
Telecom Dictionary - Definitions of terms
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
D - Telecom Dictionary for the Letter D
D-channel - In the Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN), the D-channel is the channel that carries control and signalling information. (The "D" stands for "delta" channel.) The B-channel ("B" for "bearer") carries the main data.In ISDN, there are two levels of service: the Basic Rate Interface, intended for the home and small enterprise, and the Primary Rate Interface, for larger users. Both rates include a number of B- (bearer) channels and a D- (delta) channel. The B-channels carry data, voice, and other services. The D-channel carries control and signaling information.
The Basic Rate Interface consists of two 64 Kbps B-channels and one 16 Kbps D-channel. Thus, a Basic Rate Interface user can have up to 128 Kbps service. The Primary Rate Interface consists of 23 B-channels and one 64- Kpbs D channel in the United States or 30 B-channels and 1 D-channel in Europe.
D-A - Abbreviation for digital-to-analog. See digital transmission system.
Daemon - Abbreviation for disk and execution monitor. A procedure that is invoked without being called explicitly whenever an alteration, an addition, or a deletion or other event occurs. Pronounced dee' mun. Also spelled demon.
Damping - 1. The progressive diminution with time of certain quantities characteristic of a phenomenon. 2. The progressive decay with time in the amplitude of the free oscillations in a circuit. 3. Energy dissipation mechanisms that reduce the amplification and broaden the vibratory response in the region of a resonance.
Damping Ratio: In studies of network survivability in an earthquake, the ratio of actual damping to critical damping.
Dangling Threat - Set of properties about the external environment for which there is no corresponding vulnerability and therefore no implied risk
Data - In telecommunications, data sometimes means digital-encoded information to distinguish it from analog-encoded information such as conventional telephone voice calls. In general, "analog" or voice transmission requires a dedicated continual connection for the duration of a related series of transmissions. Data transmission can often be sent with intermittent connections in packets that arrive in piecemeal fashion. In computing, data is information that has been translated into a form that is more convenient to move or process. Generally and in science, data is a gathered body of facts.
Data Authentication - A process used to verify data integrity, e.g., verification that data received are identical to data sent, or verification that a program is not infected by a virus.
Database - 1. A set of data that is required for a specific purpose or is fundamental to a system, project, enterprise, or business. Note: A database may consist of one or more data banks and be geographically distributed among several repositories. 2. A formally structured collection of data. Note: In automated information systems, the database is manipulated using a database management system.
Database Management System (DBMS): A software system that facilitates (a) the creation and maintenance of a database or databases, and (b) the execution of computer programs using the database or databases.
Datacasting -Also known as "enhanced TV," this is digital programming that provides additional features to viewers (with program material or non-program-related resources) such as the ability to download data (video, audio, text, graphics, maps, services, etc.) to specially equipped computers, cache boxes, set-top boxes, or DTV receivers.
Data Communication - The transfer of information between functional units by means of data transmission according to a protocol. Note: Data are transferred from one or more sources to one or more sinks over one or more data links.
Data Compaction - The reduction of the number of data elements, bandwidth, cost, and time for the generation, transmission, and storage of data without loss of information by eliminating unnecessary redundancy, removing irrelevancy, or using special coding. Note 1: Examples of data compaction methods are the use of fixed-tolerance bands, variable-tolerance bands, slope-keypoints, sample changes, curve patterns, curve fitting, variable-precision coding, frequency analysis, and probability analysis. Note 2: Simply squeezing noncompacted data into a smaller space, for example by increasing packing density or by transferring data on punched cards onto magnetic tape, is not data compaction. Note 3: Whereas data compaction reduces the amount of data used to represent a given amount of information, data compression does not.
Data Compression - 1. Increasing the amount of data that can be stored in a given domain, such as space, time, or frequency, or contained in a given message length. 2. Reducing the amount of storage space required to store a given amount of data, or reducing the length of message required to transfer a given amount of information. Note 1: Data compression may be accomplished by simply squeezing a given amount of data into a smaller space, for example, by increasing packing density or by transferring data on punched cards onto magnetic tape. Note 2: Data compression does not reduce the amount of data used to represent a given amount of information, whereas data compaction does. Both data compression and data compaction result in the use of fewer data elements for a given amount of information.
Data Conferencing Repeater - A device that enables any one user of a group of users to transmit a message to all other users in that group. Synonym technical control hubbing repeater.
Datagram - In packet switching, a self-contained packet, independent of other packets, that contains information sufficient for routing from the originating data terminal equipment (DTE) to the destination DTE without relying on prior exchanges between the equipment and the network. Note: Unlike virtual call service, when datagrams are sent there are no call establishment or clearing procedures. Thus, the network may not be able to provide protection against loss, duplication, or misdelivery.
Data Integrity - 1. The condition existing when data is unchanged from its source and has not been accidentally or maliciously modified, altered, or destroyed. 2. The condition in which data are identically maintained during any operation, such as transfer, storage, and retrieval. 3. The preservation of data for their intended use. 4. Relative to specified operations, the a priori expectation of data quality.
Data Link - 1. The means of connecting one location to another for the purpose of transmitting and receiving data. 2. An assembly, consisting of parts of two data terminal equipments (DTEs) and the interconnecting data circuit, that is controlled by a link protocol enabling data to be transferred from a data source to a data sink.
Data Link Layer - See Open Systems Interconnection--Reference Model. Layer 2. This layer responds to service requests from the Network Layer and issues service requests to the Physical Layer. The Data Link Layer provides the functional and procedural means to transfer data between network entities and to detect and possibly correct errors that may occur in the Physical Layer. Note: Examples of data link protocols are HDLC and ADCCP for point-to-point or packet-switched networks and LLC for local area networks.
Data Processing - The systematic performance of operations upon data such as handling, merging, sorting, and computing. Note: The semantic content of the original data should not be changed. The semantic content of the processed data may be changed. Synonym information processing.
Data Signaling Rate (DSR) - The aggregate rate at which data pass a point in the transmission path of a data transmission system. Note 1: The DSR is usually expressed in bits per second. Note 2: The data signaling rate is given by
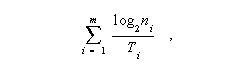
where m is the number of parallel channels, ni is the number of significant conditions of the modulation in the I-th channel, and Ti is the unit interval, expressed in seconds, for the I-th channel. Note 3: For serial transmission in a single channel, the DSR reduces to (1/T) log 2 n; with a two-condition modulation, i.e., n =2, the DSR is 1/T. Note 4: For parallel transmission with equal unit intervals and equal numbers of significant conditions on each channel, the DSR is (m /T)log2 n; in the case of a two-condition modulation, this reduces to m /T. Note 5: The DSR may be expressed in bauds, in which case, the factor log2 ni in the above summation formula should be deleted when calculating bauds. Note 6: In synchronous binary signaling, the DSR in bits per second may be numerically the same as the modulation rate expressed in bauds. Signal processors, such as four-phase modems, cannot change the DSR, but the modulation rate depends on the line modulation scheme, in accordance with Note 4. For example, in a 2400 b/s 4-phase sending modem, the signaling rate is 2400 b/s on the serial input side, but the modulation rate is only 1200 bauds on the 4-phase output side.
Data Stream - A sequence of digitally encoded signals used to represent information in transmission.
Data Transfer Rate (or often just data rate) - The amount of digital data that is moved from one place to another in a given time, usually in a second's time. The data transfer rate can be viewed as
the speed of travel of a given amount of data from one place to another. In general, the greater the bandwidth of a given path, the higher the data transfer rate.In telecommunications, data transfer is usually measured in bits per second. For example, a typical low-speed connection to the Internet may be 33.6 kilobits per second (Kbps). On Ethernet local area networks, data transfer can be as fast as 10 megabits per second. Network switches are planned that will transfer data in the terabit range. In earlier telecommunication systems, data transfer was sometimes measured in characters or blocks (of a certain size) per second.
Data Transmission - The sending of data from one place to another by means of signals over a channel.
dB - Abbreviation for decibel (s). One tenth of the common logarithm of the ratio of relative powers, equal to 0.1 B (bel). Note 1: The decibel is the conventional relative power ratio, rather than the bel, for expressing relative powers because the decibel is smaller and therefore more convenient than the bel. The ratio in dB is given by
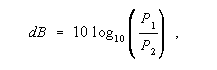
where P 1 and P 2 are the actual powers. Power ratios may be expressed in terms of voltage and impedance, E and Z, or current and impedance, I and Z, since
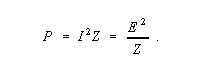
Thus dB is also given by
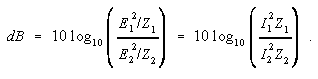
If Z 1= Z 2, these become
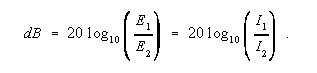
Note 2: The dB is used rather than arithmetic ratios or percentages because when circuits are connected in tandem, expressions of power level, in dB, may be arithmetically added and subtracted. For example, in an optical link, if a known amount of optical power, in dBm, is launched into a fiber, and the losses, in dB, of each component (e.g., connectors, splices, and lengths of fiber) are known, the overall link loss may be quickly calculated with simple addition and subtraction.
dBa - Abbreviation for decibels adjusted. Weighted absolute noise power, calculated in dB referenced to 3.16 picowatts (-85 dBm), which is 0 dBa. Note: The use of F1A-line or HA1-receiver weighting must be indicated in parentheses as required. A one-milliwatt, 1000-Hz tone will read +85 dBa, but the same power as white noise, randomly distributed over a 3-kHz band (nominally 300 to 3300 Hz), will read +82 dBa, due to the frequency weighting. Synonym dBrn adjusted.
dBm - Abbreviation. dB referenced to one milliwatt. Note 1: dBm is used in communication work as a measure of absolute power values. Zero dBm equals one milliwatt. Note 2: In DOD practice, unweighted measurement is normally understood, applicable to a certain bandwidth, which must be stated or implied. Note 3: In European practice, psophometric weighting may be implied, as indicated by context; equivalent to dBm0p, which is preferred.
dBm0 - Power in dBm referred to or measured at a zero transmission level point (0TLP). Note 1: A 0TLP is also called a point of zero relative transmission level (0 dBr0). Note 2: Some international documents use dBm0 to mean noise power in dBm0p (psophometrically weighted dBm0). In the United States, dBm0 is not so used.
dBm0p - Noise power in dBm0, measured by a psophometer or noise measuring set having psophometric weighting.
dBrnC - Weighted noise power in dBrn, measured by a noise measuring set with C-message weighting.
DBS -Digital Broadcast Satellite. TV programming delivered via high-powered satellite. Signals are transmitted to a small dish (usually 18-24 inches across) mounted outdoors.
DCR -Digital Cable Ready TV. Also referred to as "Plug-and-Play," this is a DTV or other device for digital cable customers that plugs directly into the cable jack and does not require a separate set-top box to view analog and unscrambled digital cable. Used with a CableCARD, it can receive scrambled programming such as premium services.
Decibel - See dB.
Decision Circuit - A circuit that measures the probable value of a signal element and makes an output signal decision based on the value of the input signal and a predetermined criterion or criteria.
Decision Instant - In the reception of a digital signal, the instant at which a decision is made by a receiving device as to the probable value of a signal condition. Synonym selection position.
Decoder - A device or program that translates encoded data into its original format — i.e., it decodes the data.
Decrypt - 1. A generic term encompassing decode and decypher. 2. To convert encrypted text into its equivalent plain text by means of a cryptosystem. (This does not include solution by cryptanalysis.) Note: The term "decrypt" covers the meanings of " decipher " and "decode."
Dedicated Line - A telecommunications path between two points that is available 24 hours a day for use by a designated user (individual or company). It is not shared in common among multiple users as dial-up lines are. A dedicated line can be a physical path owned by the user or rented from a telephone company, in which case it is called a leased line. A synonym is nonswitched line (as opposed to a switched or dial-up line).
Dedicated Service - A connection to the Internet using a leased line that provides for very fast, high bandwidth connections. Also called permanent direct service.
Defense Communications System (DCS) - Department of Defense long-haul voice, data, and record traffic system which includes the Defense Data Network, Defense Satellite Communications Systems, and Defense Switched Network.
Defense Data Network (DDN): A component of the Defense Communications System used for switching Department of Defense automated data processing systems.
Degradation - 1. The deterioration in quality, level, or standard of performance of a functional unit. 2. In communications, a condition in which one or more of the required performance parameters fall outside predetermined limits, resulting in a lower quality of service. Note: Degradation is usually categorized as either "graceful" or "catastrophic."
Degree of Coherence - A dimensionless unit, expressed as a ratio, used to indicate the extent of coherence of an electromagnetic wave such as a lightwave. Note 1: For lightwaves, the magnitude of the degree of coherence is equal to the visibility, V, of the fringes of a two-beam interference test, as given by
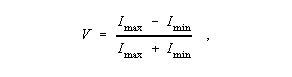
where I max is the intensity at a maximum of the interference pattern, and I min is the intensity at a minimum. Note 2: Light is considered to be highly coherent when the degree of coherence exceeds 0.88, partially coherent for values less than 0.88 but more than nearly zero values, and incoherent for nearly zero and zero values.
Delay - 1. The amount of time by which an event is retarded. 2. The time between the instant at which a given event occurs and the instant at which a related aspect of that event occurs. Note 1: The events, relationships, and aspects of the entity being delayed must be precisely specified. Note 2: Total delay may be demonstrated by the impulse response of a device or system. Note 3: In analog systems, total delay is described in terms of the transfer functions in the frequency domain. Synonym delay time. 3. In radar, the electronic delay of the start of the time base used to select a particular segment of the total.
Delay Time: Synonym delay.
Delivered Block - A successfully transferred block.
Demon - A procedure that is invoked without being called explicitly whenever an alteration, an addition, or a deletion or other event occurs. Pronounced dee' mun. Also spelled daemon.
Demarc (an abbreviation for demarcation point) - Marks the point where communications facilities owned by one organization interface with that of another organization. In telephone terminology, this is the interface between customer-premises equipment and network service provider equipment.
Demultiplexing - The separation of two or more channels previously multiplexed; i.e., the reverse of multiplexing.
Denial of Service - 1. The prevention of authorized access to resources or the delaying of time-critical operations. 2. The result of any action or series of actions that prevents any part of an information system (IS) from functioning.
Density - 1. In a facsimile system, a measure of the light transmission or reflection properties of an area of an object. Note 1: Density is usually expressed as the logarithm to the base 10 of the ratio of incident to transmitted or reflected irradiance. Note 2: There are many types of density, such as diffuse, double diffuse, and specular density, each of which will usually have different numerical values for different materials. The relevant type of density depends on the type of optical system, the component materials of the object, and the surface characteristics of the object. 2. In video, the degree of darkness of an image, or the percent of the screen used in an image. 3. In optics, a figure of merit that describes the degree of attenuation introduced by a filter.
Departure Angle - The angle between the axis of the main lobe of an antenna pattern and the horizontal plane at the transmitting antenna. Synonym takeoff angle.
De-Stuffing - The controlled deletion of stuffing bits from a stuffed digital signal, to recover the original signal. Synonyms negative justification, negative pulse stuffing.
Destination User - In an information transfer transaction, the user that receives information from the source, i.e., from the originating user.
Detection - 1. The recovery of information from an electrical or electromagnetic signal. Note: Conventional radio waves are usually detected by heterodyning, i.e., coherent reception/detection. In this method of reception/detection, the received signal is mixed, in some type of nonlinear device, with a signal from a local oscillator, to produce an intermediate frequency, i.e., beat frequency, from which the modulating signal is recovered, i.e., detected. The inherent instabilities of available optical sources have, until relatively recently, prevented practical use of coherent reception/detection in optical communication receivers. At present, coherent optical receivers, using sophisticated technology, are just beginning to emerge from the laboratory into the field. Virtually all existing optical receivers employ direct detection; that is, the received optical signal impinges directly onto a detector. Direct detection is less sensitive than coherent detection. 2. In tactical operations, the perception of an object of possible military interest but unconfirmed by recognition. 3. In surveillance, the determination and transmission by a surveillance system that an event has occurred.
Detector - 1. A device that is responsive to the presence or absence of a stimulus. 2. In an AM radio receiver, a circuit or device that recovers the signal of interest from the modulated wave. Note: In FM reception, a circuit called a discriminator is used to convert frequency variations to amplitude variations. 3. In an optical communications receiver, a device that converts the received optical signal to another form. Note: Currently, this conversion is from optical to electrical power; however, optical-to-optical techniques are under development.
Device Driver - Software that interfaces a computer with a specific peripheral device, e.g. a videodisk player or a printer.
Dial Pulse - A dc pulse produced by an end instrument that interrupts a steady current at a sequence and rate determined by the selected digit and the operating characteristics of the instrument.
Dial-Pulse Signaling - A method of transmitting a telephone address over a direct-current path. The dc current is interrupted at the transmitting end in a defined pattern representing a particular digit in a telephone number. The number of interruptions in the dc current specifies the address digit.
Dielectric - 1. A substance in which an electric field may be maintained with zero or near-zero power dissipation, i.e., the electrical conductivity is zero or near zero. Note 1: A dielectric material is an electrical insulator. Note 2: In a dielectric, electrons are bound to atoms and molecules, hence there are few free electrons. 2. Pertaining to a substance that has a zero or near zero electrical conductivity.
Digest - 1. In e-mail, a periodic mailing of a collection of messages compiled from a mailing list or interest group. 2. A command issued to a list server or to a list processor requesting that postings be delivered to a subscriber in summary form.
Digit - A symbol, numeral, or graphic character that represents an integer. Note 1: Examples of digits include any one of the decimal characters "0" through "9" and either of the binary characters "0" or "1." Note 2: In a given numeration system, the number of allowable different digits, including zero, is always equal to the base (radix).
Digital - 1. An advanced type of radio transmission that broadcasts voice or data intact via radio waves, which allows for greater call clarity, advanced wireless features and improved voice capacity. The industry uses three types of digital technology: TDMA, CDMA and GSM.
Digital describes electronic technology that generates, stores, and processes data in terms of two states: positive and non-positive. Positive is expressed or represented by the number 1 and non-positive by the number 0. Thus, data transmitted or stored with digital technology is expressed as a string of 0's and 1's. Each of these state digits is referred to as a bit (and a string of bits that a computer can address individually as a group is a byte).
Prior to digital technology, electronic transmission was limited to analog technology, which conveys data as electronic signals of varying frequency or amplitude that are added to carrier waves of a given frequency. Broadcast and phone transmission has conventionally used analog technology.
Digital technology is primarily used with new physical communications media, such as satellite and fiber optic transmission. A modem is used to convert the digital information in your computer to analog signals for your phone line and to convert analog phone signals to digital information for your computer.
2. Describes a new, more efficient method of storing, processing and transmitting information through the use of computer code. Digital can also refer to the circuitry in which data-carrying signals are restricted to one of two voltage levels, corresponding to logic 1 or 0.
Digital Cable - A service provided by many cable providers, digital cable offers viewers more channels. Contrary to what many consumers believe, digital cable is not the same thing as HDTV or DTV; rather, digital cable simply offers cable subscribers the option of paying for more services.
Digital Channel (Pre-Transition) - A communications path that handles only digital signals. All voice and video signals have to be converted from analog to digital in order to be carried over a digital channel. In regard to the DTV Transition, this is the digital channel number used before the transition was completed.
Digital Channel (Post -Transition) - A communications path that handles only digital signals. All voice and video signals have to be converted from analog to digital in order to be carried over a digital channel. In regard to the DTV Transition, this is the corresponding digital channel number used after the channel has transitioned.
Digital Data - 1. Data represented by discrete values or conditions, as opposed to analog data. 2. Discrete representations of quantized values of variables, e.g., the representation of numbers by digits, perhaps with special characters and the "space" character.
Digital Loop Carrier (DLC) - Equipment that bundles a number of individual phone line signals into a single multiplexed digital signal for local traffic between a telephone company central office and a business complex or other outlying service area. Typically, up to 24 analog voice calls are combined into a single signal and transmitted over a single copper T-carrier system or
E-carrier line, an optical fiber cable, or a wireless connection. In a home, business, or other installation using digital loop carrier, the analog phone lines of individual users are connected to a local DLC box which then converts the analog signals into digital and combines (multiplexes) them into one signal that it sent to the phone company's central office on the single line. At the central office, the combined signal is separated back into the original signals. An estimated 20% of today's telephone users are being served by digital loop carriers.Digital loop carrier can carry traffic for regular phone calls (plain old telephone service) and Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) service. More recently, approaches have been developed for using DLC to handle the higher bandwidth of Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) service.
Digital loop carrier is typically used as an efficient way to provide service to an office building or complex and to extend service to new areas outside the current local loop. DLC is also used to set up telephone service in emergency situations. Customers can easily migrate from a T-1 or E-1 line to fiber optic when it becomes needed and is available.
Digital Monitor - Digital monitors are TV sets that can display a digital signal, but lack an integrated tuner (unlike an integrated digital TV set), and thus cannot receive a digital broadcast signal without an additional set-top box.
Digital Signal (DS) - 1. A signal in which discrete steps are used to represent information. Note 1: In a digital signal, the discrete steps may be further characterized by signal elements, such as significant conditions, significant instants, and transitions. Note 2: Digital signals contain m-ary significant conditions. 2. A signal that takes on only two values — off or on — typically represented by "0" or "1." Digital signals require less power but typically more bandwidth than analog, and copies of digital signals can be made exactly like the original.
Digital Signal Processors - All digital audio systems use DSP technology in order to differentiate between signal and noise. In telephone communication, too, much noise creates problems in maintaining connections, and in VoIP systems the DSP component provides features such as tone generation, echo cancellation, and buffering
Digital Speech Interpolation (DSI) - 1. In digital speech transmission, the use of periods of inactivity or constant signal level to increase the transmission efficiency by insertion of additional signals. 2. A process that takes advantage of inactive periods of a conversation to insert speech from other conversations and to remove silent periods.
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) – A DSL line transmits simultaneous voice and high-speed data over existing copper telephone wires without the need of additional phone lines. DSL provides an Internet connection over regular telephone lines, but much faster. Speed may vary from 128 kilobit per second, up to 9 megabit per second. A Digital Subscriber Line is a popular alternative to Leased Lines and ISDN, being faster than ISDN and less costly than traditional Leased Lines. Digital Subscriber Line or Digital Subscriber Loop is often referred to as xDSL. DSL is an always-on connection to the Internet that allows for simultaneous PC and telephone use.
Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer - (see DSLAM)
Digital -to-Analog Converter Box - Also referred to as a "converter box" or a "digital converter box," this is a stand-alone device that receives, decodes, and converts over-the-air digital programming into analog. When connected to an analog television, it permits digital programming to be displayed in analog.
Digital -to-Analog Converter Coupon Program - To help defray some of the cost for consumers who are transitioning to DTV, the Government established the Digital-to-Analog Converter Box Coupon Program. The NTIA, a part of the Department of Commerce, administers this program.
Digital Transmission System - A transmission system in which (a) all circuits carry digital signals and (b) the signals are combined into one or more serial bit streams that include all framing and supervisory signals. Note: A-D / D-A conversion, if required, is accomplished external to the system.
Digital Tuner - A digital tuner serves as the decoder required to receive and display digital broadcasts. It can be included inside a TV set or in a set-top box.
Dialup Service - A connection that allows you to access the Internet by dialing into a computer through a modem and telephone line.
Direct Detection - See detection. The recovery of information from an electrical or electromagnetic signal. Note: Conventional radio waves are usually detected by heterodyning, i.e., coherent reception/detection. In this method of reception/detection, the received signal is mixed, in some type of nonlinear device, with a signal from a local oscillator, to produce an intermediate frequency, i.e., beat frequency, from which the modulating signal is recovered, i.e., detected. The inherent instabilities of available optical sources have, until relatively recently, prevented practical use of coherent reception/detection in optical communication receivers. At present, coherent optical receivers, using sophisticated technology, are just beginning to emerge from the laboratory into the field. Virtually all existing optical receivers employ direct detection; that is, the received optical signal impinges directly onto a detector. Direct detection is less sensitive than coherent detection.
Direct Inward Dialing (DID) - A service of a local phone company (or local exchange carrier) that provides a block of telephone numbers for calling into a company's private branch exchange (PBX) system. Using DID, a company can offer its customers individual phone numbers for each person or workstation within the company without requiring a physical line into the PBX for each possible connection.
For example, a company might rent 100 phone numbers from the phone company that could be called over eight physical telephone lines (these are called "trunk lines"). This would allow up to eight ongoing calls at a time; additional inbound calls would get a busy signal until one of the calls completed or be able to leave a voice mail message. The PBX automatically switches a call for a given phone number to the appropriate workstation in the company. A PBX switchboard operator is not involved.
A DID system can be used for fax and voice mail as well as for live voice connections. Compared to regular PBX service, DID saves the cost of a switchboard operator, calls go through faster, and callers feel they are calling a person rather than a company.
Direct Orbit - For a satellite orbiting the Earth, an orbit in which the projection of the satellite on the equatorial plane revolves about the Earth in the same direction as the rotation of the Earth.
Directory - While there is no single source or official Internet directory, there are several search vehicles available to research or access information on the WWW. Directories categorize and list information in specific headings or categories.Directory Access Protocol (DAP) - A directory protocol that defines the exchange of requests and outcomes between user and system.
Directory number - A network (sub) address (from a telephone user perspective) such as the telephone number in the telecommunication network. For the purpose of this configuration management model, the directory number is described in a managed object that contains references to other objects or attributes related to the services of subscribers. For service providers, the directory number is the key element used to manage subscriber services.
Direct Outward Dialing (DOD) - A service of a local phone company (or local exchange carrier) that allows subscribers within a company's private branch exchange (PBX) system to connect to outside lines directly. Using DOD, a company can offer each person or workstation within the company the ability to dial numbers direct, without the need to go through an operator or dial other numbers first. DOD is often used together with Direct Inward Dialing (DID).
When DOD is used in a company with 100 workstations, for example, eight physical telephone lines (called
trunk line s) might be rented from the telephone copmany. This would allow up to eight ongoing calls at a time; additional outbound call attempts would produce a busy signal until one of the calls completed. A DOD system can be used for fax, dial-up Internet, and voice mail, as well as for live voice connections. Compared to regular PBX service, DOD saves the cost of a switchboard operator, and calls go through faster.Directional Coupler - A transmission coupling device for separately sampling (through a known coupling loss) either the forward (incident) or the backward (reflected) wave in a transmission line. Note: A directional coupler may be used to sample either a forward or backward wave in a transmission line. A unidirectional coupler has available terminals or connections for sampling only one direction of transmission; a bidirectional coupler has available terminals for sampling both directions. Synonyms splitter, T-coupler, tee coupler.
Disclosure - A violation of computer security whereby data have been made available to unauthorized entities.
Discone Antenna - See biconical antenna.
Disconnect - In telephony, the disassociation or release of a switched circuit between two stations.
Discriminator - The part of an FM receiver that extracts the desired signal from an incoming FM wave by changing frequency variations into amplitude variations.
Disengagement Attempt - An attempt to terminate a telecommunications system access. Note: Disengagement attempts may be initiated by a user or the telecommunications system.
Disengagement Originator - The user or functional unit that initiates a disengagement attempt. Note 1: A disengagement originator may be the originating user, the destination user, or the communications system. Note 2: The communications system may deliberately originate the disengagement because of preemption or inadvertently because of system malfunction.
Disengagement Request - A control or overhead signal issued by a disengagement originator for the purpose of initiating a disengagement attempt.
Disk and Execution Monitor (daemon) - See daemon. A procedure that is invoked without being called explicitly whenever an alteration, an addition, or a deletion or other event occurs. Pronounced dee' mun. Also spelled demon.
Diskette - In computer technology, a small disk of flexible plastic, coated with a magnetizable material and enclosed in a protective jacket, used to store digital data. Note: A diskette is distinguished from a hard disk by virtue of the fact that it is flexible, and unlike most hard disks, is removable from its drive. Synonyms flexible disk, floppy disk.
Dispersion - Any phenomenon in which the velocity of propagation of an electromagnetic wave is wavelength dependent. Note 1: In communication technology, "dispersion" is used to describe any process by which an electromagnetic signal propagating in a physical medium is degraded because the various wave components (i.e., frequencies) of the signal have different propagation velocities within the physical medium. Note 2: In an optical fiber, there are several significant dispersion effects, such as material dispersion, profile dispersion, and waveguide dispersion, that degrade the signal. Note 3: In optical fiber communications, the incorrect terms " multimode dispersion " and " intermodal dispersion " should not be used as synonyms for the correct term " multimode distortion." Note 4: In classical optics, "dispersion" is used to denote the wavelength dependence of refractive index in matter, (dn/d
, where n is the refractive index and
is the wavelength) caused by interaction between the matter and light. "Dispersion," as used in fiber optic communications, should not be confused with "dispersion" as used by optical lens designers. Note 5: Three types of dispersion, relating to optical fibers, are defined as follows:
- material dispersion: In optical fiber communication, the wavelength dependence of the velocity of propagation (of the optical signal) on the bulk material of which the fiber is made. Note 1: Because every optical signal has a finite spectral width, material dispersion results in spreading of the signal. Note 2: Use of the redundant term " chromatic dispersion " is discouraged. Note 3: In pure silica, the basic material from which the most common telecommunication-grade fibers are made, material dispersion is minimum at wavelengths in the vicinity of 1.27
m (slightly longer in practical fibers).
- profile dispersion: In an optical fiber, that dispersion attributable to the variation of refractive index contrast with wavelength. Profile dispersion is a function of the profile dispersion parameter.
- waveguide dispersion: Dispersion, of importance only in single-mode fibers, caused by the dependence of the phase and group velocities on core radius, numerical aperture, and wavelength. Note 1: For circular waveguides, the dependence is on the ratio, a /
, where a is the core radius and
is the wavelength. Note 2: Practical single-mode fibers are designed so that material dispersion and waveguide dispersion cancel one another at the wavelength of interest.
Display Device - An output unit that gives a visual representation of data.
Distinctive Ring - An inexpensive service that lets businesses and homes to have two or three different phone numbers on one phone line. What distinguishes the different telephone numbers coming in on the same line is their signature ring, a pattern of long and/or short rings. Each number has its own special ring.
Most telephone companies throughout the US and Canada offer distinctive ring. These "Distinctive Ring" services go by different names depending on your phone company -custom Ringing by US West, SmartRing by GTE, RingMaster by Bell South, RingMate by NYNEX, Personalized Ringing by Southwestern Bell and SBC, Multi-Ring by Ameritech, Distinctive Ring by ATT and SBC and IdentaRing by Bell Atlantic.
Note: Without distinctive ringing, all the instruments on the party line will ring at the same time, selection being made by the number of rings. Two popular Distinctive Ring Devices are the SR-Series Call Processors and The Line Hunter. For deteailed info see Distinctive Ring Definition and Use.
Distinctive Ring Device - A device that tests a phone line for a distinctive ring signal and routes the call to a specific device (example: phone, phone system, answering machine, fax machine. fax modem). For more info see Fax Switch. For more info see Distinctive Ring Definition and Use.
Distinctive Ring Service - Provides a distinctive ringing pattern for up to six different telephone numbers on a screening list. The telephone numbers on the screening list may be changed or reprogrammed at any time. See Distinctive Ring. For more info see Distinctive Ring Definition and Use.
Distortion - 1. In a system or device, any departure of the output signal waveform from that which should result from the input signal waveform's being operated on by the system's specified, i.e., ideal, transfer function. Note: Distortion may result from many mechanisms. Examples include nonlinearities in the transfer function of an active device, such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or operational amplifier. Distortion may also be caused by a passive component such as a coaxial cable or optical fiber, or by inhomogeneities, reflections, etc., in the propagation path. 2. In start-stop teletypewriter signaling, the shifting of the significant instants of the signal pulses from their proper positions relative to the beginning of the start pulse. Note: The magnitude of the distortion is expressed in percent of an ideal unit pulse length.
Distributed-Queue Dual-Bus (DQDB) [network] - A distributed multi-access network that (a) supports integrated communications using a dual bus and distributed queuing, (b) provides access to local or metropolitan area networks, and (c) supports connectionless data transfer, connection-oriented data transfer, and isochronous communications, such as voice communications.
Distribution Frame - In communications, a structure with terminations for connecting the permanent wiring of a facility in such a manner that interconnection by cross-connections may readily be made.
Distribution List Server - Synonym list server. - A functional unit (hardware and software) for operating a computer conferencing system by acting as a repository for electronic messages and redistributing those messages automatically or on-demand.
Diversity Combiner - A circuit or device for combining two or more signals carrying the same information received via separate paths or channels with the objective of providing a single resultant signal that is superior in quality to any of the contributing signals.
Divestiture - The court-ordered separation of the Bell Operating Telephone Companies from AT&T.
DMA - Designated Market Area. A term used by Nielsen Media Research to identify an exclusive geographic area of counties in which the home market television stations hold a dominance of total hours viewed. There are 210 DMA in the U.S.
DNS - See Domain Name System
DOD - Abbreviation for Department of Defense, direct outward dialing.
Dolby® Digital - A form of multi-channel digital sound, it provides efficient encoding and noise reduction for high-quality surround sound — technology used in movie theaters and upscale home theater systems that enhances audio. Home theater components with this technology work in conjunction with a "5.1-speaker" system (five speakers plus a low-frequency subwoofer) to produce true-to-life audio that draws the listener into the onscreen action.
Domain - 1. The independent variable used to express a function. Note: Examples of domains are time, frequency, and space. 2. In distributed networks, all the hardware and software under the control of a specified set of one or more host processors. [From Weik '89] 3. [A] unique context (e.g., access control parameters) in which a program is operating; in effect, the set of objects a subject has the privilege to access.
Domain Name - A unique name that identifies an Internet site; the Domain Name will always have at least two parts separated by dots (for example: tds.net or tdsnet.com). These names are granted and controlled by a centralized Internet Network Information Center (InterNIC), administered by the National Science Foundation.
Domain Name System (DNS) - A system by which one Internet host can find another. DNS translates words (Domain Names) into numbers that Internet computers can understand.Double Refraction - Synonym birefringence. - In a transparent material, anisotropism of the refractive index, which varies as a function of polarization as well as orientation with respect to the incident ray. Note 1: The term "birefringence" means, literally, " double refraction." Note 2: All crystals except those of cubic lattice structure exhibit some degree of anisotropy with regard to their physical properties, including refractive index. Other materials, such as glasses or plastics, become birefringent when subjected to mechanical strain. Note 3: Birefringent materials, including crystals, have the ability to refract an unpolarized incident ray into two separate, orthogonally polarized rays, which in the general case take different paths, depending on orientation of the material with respect to the incident ray. The refracted rays are referred to as the "ordinary," or "O" ray, which obeys Snell's Law, and the "extraordinary," or "E" ray, which does not.
Downconvert - A process by which a high-resolution signal is reduced to a lower resolution for display. Usually, extra lines are simply ignored when drawing the lower resolution image; however, more sophisticated methods are sometimes used.
Download - To transfer of a file or information from another computer to yours.Downstream - 1. In communications, the direction of transmission flow from the source toward the sink. 2. With respect to the flow of data in a communications path: at a specified point, the direction toward which data are received later than at the specified point.
DQDB - Abbreviation for distributed-queue dual-bus. - A distributed multi-access network that (a) supports integrated communications using a dual bus and distributed queuing, (b) provides access to local or metropolitan area networks, and (c) supports connectionless data transfer, connection-oriented data transfer, and isochronous communications, such as voice communications.
Drift - A comparatively long-term change in an attribute or value of a system or equipment operational parameter. Note 1: The drift should be characterized, such as "diurnal frequency drift" and "output level drift." Note 2: Drift is usually undesirable and unidirectional, but may be bidirectional, cyclic, or of such long-term duration and low excursion rate as to be negligible.
Driver - See device driver. - Software that interfaces a computer with a specific peripheral device, e.g. a videodisk player or a printer.
Droid - 1. In the Internet, an intelligent search tool that automatically seeks out relevant online information based on the user's specifications. Synonyms agent, bot, crawler, hotbot, infobot, information agent, intelligent agent, Internet search engine, knowbot, knowledge robot, personal agent, robotic librarian, search robot, spider, Web crawler, Web spider, wizard. 2. In artificial intelligence, an entity with the ability to sense its environment and to act in such a way or to affect that environment; typically knowledge-based entities that can communicate with each other through some message-passing scheme.
DSL - Stands for Digital Subscriber Line, a recently developed (late 1990s) digital communications technology that can provide high-speed transmissions over standard copper telephone wiring. It uses a twisted-pair copper wire connection with a special modem at either end that filters out background noise and interference and allows high-speed data transfer. It is limited to a transmission distance of 18 000 feet. DSL offers speeds in excess of dial-up. Speed may vary from 128 kilobit per second, up to 9 megabit per second.. DSL is a broadband technology that enables high-speed Internet access to a home or business. DSL is an always-on connection to the Internet that allows for simultaneous PC and telephone use. This is a method of transmitting data over telephone lines prevalent in the United States. The UK uses a variant called ADSL for providing broadband to users.
DSLAM (Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer) - A network device, usually at a telephone company central office, that receives signals from multiple customer Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) connections and puts the signals on a high-speed backbone line using multiplexing techniques. Depending on the product, DSLAM multiplexers connect DSL lines with some combination of asynchronous transfer mode (ATM), frame relay, or Internet Protocol networks. DSLAM enables a phone company to offer business or homes users the fastest phone line technology (DSL) with the fastest backbone network technology (ATM).
DSP (Digital Signal Processors) - All digital audio systems use DSP technology in order to differentiate between signal and noise. In telephone communication, too, much noise creates problems in maintaining connections, and in VoIP systems the DSP component provides features such as tone generation, echo cancellation, and buffering
DSR - Abbreviation for data signaling rate.
DTMF (DUAL TONE , MULTIFREQUENCY) - This tone is commonly called "touch-tone". Not all push-button phones are capable of producing the DTMF tones. Abbreviation for Dual Tone Multi Frequency
DTTV (digital terrestrial television, sometimes also abbreviated DTT) - Digital television (DTV) broadcast entirely over earthbound circuits. A satellite is not used for any part of the link between the broadcaster and the end user.
DTTV signals are broadcast over essentially the same media as the older analog terrestrial TV signals. The most common circuits use coaxial cable at the subscriber end to connect the network to the TV receiver. fiber optic and/or microwave links may be used between the studio and the broadcast station, or between the broadcast station and local community networks.
DTTV provides a clearer picture and superior sound quality when compared to analog TV, with less interference. DTTV offers far more channels, thus providing the viewer with a greater variety of programs to choose from. DTTV can be viewed on personal computers. Using a split-screen format, a computer user can surf the Web while watching TV.
In regions not served by cable, DTTV is generally impractical. For this reason, digital satellite TV (
DSTV ) has become popular, especially in rural areas and in some small towns. A few city dwellers prefer DSTV even when they have the option of subscribing to DTTV.DTV - Digital Television. An advanced broadcasting technology that uses radio frequency (RF) to transmit computer code and display it as pictures and sound. DTV is the umbrella term encompassing HDTV and several other applications, including SDTV, datacasting, multicasting and interactivity.
Dual Bus - A pair of parallel buses arranged such that the direction of data flow in one bus is opposite to the direction of data flow in the other bus.
Dual Seizure - The condition that occurs when, in both-way operation, two exchanges attempt to seize the same circuit at approximately the same time. Synonyms call collision, glare [deprecated].
Dual Tone Multifrequency (DTMF)- This tone is commonly called "touch-tone". Not all push-button phones are capable of producing the DTMF tones.
Duct - 1. In interfacility cabling, a conduit, which may be direct-earth buried or encased in concrete, used to enclose communications or power cables. Note: For maximum resistance to rodent attack, direct-earth-buried conduit should have an outside diameter equal to or greater than 6 cm (2.25 in.). 2. See atmospheric duct.
Ducting - The propagation of radio waves within an atmospheric duct.
Duplex Communication - means that both ends of the communication can send and receive signals at the same time. full-duplex communication is the same thing. half-duplex is also bidirectional communication but signals can only flow in one direction at a time. Simplex communication means that communication can only flow in one direction and never flow back the other way.
An ordinary telephone conversation is a duplex communication. Most inexpensive speakerphones in conference rooms are half-duplex communication. (If you're speaking, you can't hear anyone else interrupt. You have to pause to let others speak.)
DVI - Digital Video Interface. A high-quality digital connector. Similar to HDMI and sometimes with HDCP, DVI can digitally transmit uncompressed, high-definition video, preserving perfect picture quality. Unlike HDMI or Firewire, DVI requires a separate audio connection.
DVR - Digital Video Recorder. A device that records video in a digital format to a disk drive or other memory medium within a device. The term includes stand-alone set-top boxes, Portable Media Players (PMP) and software for personal computers, which enables video capture and playback to and from disk.
Dynamic Range - 1. In a system or device, the ratio of (a) a specified maximum level of a parameter, such as power, current, voltage, or frequency to (b) the minimum detectable value of that parameter. Note: The dynamic range is usually expressed in dB. 2. In a transmission system, the ratio of (a) the overload level, i.e., the maximum signal power that the system can tolerate without distortion of the signal, to (b) the noise level of the system. Note: The dynamic range of transmission systems is usually expressed in dB. 3. In digital systems or devices, the ratio of maximum and minimum signal levels required to maintain a specified bit error ratio.
Fax Switch Products
|
*Note: All prices include shipping and handling in the continental US and most of Canada. We reserve the right to charge up to the actual price of shipping on all orders outside the continental United States. Customer is responsible for any taxes, duties or brokerage charges that may apply. All orders shipped UPS Ground unless specified. For air and express shipments, appropriate charges will be applied to your order.
Need Help?
- Call now for free phone consultation at 1-866-337-0965.
Click here if you want to share 2 devices on 1 line and don't know which device to choose.
Click here if you want to share 3 or more devices on one line and don't know what type to choose.
"Albert Einstein Presents Fax Switch "
"Dancing Bear Fax Switch Presentation"
![]()
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Can't find your phone equipment here?
Please visit our sister company, SuperPhoneStore.com for wholesale to the public telephones, phone accessories or the latest electronics. We have over 4500 different products in stock.