the number of transmitters over which it is simultaneously broadcast by a station during that hour.
Frequency Instability - See frequency stability. The degree to which variations of the frequency of an oscillator deviate from the mean frequency over a specified period of time.
Frequency Lock - The condition in which a frequency -correcting feedback loop maintains control of an oscillator within the limits of one cycle. Note: Frequency lock does not imply phase lock, but phase lock does imply frequency lock.
Frequency Modulation (FM) - Modulation in which the instantaneous frequency of a sine wave carrier is caused to depart from the center frequency by an amount proportional to the instantaneous value of the modulating signal. Note 1: In FM, the carrier frequency is called the center frequency. Note 2: FM is a form of angle modulation. Note 3: In optical communications, even if the electrical baseband signal is used to frequency-modulate an electrical carrier (an "FM" optical communications system), it is still the intensity of the lightwave that is varied (modulated) by the electrical FM carrier. In this case, the "information," as far as the lightwave is concerned, is the electrical FM carrier. The lightwave is varied in intensity at an instantaneous rate corresponding to the instantaneous frequency of the electrical FM carrier.
Frequency Offset - The difference between the frequency of a source and a reference frequency.
Frequency of Optimum Traffic - Synonym FOT. In the transmission of radio waves via ionospheric reflection, the highest effective, i.e., working, frequency that is predicted to be usable for a specified path and time for 90% of the days of the month. Note 1: The FOT is normally just below the value of the maximum usable frequency (MUF). In the prediction of usable frequencies, the FOT is commonly taken as 15% below the monthly median value of the MUF for the specified time and path. Note 2: The FOT is usually the most effective frequency for ionospheric reflection of radio waves between two specified points on Earth. Synonyms frequency of optimum transmission, optimum traffic frequency, optimum transmission frequency, optimum working frequency.
Frequency of Optimum Transmission (FOT) - Abbreviation for FOT. In the transmission of radio waves via ionospheric reflection, the highest effective, i.e., working, frequency that is predicted to be usable for a specified path and time for 90% of the days of the month. Note 1: The FOT is normally just below the value of the maximum usable frequency (MUF). In the prediction of usable frequencies, the FOT is commonly taken as 15% below the monthly median value of the MUF for the specified time and path. Note 2: The FOT is usually the most effective frequency for ionospheric reflection of radio waves between two specified points on Earth. Synonyms frequency of optimum traffic, optimum traffic frequency, optimum transmission frequency, optimum working frequency.
Frequency Prediction - A prediction of the maximum usable frequency ( MUF ), the optimum traffic frequency, and the lowest usable frequency ( LUF ) for transmission between two specific locations or geographical areas during various times throughout a 24-hour period. Note: The prediction is usually indicated by means of a graph for each frequency plotted as a function of time.
Frequency Range - A continuous range or spectrum of frequencies that extends from one limiting frequency to another. Note 1: The frequency range for given equipment specifies the frequencies at which the equipment is operable. For example, filters pass or stop certain bands of frequencies. The frequency range for propagation indicates the frequencies at which electromagnetic wave propagation in certain modes or paths is possible over given distances. Frequency allocation, however, is made in terms of bands of frequencies. There is little, if any, conceptual difference between a range of frequencies and a band of frequencies. Note 2: " Frequency band " usually identifies a specific band of frequencies in the Tables of Frequency Allocations.
Frequency Response - See insertion-loss-vs.-frequency characteristic. Of a system or device, a plot of the amplitude as a function of frequency. Note: The insertion-loss-vs.-frequency characteristic may be expressed as absolute gain or loss, or it may be normalized with respect to gain or loss at a specified reference frequency.
Frequency Response Curve - A plot of the gain or attenuation of a device, such as an amplifier or a filter, as a function of frequency. Note: A flat curve indicates a uniform gain or attenuation over the range of frequencies for which the curve is flat. Most amplifiers have a flat frequency response over a certain band, above and below which the gain is reduced. The frequency response curve of a filter has one or more peaks or troughs.
Frequency Scanning - Conducting a search for signals over a band or range of frequencies by means of a manually or automatically tuned receiver. Note: The tuning rate, i.e., the frequency change rate, may be fixed or variable, or it may be performed mechanically at low speed or electronically at high speed. Frequency scanning may be used to enable a radar to transmit on a clear frequency, i.e., a no- interference frequency, by searching a frequency band and then tuning the system to a clear portion of that band.
Frequency Sharing - The assignment to or use of the same radio frequency by two or more stations that are separated geographically or that use the frequency at different times. Note 1: Frequency sharing reduces the potential for mutual interference where the assignment of different frequencies to each user is not practical or possible. Note 2: In a communications net, frequency sharing does not pertain to stations that use the same frequency.
Frequency Spectrum - See electromagnetic spectrum. The range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation from zero to infinity. Note: The electromagnetic spectrum was, by custom and practice, formerly divided into 26 alphabetically designated bands. This usage still prevails to some degree. However, the ITU formally recognizes 12 bands, from 30 Hz to 3000 GHz. New bands, from 3 THz to 3000 THz, are under active consideration for recognition.
Fresnel Reflection - In optics, the reflection of a portion of incident light at a discrete interface between two media having different refractive indices. Note 1: Fresnel reflection occurs at the air-glass interfaces at the entrance and exit ends of an optical fiber. Resultant transmission losses, on the order of 4% per interface, can be reduced considerably by the use of index-matching materials. Note 2: The coefficient of reflection depends upon the refractive index difference, the angle of incidence, and the polarization of the incident radiation. For a normal ray, the fraction of reflected incident power is given by
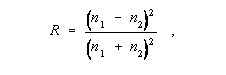
where R is the reflection coefficient and n 1and n 2 are the respective refractive indices of the two media. In general, the greater the angle of incidence with respect to the normal, the greater the Fresnel reflection coefficient, but for radiation that is linearly polarized in the plane of incidence, there is zero reflection at Brewster's angle. Note 3: Macroscopic optical elements may be given antireflection coatings consisting of one or more dielectric thin-film layers having specific refractive indices and thicknesses. Antireflection coatings reduce overall Fresnel reflection by mutual interference of individual Fresnel reflections at the boundaries of the individual layers.
Front-End Processor (FEP) - A programmed-logic or stored-program device that interfaces data communication equipment with an input / output bus or memory of a data processing computer.
Front Projectors - These are TV sets that create the image on a small display, and then enlarge it by projecting it onto a wall or stand-alone screen (much like a movie theater). Front projectors tend to be dimmer than direct flat panels or CRTs, and often require the room to be dark to be able to see the image clearly.
FTAM - Abbreviation for file transfer, access, and management. An application's service and protocol based on the concept of virtual file store. Note: FTAM allows remote access to various levels in a file structure and provides a comprehensive set of file management capabilities.
FTS2000 - Abbreviation for Federal Telecommunications System 2000. The designation for a defunct Federal telecommunications contract replaced by the contract designated by the title "FTS2001."
FTP is the abbreviation for File Transfer Protocol. The Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) protocol that is (a) a standard high-level protocol for transferring files from one computer to another, (b) usually implemented as an application level program, and (c) uses the Telnet and TCP protocols. Note: In conjunction with the proper local software, FTP allows computers connected to the Internet to exchange files, regardless of the computer platform. See File Transfer Protocol
FTP Archive - A collection of files that are available by using file transfer protocol (FTP). Synonyms file archive, file site.
FTTP (Fiber to the Premises) - A fiber-optic network that connects directly from the carrier network to the user premises. Another fiber-optic network is FTTC (Fiber to the Curb) that connects from the carrier network to the curb, and from there to the premises by copper wire or coaxial cable.
Full-Duplex (FDX) Circuit - A circuit that permits simultaneous transmission in both directions.
Full-Duplex (FDX) Operation - Synonym duplex operation. Operating method in which transmission is possible simultaneously, in both directions of a telecommunication channel. [NTIA] [RR] Note 1: This definition is not limited to radio transmission. Note 2: In general, duplex operation and semi-duplex operation require two frequencies in radiocommunication; simplex operation may use either one or two. Synonym two-way simultaneous operation.
Full Width at Half Maximum (FWHM) - An expression of the extent of a function, given by the difference between the two extreme values of the independent variable at which the dependent variable is equal to half of its maximum value. Note 1: FWHM is applied to such phenomena as the duration of pulse waveforms and the spectral width of sources used for optical communications. Note 2: The term full duration at half maximum (FDHM) is preferred when the independent variable is time.
Fully Connected Mesh Network - See network topology.
Fully Connected Topology - See network topology.
Functionality - The ability of equipment to operate as expected during actual service conditions in a central office.
Functional Component (FC) - In intelligent networks, an elemental call-processing component that directs internal network resources to perform specific actions, such as collecting dialed digits. Note: An FC is unique to the intelligent-network-IN/2 architecture.
Functional Unit - An entity of hardware, software, or both, capable of accomplishing a specified purpose.
Fundamental - Of a periodic wave, the sinusoidal component, i.e., Fourier component, having the lowest frequency. Note: Every periodic waveform may be expressed as the summation of the fundamental and its harmonics. For example, a square wave may be expressed as the summation of sine waves equal in frequency to the fundamental and all odd harmonics, each frequency having an appropriate amplitude and phase. A pure sinusoidal wave has only one component, i.e., the fundamental.
Fundamental Mode - The lowest order mode of a waveguide. Note: In optical fibers, the fundamental mode is designated LP01 or HE11.
Fusion - Synonym (in cryptosystems) linkage. - In computer security, the purposeful combining of data or information from one data processing system with data or information from another system to derive protected information.
Fusion Splice - In fiber optics, a splice created by localized heating of the ends of the two fibers to be joined. Note: A properly made fusion splice results in a continuous length of material with minimal discontinuities at the splice.
Fax Switch Products
|
*Note: All prices include shipping and handling in the continental US and most of Canada. We reserve the right to charge up to the actual price of shipping on all orders outside the continental United States. Customer is responsible for any taxes, duties or brokerage charges that may apply. All orders shipped UPS Ground unless specified. For air and express shipments, appropriate charges will be applied to your order.
Need Help?
- Call now for free phone consultation at 1-866-337-0965.
Click here if you want to share 2 devices on 1 line and don't know which device to choose.
Click here if you want to share 3 or more devices on one line and don't know what type to choose.
"Albert Einstein Presents Fax Switch "
![]()
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
If you didn't find what you need here?
Please visit our sister company, SuperPhoneStore.com for wholesale to the public telephones, phone accessories or the latest electronics. We have over 4500 different products in stock.