
Telecom Dictionary - Definitions of terms
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
M
MAC - Abbreviation for medium access control.
MAC Abbreviation for Message Authentication Code - 1. A bit string that is a function of both data (either plaintext or ciphertext) and a secret key, and that is attached to the data in order to allow data authentication. Note: The function used to generate the message authentication code must be a one-way function. 2. Data associated with an authenticated message allowing a receiver to verify the integrity of the message.
Machine-Independent - In telecommunications, computer, and data processing systems, pertaining to operations, procedures, computer programs, and processing that do not depend upon specific hardware for their successful execution.
Machine Instruction - An instruction that is written in a machine language and can be executed directly by the processor for which it was designed without translation or interpretation.
Machine Learning - The ability of a device to improve its performance based on its past performance.
Machine Language - A language that need not be modified, translated, or interpreted before it can be used by the processor for which it was designed. Note 1: The operation codes and addresses used in instructions written in machine language can be directly sensed by the arithmetic and control unit circuits of the processor for which the language is designed. Note 2: Instructions written in an assembly language or a high-level language must be translated into machine language before they can be executed by a processor. Note 3: Machine languages are usually used by computer designers rather than computer users.
Machine-Oriented Language - Synonym computer-oriented language. - A programming language in which words and syntax are designed for use on a specific computer or class of computers.
Machine-Readable Medium - A medium capable of storing data in a form that can be accessed by an automated sensing device. Note: Examples of machine-readable media include (a) magnetic disks, cards, tapes, and drums, (b) punched cards and paper tapes, (c) optical disks, and (d) magnetic ink characters. Synonym automated data medium.
Machine Word - Synonym computer word. - In computing, a group of bits or characters that occupies one or more storage locations and is treated by computers as a unit.
Macrobend - A relatively large-radius bend in an optical fiber, such as might be found in a splice organizer tray or a fiber-optic cable that has been bent. Note: A macrobend will result in no significant radiation loss if it is of sufficiently large radius. The definition of "sufficiently large" depends on the type of fiber. Single-mode fibers have a low numerical aperture, typically less than 0.15, and are therefore are more susceptible to bend losses than other types. Normally, they will not tolerate a minimum bend radius of less than 6.5 to 7.5 cm (2.5 to 3 inches). Certain specialized types of single-mode fibers, however, can tolerate a far shorter minimum bend radius without appreciable loss. A graded-index multimode fiber having a core diameter of 50
m and a numerical aperture of 0.20 will typically tolerate a minimum bend radius of not less than 3.8 cm (1.5 inches). The fibers commonly used in customer-premises applications (62.5-
m core) typically have a relatively high numerical aperture, (approximately 0.27), and can tolerate a bend radius of less than an inch (2.5 cm).
Macrobend Loss - In an optical fiber, that loss attributable to macrobending. Synonym curvature loss.
Magic Cookie - Synonym cookie. -1. A small piece of information that is automatically stored on a client computer by a Web browser and referenced to identify repeat visitors to a Web site and to tailor information in anticipation of the visitor's interests. Note: Some privacy advocates have objected to the use of cookies without a user's consent. 2. A general mechanism that server side connections (such as CGI scripts) can use both to store and to retrieve information on the client side of the connection. Note 1: A server, when returning an HTTP object to a client, may also send a piece of state information that the client will store. Included in that state object is a description of the range of URLs for which that state is valid. Any future HTTP requests made by the client that fall in that range will include a transmittal of the current value of the state object from the client back to the server. The state object is called a cookie. This simple mechanism provides a tool that enables new types of applications to be written for Web-based environments. Shopping applications can now store information about the currently selected items, for-fee services can send back registration information and free the client from retyping a user ID on subsequent connections, sites can store per-user preferences on the client, and have the client supply those preferences every time that site is accessed. Note 2: Session cookies are volatile in that they disappear at the end of a session, whereas persistent cookies are retained from one session to the next.
Magnetic Card - A card with a magnetizable surface on which data can be stored and retrieved.
Magnetic Circuit - 1. The complete closed path taken by magnetic flux. 2. A region of ferromagnetic material, such as the core of a transformer or solenoid, that contains essentially all of the magnetic flux.
Magnetic Core Storage - In computer technology, a storage device that uses ferromagnetic materials such as iron, iron oxide, or ferrite and in such shapes as wires, toroids, and rods.
Magnetic Disk - See diskette, hard disk.
Magnetic Drum - A right circular cylinder with a magnetizable surface on which digital data can be stored and retrieved.
Magnetic Remanence - A magnetic representation of residual information remaining on a magnetic medium after the medium has been cleared.
Magnetic Storm - A perturbation of the Earth's magnetic field, caused by solar disturbances, usually lasting for a brief period (several days) and characterized by large deviations from the usual value of at least one component of the field. Note: Magnetic storms can affect radio propagation because they disturb the ionosphere.
Magnetic Tape - 1. A tape with a magnetizable surface on which data can be stored and retrieved. 2. A tape or ribbon of any material impregnated or coated with magnetic or other material on which information may be placed in the form of magnetically polarized spots.
Magneto-Ionic Double Refraction - The combined effect of the Earth's magnetic field and atmospheric ionization, whereby a linearly polarized wave entering the ionosphere is split into two components called the ordinary wave and the extraordinary wave. Note: The component waves follow different paths, experience different attenuations, have different phase velocities, and, in general, are elliptically polarized in opposite senses.
Magneto-Optic - See magneto-optic effect.
Magneto-Optic Effect - Any one of a number of phenomena in which an electromagnetic wave interacts with a magnetic field, or with matter under the influence of a magnetic field. Note: The most important magneto-optic effect having application to optical communication is the Faraday effect, in which the plane of polarization is rotated under the influence of a magnetic field parallel to the direction of propagation. This effect may be used to modulate a lightwave.
Mail Bombing - Synonym spamming. See flooding, spam. - Slang 1. Unwanted or unsolicited e-mail messages or mailing-list or newsgroup postings. 2. To send an advertisement or solicitation to large numbers of unsolicited recipients, usually via mailing lists or newsgroups.
Mailbox-Type Facility - A facility in which a message from an originating user is stored until the destination user requests delivery of that message.
Mail Exchange Record (MX record) - An entry in a domain name system database that directs the routing of mail by mail transfer agents.
Mail Exploder - Part of an e-mail delivery system that allows a message to be automatically and efficiently delivered to a list of addresses, thus implementing mailing lists. Synonym exploder.
Mail Gateway - A computer that connects two or more electronic mail systems (especially dissimilar mail systems on two different networks) and transfers messages between them. Note: The mapping and translation can be quite complex, and can require a store-and-forward scheme whereby the message is received from one system completely before it is transmitted to the next system after suitable translations.
Mailing List - Any one of a number of automated e-mail distribution programs that provide a forum for information exchange for professional, educational, and special interest groups. Note: Subscribers post messages to the list address and messages are then distributed to all subscribers.
Mailing List Server - Synonym list server. - A functional unit (hardware and software) for operating a computer conferencing system by acting as a repository for electronic messages and redistributing those messages automatically or on-demand.
Mail Path - A series of machine names used to direct electronic mail from one user to another.
Mail Reflector - 1. Synonyms e-mail exploder, mail exploder. 2. A program that forwards e-mail to individuals at a (usually) unchanging e-mail address, even when the individuals change Internet service providers.
Mailserver - A computer that provides e-mail management and storage space for messages pertaining to a group of subscribers.
Mail User Agent - The software used to access and manage a user's electronic mail.
Main Beam - Synonym main lobe. - Of an antenna radiation pattern, the lobe containing the maximum power (exhibiting the greatest field strength). Note: The horizontal radiation pattern, i.e., that which is plotted as a function of azimuth about the antenna, is usually specified. The width of the main lobe is usually specified as the angle encompassed between the points where the power has fallen 3 dB below the maximum value. The vertical radiation pattern, i.e., that which is plotted as a function of elevation from a specified azimuth, is also of interest and may be similarly specified.
Main Distribution Frame (MDF) - A distribution frame on one part of which the external trunk cables entering a facility terminate, and on another part of which the internal user subscriber lines and trunk cabling to any intermediate distribution frames terminate. Note 1: The MDF is used to cross-connect any outside line with any desired terminal of the multiple cabling or any other outside line. Note 2: The MDF usually holds central office protective devices and functions as a test point between a line and the office. Note 3: The MDF in a private exchange performs functions similar to those performed by the MDF in a central office. Synonym (in telephony) main frame.
Main Frame - A distribution frame on one part of which the external trunk cables entering a facility terminate, and on another part of which the internal user subscriber lines and trunk cabling to any intermediate distribution frames terminate. Note 1: The MDF is used to cross-connect any outside line with any desired terminal of the multiple cabling or any other outside line. Note 2: The MDF usually holds central office protective devices and functions as a test point between a line and the office. Note 3: The MDF in a private exchange performs functions similar to those performed by the MDF in a central office. Synonym (in telephony) main distribution frame.
Mainframe - A large computer, usually one to which other computers and/or terminals are connected to share its resources and computing power.
Main Lobe - Of an antenna radiation pattern, the lobe containing the maximum power (exhibiting the greatest field strength). Note: The horizontal radiation pattern, i.e., that which is plotted as a function of azimuth about the antenna, is usually specified. The width of the main lobe is usually specified as the angle encompassed between the points where the power has fallen 3 dB below the maximum value. The vertical radiation pattern, i.e., that which is plotted as a function of elevation from a specified azimuth, is also of interest and may be similarly specified. Synonym main beam.
Main Station - A user instrument, e.g., telephone set or terminal, with a distinct call number designation, connected to a local loop, used for originating calls, and on which incoming calls from the exchange are answered.
Main Storage - In a computer, program-addressable storage from which instructions and other data may be loaded directly into registers for subsequent execution or processing. Note 1: Main storage includes the total program-addressable execution space that may include one or more storage devices. Note 2: "Main storage" usually refers to large and intermediate computers, whereas " memory " usually refers to microcomputers, minicomputers, and calculators.
Maintainability - 1. A characteristic of design and installation, expressed as the probability that an item will be retained in or restored to a specified condition within a given period of time, when the maintenance is performed in accordance with prescribed procedures and resources. 2. The ease with which maintenance of a functional unit can be performed in accordance with prescribed requirements.
Maintenance - 1. Any activity, such as tests, measurements, replacements, adjustments and repairs, intended to restore or retain a functional unit in a specified state in which the unit can perform its required functions. 2. [For materiel], All action taken to retain materiel in a serviceable condition or to restore it to serviceability. It includes inspection, testing, servicing, classification as to serviceability, repair, rebuilding, and reclamation. 3. [For materiel], All supply and repair action taken to keep a force in condition to carry out its mission. 4. [For materiel], The routine recurring work required to keep a facility (plant, building, structure, ground facility, utility system, or other real property) in such condition that it may be continuously used, at its original or designed capacity and efficiency for its intended purpose.
Maintenance Control Circuit (MCC) - In a communications link, a circuit used by maintenance personnel for coordination. Note: An MCC is not available to operations or technical control personnel.
Maintenance Hook - 1. A trapdoor in software that allows easy maintenance and development of additional features and that may allow entry into the program at unusual points or without the usual checks. 2. Special instructions (trapdoors) in software allowing easy maintenance and additional feature development. Since maintenance hooks frequently allow entry into the code without the usual checks, they are a serious security risk if they are not removed prior to live implementation.
Maintenance Key - Key intended only for in-shop use.
Major Lobe - See main lobe. - Of an antenna radiation pattern, the lobe containing the maximum power (exhibiting the greatest field strength). Note: The horizontal radiation pattern, i.e., that which is plotted as a function of azimuth about the antenna, is usually specified. The width of the main lobe is usually specified as the angle encompassed between the points where the power has fallen 3 dB below the maximum value. The vertical radiation pattern, i.e., that which is plotted as a function of elevation from a specified azimuth, is also of interest and may be similarly specified.
Major Trading Area (MTA) – An area defined by the U.S. government and used by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to designate personal communications services market areas.
Make Interval - 1. In dial-pulse signaling, that portion of the dial pulse in which the network applies a low resistance between the tip and ring conductors at the network interface (NI). 2. In dial-pulse signaling, that portion of the dial pulse in which the pulsing circuit is in its low-impedance condition.
Malicious Applets - Small application programs automatically downloaded and executed that perform an unauthorized function on an information system.
Malicious Code - Software or firmware capable of performing an unauthorized function on an information system (IS).
Malicious Logic - 1. A program implemented in hardware, firmware, or software, and whose purpose is to perform some unauthorized or harmful action. Note: Examples of malicious logic are a logic bomb, a Trojan horse, a virus, a worm. [2382-pt.8] 2. Hardware, software, or firmware capable of performing an unauthorized function on an information system.
MAN - Acronym for metropolitan area network. - A data communications network that (a) covers an area larger than a campus area network and smaller than a wide area network (WAN), (b) interconnects two or more LANs, and (c) usually covers an entire metropolitan area, such as a large city and its suburbs.
Managed Object - 1. In a network, an abstract representation of network resources that are managed. Note: A managed object may represent a physical entity, a network service, or an abstraction of a resource that exists independently of its use in management. 2. In telecommunications management, a resource within the telecommunications environment that may be managed through the use of operation, administration, maintenance, and provisioning application protocols.
Management Domain - A collection of one or more management systems, and zero or more managed systems and management subdomains, that is administered by a single organization.
Management Information System (MIS) - An organized assembly of resources and procedures required to collect, process, and distribute data for use in decision making.
Management Inhibit - A procedure used in signaling traffic management to keep a signaling link unavailable to user-part-generated signaling traffic except for test and maintenance traffic.
Management System - An application process within a management domain that affects monitoring and control functions on managed objects, management subdomains, or both. A management system may also communicate with its peers (that may be resident in other management domains). Synonym managing system.
Managing System - Synonym management system. - An application process within a management domain that affects monitoring and control functions on managed objects, management subdomains, or both. A management system may also communicate with its peers (that may be resident in other management domains).
Manchester Code - A code in which (a) data and clock signals are combined to form a single self-synchronizing data stream, (b) each encoded bit contains a transition at the midpoint of a bit period, (c) the direction of transition determines whether the bit is a "0" or a "1," and (d) the first half is the true bit value and the second half is the complement of the true bit value.
Mandatory Fixed Part - Part of a message that contains those parameters that are mandatory and of fixed length for a particular message type.
Mandatory Variable Part - Part of a message that contains mandatory parameters of variable length.
Mandrel Wrapping - In multimode fiber optics, a technique used to modify the modal distribution of a propagating optical signal. Note: A cylindrical rod wrap consists of a specified number turns of fiber on a mandrel of specified size, depending on the fiber characteristics and the desired modal distribution. It has application in optical transmission performance tests, to simulate, i.e., establish, equilibrium mode distribution in a launch fiber (a fiber used to inject a test signal in another fiber that is under test). If the launch fiber is fully filled ahead of the mandrel wrap, the higher-order modes will be stripped off, leaving only lower-order modes. If the launch fiber is underfilled, e.g., as a consequence of being energized by a laser diode or edge-emitting LED, there will be a redistribution to higher-order modes until modal equilibrium is reached.
Manipulation Detection - A procedure that is used to detect whether data have been modified either accidentally or intentionally. Synonym modification detection.
Manipulation Detection Code (MDC) - In cryptosystems, a bit string that is a function of data to which it is attached for the purpose of manipulation detection. Note 1: The resulting message (data plus MDC) may then be encrypted to achieve secrecy or data authentication. Note 2: The function used to generate the MDC must be public.
Man-Machine System - A system in which the functions of a human operator and a machine are integrated.
Manual Remote Rekeying - A procedure by which a distant crypto-equipment is rekeyed electrically, with specific actions required by the receiving terminal operator.
MAP Pricing - Minimum Advertised Price (MAP Reicing) is the practice whereby a manufacturer and its distributors agree that the latter’s resellers will advertise the former's product at certain prices, at or above a price floor (minimum advertised price). These rules prevent resellers from competing too fiercely on price, thus driving down profits and lowering the manufacturer’s reputation as a creator of quality made products. A manufacturer may do this because it wishes to keep resellers profitable, and thus keeping the manufacturer profitable. Others contend that minimum advertised price maintenance, for instance, overcomes a failure in the market for distributional services by ensuring that distributors who invest in promoting the manufacturer's product are able to recoup the additional costs of such promotion in the price they charge consumers. Manufacturers also defend retail minimum advertised price by saying it ensures fair returns, both for manufacturer. According to such agreements, retailers can usually sell M.A.P. restricted items for any price they choose, but may not display in any print or online advertising, a price below the Minimum Advertisable Price.
Definition: A suppliers pricing policy that does not permit its resellers to advertise prices below some specified amount. It can include the resellers' retail price as well (Source: retail.about.com)MAP Pricing enhances customer loyalty, product image and profits. Minimum Advertised Price or (MAP) requirements are common in the marketing world. Manufacturers often assign a minimum price point below which a retailer cannot advertise certain products. MAP pricing ensures that their product maintains a certain level of exclusivity and doesn’t become known as a cheap product. A Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) Policy alleviates brand degradation and reinforces the advantages of our products in the areas of quality, design, warranty, and service delivered by Multi-Link, Inc. It will protect stocking dealers from “unfair” online competition and makes sure that everyone makes money.
Margin - 1. In communications systems, the maximum degree of signal distortion that can be tolerated without affecting the restitution, i.e., without its being interpreted incorrectly by the decision circuit. 2. The allowable error rate, deviation from normal, or degradation of the performance of, a system or device.
Marine Broadcast Station - A coast station which makes scheduled broadcasts of time, meteorological, and hydrographic information.
Marine Utility Station - A station in the maritime mobile service consisting of one or more hand-held radiotelephone units licensed under a single authorization. Each unit is capable of operation while being hand-carried by an individual.
Maritime Air Communications - Communications systems, procedures, operations, and equipment that are used for message traffic between aircraft stations and ship stations in the maritime service. Note: Commercial, private, naval, and other ships are included in maritime air communications.
Maritime Broadcast Communications Net - A communications net that is used for international distress calling, including international lifeboat, lifecraft, and survival-craft high-frequency (HF); aeronautical emergency very high-frequency (VHF); survival ultra high-frequency (UHF); international calling and safety very high-frequency (VHF); combined scene-of-search-and-rescue; and other similar and related purposes. Note: Basic international distress calling is performed at either medium frequency (MF) or at high frequency (HF).
Maritime Mobile-Satellite Service - A mobile-satellite service in which mobile Earth stations are located on board ships; survival craft stations and emergency position-indicating radiobeacon stations may also participate in this service.
Maritime Mobile Service - A mobile service between coast stations and ship stations, or between ship stations, or between associated on-board communication stations; survival craft stations and emergency position-indicating radiobeacon stations may also participate in this service.
Maritime Radionavigation-Satellite Service - A radionavigation-satellite service in which Earth stations are located on board ships.
Maritime Radionavigation Service - A radionavigation service intended for the benefit and for the safe operation of ships.
Mark - 1. In telegraphy, one of the two significant conditions of encoding. Note 1: The complementary significant condition is called a "space." Note 2: In modern digital communications, the two corresponding significant conditions of encoding are called "1" and "0." Synonyms marking pulse, marking signal. 2. A symbol or symbols that indicate the beginning or the end of a field, of a word, or of a data item in a file, record, or block.
Marker Beacon - A transmitter in the aeronautical radionavigation service which radiates vertically a distinctive pattern for providing position information to aircraft.
Marking Bias - The uniform lengthening of all marking signal pulse widths at the expense of the pulse widths of all spacing pulses.
Marking End Distortion - See end distortion. - The continuation of marking pulses past the proper time.
Marking Pulse - Synonym mark. - 1. In telegraphy, one of the two significant conditions of encoding. Note 1: The complementary significant condition is called a "space." Note 2: In modern digital communications, the two corresponding significant conditions of encoding are called "1" and "0." Synonyms marking signal. 2. A symbol or symbols that indicate the beginning or the end of a field, of a word, or of a data item in a file, record, or block.
Marking Signal - Synonym mark. - 1. In telegraphy, one of the two significant conditions of encoding. Note 1: The complementary significant condition is called a "space." Note 2: In modern digital communications, the two corresponding significant conditions of encoding are called "1" and "0." Synonyms marking pulse. 2. A symbol or symbols that indicate the beginning or the end of a field, of a word, or of a data item in a file, record, or block.
Mark Sequence - A string of mark bits (sent immediately before message transmission starts) to alert the customer installation (CI) to initiate certain actions.
Marquee - 1. In computer display, a line of alphanumeric characters that scrolls through, and within, a defined area (window). 2. An HTML tag that enables the display of a marquee.
Martian - 1. [Slang] Pertaining to packets that are delivered to the wrong network as the result of bogus routing entries. 2. [Slang] A packet that has a completely bogus (nonregistered or ill-formed) Internet address.
m-ary code - See n-ary code.
m-ary signaling - See n-ary code.
MASER - Acronym for microwave amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. A member of the general class of microwave oscillators based on molecular interaction with electromagnetic radiation.
Mask - 1. In communications systems, to obscure, hide, or otherwise prevent information from being derived from a signal. Note 1: Masking is usually the result of interaction with another signal, such as noise, static, jamming, or other forms of interference. Note 2: Masking is not synonymous with erasing or deleting. 2. In computing and data processing systems, a pattern of bits that can be used to retain or suppress segments of another pattern of bits.
Masked Threshold - The level at which an indistinguishable signal of interest becomes distinguishable from other signals or noise. Note: In acoustics, the masked threshold is usually expressed in dB.
Masking - 1. In television and video technology, a process in which color signals are used to modify each other for the purpose of altering their color rendition. Note: The process is often accomplished by suitable cross coupling between primary color-signal channels. 2. One way of partial compensation for photo-receptor cot sensitivity, nonoptimum color filters, nonideal display phosphors, unwanted dye absorption, etc.
Masquerade - The pretense by an entity to be a different entity in order to gain unauthorized access.
Masquerading - A form of spoofing. Unauthorized use of legitimate Identification and Authentication (I&A) data, however it was obtained, to mimic a subject different from the attacker.
Master Clock - A device that generates periodic, accurately spaced signals that are used for such purposes as timing, regulation of the operations of a processor, or generation of interrupts.
Master File (MF) - The unique mandatory file containing access conditions and optionally DFs (dedicated files) and/or EFs (extended frames).
Master Frequency Generator - In frequency-division multiplexing (FDM), equipment used to provide system end-to-end carrier frequency synchronization and frequency accuracy of tones. Note: The following types of oscillators are used in the Defense Communications System FDM systems:
Synonym master oscillator.
- Type 1 - A master carrier oscillator as an integral part of the multiplexer set.
- Type 2 - A submaster oscillator equipment or slave oscillator equipment as an integral part of the multiplexer set.
- Type 3 - An external master oscillator equipment that has extremely accurate and stable characteristics.
Mastergroup - See group.
Master Key - Within a hierarchy of encrypting keys and transaction keys, the highest level of key-encrypting key.
Master Oscillator - In frequency-division multiplexing (FDM), equipment used to provide system end-to-end carrier frequency synchronization and frequency accuracy of tones. Note: The following types of oscillators are used in the Defense Communications System FDM systems:
- Type 1 - A master carrier oscillator as an integral part of the multiplexer set.
- Type 2 - A submaster oscillator equipment or slave oscillator equipment as an integral part of the multiplexer set.
- Type 3 - An external master oscillator equipment that has extremely accurate and stable characteristics.
Synonym master frequency generator.
Master-Slave Timing - Timing in which one station or node supplies the timing reference for all other interconnected stations or nodes.
Master Station - 1. In a data network, the station that is designated by the control station to ensure data transfer to one or more slave stations. Note: A master station controls one or more data links of the data communications network at any given instant. The assignment of master status to a given station is temporary and is controlled by the control station according to the procedures set forth in the operational protocol. Master status is normally conferred upon a station so that it may transmit a message, but a station need not have a message to send to be designated the master station. 2. In navigation systems using precise time dissemination, a station that has the clock used to synchronize the clocks of subordinate stations. 3. In basic mode link control, the data station that has accepted an invitation to ensure a data transfer to one or more slave stations. Note: At a given instant, there can be only one master station on a data link.
Matched Junction - A waveguide component having four or more ports, and so arranged that if all ports except one are terminated in the correct impedance, there will be no reflection of energy from the junction when the fourth port is driven by a transmission line having a matching impedance.
Matching Gel - See gel. Index-matching material in the form of a gel.
Material Absorption - See absorption. - In the transmission of electrical, electromagnetic, or acoustic signals, the conversion of the transmitted energy into another form, usually thermal. Note 1: Absorption is one cause of signal attenuation . Note 2: The conversion takes place as a result of interaction between the incident energy and the material medium, at the molecular or atomic level.
Material Dispersion - See dispersion. In optical fiber communication, the wavelength dependence of the velocity of propagation (of the optical signal) on the bulk material of which the fiber is made. Note 1: Because every optical signal has a finite spectral width, material dispersion results in spreading of the signal. Note 2: Use of the redundant term " chromatic dispersion " is discouraged. Note 3: In pure silica, the basic material from which the most common telecommunication-grade fibers are made, material dispersion is minimum at wavelengths in the vicinity of 1.27
m (slightly longer in practical fibers).
Material Dispersion Coefficient [M (
)]: In an optical fiber, pulse broadening per unit length of fiber and unit spectral width, usually expressed in picoseconds per (nanometer• kilometer). Note 1: For many silica-based fibers, M (
) approaches zero at a specific wavelength
0 between 1.3
m and 1.5
m. At wavelengths shorter than
0, M (
) is negative and increases with wavelength; at wavelengths longer than
0,, M (
) is positive and decreases with wavelength. Note 2: Pulse broadening caused by material dispersion in a unit length of optical fiber is given by the product of M (
) and spectral width (
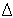
). Note 3: The material dispersion coefficient M(
) is given by
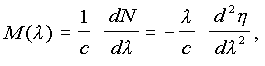
where
is the refractive index of the material, N is the group index expressed as
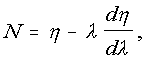
where
is the wavelength of interest, and c is the velocity of light in vacuuo.
Material Scattering - Of an electromagnetic wave, scattering that is attributable to the intrinsic properties of the material through which the wave is propagating. Note 1: Ionospheric scattering and Rayleigh scattering are examples of material scattering. Note 2: In an optical fiber, material scattering is caused by micro-inhomogeneities in the refractive indices of the materials used to fabricate the fiber, including the dopants used to modify the refractive index profile.
Matrixing - The accomplishment of a color coordinate transformation by computational, electrical, optical, or by other means.
Matte - An image or signal that represents or carries only transparent information that is intended to overlay or control another image or signal.
MATV - Master Antenna. Common or master antenna system in apartment buildings, condominiums, high-rises, co-ops or other Multiple Dwelling Units (MDU) through which residents receive local TV stations.
MAU - Abbreviation for medium access unit. - In a communications system, the equipment that adapts or formats the signal for transmittal over the communication medium. Note 1: An example of a MAU is an optical transmitter, which accepts an electrical signal at its input port and converts it to an optical signal accessible at its output port. Note 2: Some prefer to limit the term medium access unit to FDDI usage, with the term media converter being preferred for general usage. Synonym media converter.
Maximal-Ratio Combiner - A diversity combiner in which (a) the signals from each channel are added together, (b) the gain of each channel is made proportional to the rms signal level and inversely proportional to the mean square noise level in that channel, and (c) the same proportionality constant is used for all channels. Synonyms ratio-squared combiner, post-detection combiner, predetection combining, selective combiner.
Maximum Block Transfer Time - The maximum allowable waiting time between initiation of a block transfer attempt and completion of a successful block transfer.
Maximum Calling Area - Geographic calling limits permitted to a particular access line based on requirements for the particular line. Note: Maximum calling area restrictions are imposed for network control purposes.
Maximum Disengagement Time - The maximum allowable waiting time between initiation of a disengagement attempt and successful disengagement.
Maximum Justification Rate - In a bit-stream, the maximum rate at which stuffing bits can be inserted into the stream. Synonym maximum stuffing rate.
Maximum Keying Frequency - In facsimile systems, the frequency in hertz numerically equal to the spot speed divided by twice the X-dimension of the scanning spot.
Maximum Modulating Frequency - In a facsimile transmission system, the highest picture frequency that is required. Note: The maximum modulating frequency and the maximum keying frequency are not necessarily equal.
Maximum Stuffing Rate - In a bit-stream, the maximum rate at which stuffing bits can be inserted into the stream. Synonym maximum justification rate.
Maximum Time Interval Error (MTIE): The maximum error for all possible measurement intervals within the measurement period.
Maximum Usable Frequency (MUF) - In radio transmission using reflection from the regular ionized layers of the ionosphere, the upper frequency limit that can be used for transmission between two points at a specified time. Note: MUF is a median frequency applicable to 50% of the days of a month, as opposed to 90% cited for the lowest usable high frequency (LUF) and the optimum traffic frequency (OFT).
Maximum User Signaling Rate: The maximum rate, in bits per second, at which binary information can be transferred in a given direction between users over the telecommunications system facilities dedicated to a particular information transfer transaction, under conditions of continuous transmission and no overhead information. Note 1: For a single channel, the signaling rate is given by
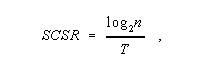
where SCSR is the single-channel signaling rate in bits per second, T is the minimum time interval in seconds for which each level must be maintained, and n is the number of significant conditions of modulation of the channel. Note 2: In the case where an individual end-to-end telecommunications service is provided by parallel channels, the parallel-channel signaling rate is given by
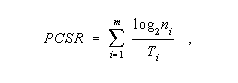
where PCSR is the total signaling rate for m channels, m is the number of parallel channels, Ti is the minimum interval between significant instants for the I-th channel, and ni is the number of significant conditions of modulation for the I-th channel. Note 3: In the case where an end-to-end telecommunications service is provided by tandem channels, the end-to-end signaling rate is the lowest signaling rate among the component channels.
Maxwell's Equations - A set of partial differential equations that describe and predict the behavior of electromagnetic waves in free space, in dielectrics, and at conductor-dielectric boundaries. Note: Maxwell's equations expand upon and unify the laws of Ampere, Faraday, and Gauss, and form the foundation of modern electromagnetic theory.
Mbone - Abbreviation for multicast backbone on the Internet. A part of the Internet designed to support IP multicasting by coordinating the transmission of messages to a single destination instead of allowing packets to travel by different routes.
Mbps - Megabytes per second (MB is also used as an abbreviation for Megabyte).
MCC - Abbreviation for maintenance control circuit. - In a communications link, a circuit used by maintenance personnel for coordination. Note: An MCC is not available to operations or technical control personnel.
MCM - Abbreviation for multicarrier modulation. - A technique of transmitting data by dividing the data into several interleaved bit streams and using these to modulate several carriers. Note: MCM is a form of frequency-division multiplexing.
MDF - Abbreviation for main distribution frame. - A distribution frame on one part of which the external trunk cables entering a facility terminate, and on another part of which the internal user subscriber lines and trunk cabling to any intermediate distribution frames terminate. Note 1: The MDF is used to cross-connect any outside line with any desired terminal of the multiple cabling or any other outside line. Note 2: The MDF usually holds central office protective devices and functions as a test point between a line and the office. Note 3: The MDF in a private exchange performs functions similar to those performed by the MDF in a central office. Synonym (in telephony) main frame.
Meaconing - A system of receiving radio beacon signals and rebroadcasting them on the same frequency to confuse navigation. The meaconing stations cause inaccurate bearings to be obtained by aircraft or ground stations.
Mean Power (of a radio transmitter) - The average power supplied to the antenna transmission line by a transmitter during an interval of time sufficiently long compared with the lowest frequency encountered in the modulation taken under normal operating conditions. Note: Normally, a time of 0.1 second, during which the mean power is greatest, will be selected.
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) - 1. An indicator of expected system reliability calculated on a statistical basis from the known failure rates of various components of the system. Note: MTBF is usually expressed in hours. 2. Of a system, over a long performance measurement period, the measurement period divided by the number of failures that have occurred during the measurement period. 3. For population of items, during a measurement period, the total functioning life of the population of items divided by the total number of failures within the population during the measurement period. Note 1: The total functioning life of the population may be calculated as the summation of the operating life of every item in the population over the measurement period. When computing the MTBF, any measure of operating life may be used, such as time, cycles, kilometers, or events. Note 2: For example, if a total of 1,000 events, such as data transfers, radio transmissions, or system boots, occurs in a population of items during a measurement period of 100 hours and there are a total of 10 failures among the entire population, the MTBF for each item is (1000)(100)/10 = 104 hours.
Mean Time Between Outages (MTBO): In a system, the mean time between equipment failures that result in loss of system continuity or unacceptable degradation. Note: The MTBO is calculated by the equation,
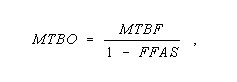
where MTBF is the nonredundant mean time between failures and FFAS is the fraction of failures for which the failed equipment is automatically bypassed.
Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) - The total corrective maintenance time divided by the total number of corrective maintenance actions during a given period of time.
Mean Time to Service Restoral (MTSR) - The mean time to restore service following system failures that result in a service outage. Note: The time to restore includes all time from the occurrence of the failure until the restoral of service.
Measured blocking threshold - A value for measured blocking above which there is a statistically significant probability that the design blocking objective is not being met.
Measured-Rate Service - Telephone service for which charges are made in accordance with the total connection time of the line.
Measurement Period - See performance measurement period. - The period during which performance parameters are measured. Note: A performance measurement period is determined by required confidence limits and may vary as a function of the observed parameter values. User time is divided into consecutive performance measurement periods to enable measurement of user information transfer reliability.
Mechanically Induced Modulation - Optical signal modulation induced by mechanical means. Note: An example of deleterious mechanically induced modulation is speckle noise created in a multimode fiber by an imperfect splice or imperfectly mated connectors. Mechanical disturbance of the fiber ahead of the joint will introduce changes in the modal structure, resulting in variations of joint loss.
Mechanically Intermateable Connectors - Connectors that are mechanically mateable, without creating mechanical damage, and without regard to attenuation properties.
Mechanical Splice - Of optical fibers, a splice, i.e., permanent joint, accomplished by aligning the mating fibers in some kind of mechanical fixture. Note 1: The fibers may be secured by mechanical means or with an optical adhesive. Note 2: When the fibers are secured by mechanical means, the gap between them is usually filled with an index-matching gel to reduce Fresnel reflection. Likewise, the optical adhesives that are used in conjunction with mechanical splices are formulated to have a refractive index that approximates that of the glass, and also serve to reduce Fresnel reflection.
Media Converter - Synonym medium access unit (MAU). - In a communications system, the equipment that adapts or formats the signal for transmittal over the communication medium. Note 1: An example of a MAU is an optical transmitter, which accepts an electrical signal at its input port and converts it to an optical signal accessible at its output port. Note 2: Some prefer to limit the term medium access unit to FDDI usage, with the term media converter being preferred for general usage.
Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) - Another protocol competing with H.323 (see also SIP), MGCP handles the traffic between media gateways and their controllers. Especially useful in multimedia applications: the media gateway converts from various formats for the switched-circuit network, and the controller handles conversion for the packet-switched network. Designed to take the workload away from IP telephones themselves and thereby make IP phones less complex and expensive.
Media Stream - A sequence of presentation units intended to convey some specific content.
Mediation - A process within the communications management network that acts on information passing between network elements (NEs) and operating systems (OSs) via a data communication network. Mediation uses standard interfaces and can be shared among several NEs, or several OSs, or between NEs and OSs.
Mediation Function - In telecommunications network management, a function that routes or acts on information passing between network elements and network operations. Note 1: Examples of mediation functions are communications control, protocol conversion, data handling, communications of primitives, processing that includes decision-making, and data storage. Note 2: Mediation functions can be shared among network elements, mediation devices, and network operation centers.
Medium - 1. In telecommunications, the transmission path along which a signal propagates, such as a wire pair, coaxial cable, waveguide, optical fiber, or radio path. 2. The material on which data are or may be recorded, such as plain paper, paper tapes, punched cards, magnetic tapes, magnetic disks, or optical disks.
Medium Access Unit (MAU) - In a communications system, the equipment that adapts or formats the signal for transmittal over the communication medium. Note 1: An example of a MAU is an optical transmitter, which accepts an electrical signal at its input port and converts it to an optical signal accessible at its output port. Note 2: Some prefer to limit the term medium access unit to FDDI usage, with the term media converter being preferred for general usage. Synonym media converter.
Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) - An orbital path configuration, between altitudes of 8,000 and 20,000 km, used by communication satellites that provide communications capabilities for such services as cellular telephone communications and GPS (global positioning system) signals.
Classification Orbital Altitude (km above the earth) LEO 500-2,000 MEO 8,000-20,000 Geostationary Orbit 35,786 Medium Frequency (MF) - Frequencies from 300 kHz to 3000 kHz. See electromagnetic spectrum.
Medium Interface Connector (MIC) - In communications systems, the connector at the interface point between the bus interface unit and the terminal, i.e., the medium interface point.
Medium Interface Point (MIP) - In communication systems, the location at which the standards for the interface parameters between a terminal and the line facility are implemented.
Medium-Power Talker - A hypothetical talker, within a log-normal distribution of talkers, whose volume lies at the medium power of all talkers determining the volume distribution at the point of interest. Note: When the distribution follows a log-normal curve (values expressed in decibels), the mean and standard deviation can be used to compute the medium-power talker. The talker volume distribution follows a log-normal curve and the medium-power talker is uniquely determined by the average talker volume. The medium-power talker volume, V, is given by V = V o+ 0.115
2, where V o is the average of the talker volume distribution in volume units (vu), and
2 is the variance of the distribution.
Medium-Term Bit Error Rate - Bit error rate that can be encountered for relatively short time periods (e.g., minutes), due to temporary malfunctions of, for example, transmission equipment.
Megabyte (MB)- A million bytes or a thousand kilobytes.
Megahertz (MHz) - A unit of frequency denoting one million (106) Hz.
Memory - 1. All of the addressable storage space in a processing unit and other internal memory that is used to execute instructions. 2. Loosely, the volatile, main storage in computers. See random access memory.
Memory Scavenging - The collection of residual information from data storage.
Menu - A displayed list of options from which a user selects actions to be performed.
MEO - Abbreviation for medium Earth orbit. An orbital path configuration, between altitudes of 8,000 and 20,000 km, used by communication satellites that provide communications capabilities for such services as cellular telephone communications and GPS (global positioning system) signals.
MERCAST - Acronym for merchant-ship broadcast system.
Merchant-Ship Broadcast System (MERCAST) - A maritime shore-to-ship broadcast system in which the ocean areas are divided into primary broadcast areas each covered by a high-powered shore radio station that broadcasts simultaneously on one medium frequency (MF) and one or more high frequencies (HF) for routing messages to ocean-going ships. Note: In some instances, coast stations may repeat the messages.
Meridional Ray - In fiber optics, a ray that passes through the optical axis of an optical fiber (in contrast with a skew ray, which does not).
Mesh Network - See network topology. A network topology in which there are at least two nodes with two or more paths between them.
Mesh Topology - See network topology. A network topology in which there are at least two nodes with two or more paths between them.
Mesochronous - The relationship between two signals such that their corresponding significant instants occur at the same average rate.
Message - 1. Any thought or idea expressed briefly in a plain or secret language, prepared in a form suitable for transmission by any means of communication. Note: A message may be a one-unit message or a multiunit message. 2. [In telecommunications,] Record information expressed in plain or encrypted language and prepared in a format specified for intended transmission by a telecommunications system. 3. An arbitrary amount of information whose beginning and end are defined or implied. 4. A completed call, i.e., a communication in which a conversation or exchange of information took place between the calling and called parties.
Message Alignment Indicator - In a signal message, data transmitted between the user part and the message transfer part to identify the boundaries of the signal message.
Message Authentication - Determining that a message has not been changed since leaving its point of transmission, where: (a) the identity of the originator is verified, and (b) the source, uniqueness, and integrity of the message are verified.
Message Authentication Code (MAC) - 1. A bit string that is a function of both data (either plaintext or ciphertext) and a secret key, and that is attached to the data in order to allow data authentication. Note: The function used to generate the message authentication code must be a one-way function. 2. Data associated with an authenticated message allowing a receiver to verify the integrity of the message.
Message Body - 1. For the single message format, the message words. 2. For the multiple message format, the parameter messages.
Message Broadcast - An electronic-mail conference capability using data terminals. Note: Control can be maintained by the user or by the network.
Message Center - 1. An agency charged with the responsibility for handling and controlling communications traffic. The center normally includes message center, transmitting, and receiving facilities. 2. A facility that (a) serves as a node for a communications network, (b) is equipped for technical control and maintenance of the circuits originating, transiting, or terminating at the node, (c) may contain message-center facilities, and (d) may serve as a gateway. Synonyms comm center, communications center.
Message Digest - See digest.
Message Format - A predetermined or prescribed spatial or time-sequential arrangement of the parts of a message that is recorded in or on a data storage medium. Note: Messages prepared for electrical transmission are usually composed on a printed blank form with spaces for each part of the message and for administrative entries.
Message Handling System (MHS) - In the ITU-T X.400 Recommendations, the family of services and protocols that provides the functions for global electronic-mail (e-mail) transfer among local mail systems.
Message Switching - A method of handling message traffic through a switching center, either from local users or from other switching centers, whereby the message traffic is stored and forwarded through the system.
Message Transfer Agent (MTA) - An OSI application process used to store and forward messages as described in the X.400 message handling system. Synonym Internet mail agent.
Message Transfer Part - The part of a common-channel signaling system that transfers signal messages and performs associated functions, such as error control and signaling link security.
Message Type - An assigned value used to identify the feature generating the message.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) - A data communications network that (a) covers an area larger than a campus area network and smaller than a wide area network (WAN), (b) interconnects two or more LANs, and (c) usually covers an entire metropolitan area, such as a large city and its suburbs.
MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol) - Another protocol competing with H.323 (see also SIP), MGCP handles the traffic between media gateways and their controllers. Especially useful in multimedia applications: the media gateway converts from various formats for the switched-circuit network, and the controller handles conversion for the packet-switched network. Designed to take the workload away from IP telephones themselves and thereby make IP phones less complex and expensive.
MHS (Message Handling System) - In the ITU-T X.400 Recommendations, the family of services and protocols that provides the functions for global electronic-mail (e-mail) transfer among local mail systems.
MHz - Abbreviation for megahertz.
MIC - Abbreviation for Medium Interface Connector - In communications systems, the connector at the interface point between the bus interface unit and the terminal, i.e., the medium interface point.
Microbend - In an optical waveguide, sharp curvatures involving local axial displacements of a few micrometers and spatial wavelengths of a few millimeters. Note: Microbends can result from waveguide coating, cabling, packaging, and installation. Microbending can cause significant radiative loss and mode coupling.
Microbending - See microbend.
Microbend Loss - In an optical fiber, the optical power loss caused by a microbend.
Microwave (mw) - Loosely, an electromagnetic wave having a wavelength from 300 mm to 10 mm (1 GHz to 30 GHz). Note: Microwaves exhibit many of the properties usually associated with waves in the optical regime, e.g., they are easily concentrated into a beam.
Mimicking - [A] form of spoofing.
Minimum Bend Radius - The radius below which an optical fiber or fiber-optic cable should not be bent. Note 1: The minimum bend radius is of particular importance in the handling of fiber-optic cables. It will vary with different cable designs. The manufacturer should specify the minimum radius to which the cable may safely be bent during installation, and for the long term. The former is somewhat shorter than the latter. Note 2: The minimum bend radius is in general also a function of tensile stresses, e.g., during installation, while being bent around a sheave while the fiber or cable is under tension. Note 3: If no minimum bend radius is specified, one is usually safe in assuming a minimum long-term low-stress radius not less than 15 times the cable diameter.
MIP - Abbreviation for Medium Interface Point - In communication systems, the location at which the standards for the interface parameters between a terminal and the line facility are implemented.
MIS - Abbreviation for Management Information System - An organized assembly of resources and procedures required to collect, process, and distribute data for use in decision making.
Miscellaneous Taxes - Like many other consumer goods and services, certain telephone services are taxed by federal, state, and local governments. These charges may appear as a “gross receipts” tax.
Misdelivered Block - A block received by a user other than the one intended by the message source.
Mobile Phone - A mobile radiotelephone, often in an automobile, that uses a network of short-range transmitters located in overlapping cells throughout a region, with a central station making connections to regular telephone lines. A hand-held mobile radiotelephone for use in an area divided into small sections (cells), each with its own short-range transmitter/receiver. Also called mobile telephone.
A mobile phone is a device which behaves as a normal telephone whilst being able to move over a wide area (compare cordless phone which acts as a telephone only within a limited range). Mobile phones allow connections to be made to the telephone network, normally by directly dialling the other party's number on an inbuilt keypad. Most current mobile phones use a combination of radio wave transmission and conventional telephone circuit switching, though packet switching is already in use for some parts of the mobile phone network, especially for services such as Internet access and WAP.
Some of the world's largest mobile phone manufacturers include Alcatel, Audiovox, Kyocera (formerly the handset division of Qualcomm), LG, Motorola, Nokia, Panasonic (Matsushita Electric), Philips, Samsung, Sagem, Sanyo, Siemens, SK Teletech, and Sony Ericsson.
Mobile-Satellite Service - A radiocommunication service:
- between mobile earth stations and one or more space stations, or between space stations used by this service; or
- between mobile earth stations by means of one or more space stations. This service may also include feeder links necessary for its operation
Mobile Service - A radiocommunication service between mobile and land stations, or between mobile stations.
Mobile Station - 1. A station in the mobile service intended to be used while in motion or during halts at unspecified points. 2. One or more transmitters that are capable of operation while in motion.
Modal Distribution - In an optical waveguide operating at a given wavelength, the number of modes supported, and their propagation time differences.
Modal Noise - Noise generated in an optical fiber system by the combination of mode-dependent optical losses and fluctuation in the distribution of optical energy among the guided modes or in the relative phases of the guided modes. Synonym speckle noise.
Mode - 1. In a waveguide or cavity, one of the various possible patterns of propagating or standing electromagnetic fields. Note 1: Each mode is characterized by frequency, polarization, electric field strength, and magnetic field strength. Note 2: The electromagnetic field pattern of a mode depends on the frequency, refractive indices or dielectric constants, and waveguide or cavity geometry. 2. Any electromagnetic field distribution that satisfies Maxwell's equations and the applicable boundary conditions. 3. In data communications, a protocol used to transfer data from switch to switch or from switch to terminal. 4. In statistics, the value associated with the highest peak in a probability density function.
Mode Coupling - In an electromagnetic waveguide, the exchange of power among modes. Note: In a multimode optical fiber, mode coupling reaches statistical equilibrium, i.e., equilibrium mode distribution, after the equilibrium length has been traversed.
Modem - A device that allows computers and other electronic equipment to communicate through ordinary telephone lines. A modem converts digital signals from your computer into analog signals for transmission over a phone line (modulation) and also converts the analog signals from the phone into digital signals that your computer can read (demodulation).Moderator - In computer conferencing, a person who receives the prospective messages from conference attendees and may accept, modify, or reject them. Synonym conference controller.
Modification Detection - Synonym manipulation detection. A procedure that is used to detect whether data have been modified either accidentally or intentionally.
Modular Connector - A catch all term that describes a number of plugs and jacks used with telephone and other equipment Handset connectors have four contact positions. Line connectors are wider and have six positions (often, only two or four positions are loaded with contacts).See telephone jacks, RJ-11 and RJ-14.
Modulation - The process, or result of the process, of varying a characteristic of a carrier, in accordance with an information-bearing signal.
Modulation Factor - In amplitude modulation, the ratio of the peak variation actually used, to the maximum design variation in a given type of modulation. Note: In conventional amplitude modulation, the maximum design variation is considered that for which the instantaneous amplitude of the modulated signal reaches zero. When zero is reached, the modulation is considered 100%.
Modulation Rate - 1. The rate at which a carrier is varied to represent the information in a digital signal. Note: Modulation rate and information transfer rate are not necessarily the same. 2. For modulated digital signals, the reciprocal of the unit interval of the modulated signal, measured in seconds.
Modulator - A device that imposes a signal on a carrier.
Monitor - 1. Software or hardware that is used to scrutinize and to display, record, supervise, control, or verify the operations of a system. Note: Possible uses of monitors are to indicate significant departures from the norm, or to determine levels of utilization of particular functional units. 2. A device used for the real-time temporary display of computer output data. Note: Monitors usually use cathode-ray-tube or liquid-crystal technology. Synonyms CRT, video display terminal, video display unit, visual display unit.
Monitoring - 1. The act of listening, carrying out surveillance on, and/or recording the emissions of one's own or allied forces for the purposes of maintaining and improving procedural standards and security, or for reference, as applicable. 2. The act of listening, carrying out surveillance on, and/or recording of enemy emissions for intelligence purposes. 3. The act of detecting the presence of radiation and the measurement thereof with radiation measuring instruments. Synonym radiological monitoring.
Monomode Optical Fiber - Synonym single-mode optical fiber. An optical fiber in which only the lowest order bound mode can propagate at the wavelength of interest. Note 1: The lowest order bound mode is ascertained for the wavelength of interest by solving Maxwell's equations for the boundary conditions imposed by the fiber, e.g., core (spot) size and the refractive indices of the core and cladding. Note 2: The solution of Maxwell's equations for the lowest order bound mode will permit a pair of orthogonally polarized fields in the fiber, and this is the usual case in a communication fiber. Note 3: In step-index guides, single-mode operation occurs when the normalized frequency, V, is less than 2.405. For power-law profiles, single-mode operation occurs for a normalized frequency, V, less than approximately
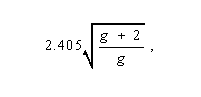
where g is the profile parameter. Note 4: In practice, the orthogonal polarizations may not be associated with degenerate modes.
MTBF - Abbreviation for Mean Time Between Failures () - 1. An indicator of expected system reliability calculated on a statistical basis from the known failure rates of various components of the system. Note: MTBF is usually expressed in hours. 2. Of a system, over a long performance measurement period, the measurement period divided by the number of failures that have occurred during the measurement period. 3. For population of items, during a measurement period, the total functioning life of the population of items divided by the total number of failures within the population during the measurement period. Note 1: The total functioning life of the population may be calculated as the summation of the operating life of every item in the population over the measurement period. When computing the MTBF, any measure of operating life may be used, such as time, cycles, kilometers, or events. Note 2: For example, if a total of 1,000 events, such as data transfers, radio transmissions, or system boots, occurs in a population of items during a measurement period of 100 hours and there are a total of 10 failures among the entire population, the MTBF for each item is (1000)(100)/10 = 104 hours.
MTBO - Abbreviation for Mean Time Between Outages - In a system, the mean time between equipment failures that result in loss of system continuity or unacceptable degradation. Note: The MTBO is calculated by the equation,
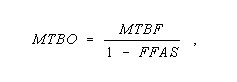
where MTBF is the nonredundant mean time between failures and FFAS is the fraction of failures for which the failed equipment is automatically bypassed.
MTIE - Abbreviation for Maximum Time Interval Error - The maximum error for all possible measurement intervals within the measurement period.
MTSR - Abbreviation for Mean Time to Service Restoral - The mean time to restore service following system failures that result in a service outage. Note: The time to restore includes all time from the occurrence of the failure until the restoral of service.
MTTR - Abbreviation for Mean Time To Repair - The total corrective maintenance time divided by the total number of corrective maintenance actions during a given period of time.
MUF - Abbreviation for Maximum Usable Frequency - In radio transmission using reflection from the regular ionized layers of the ionosphere, the upper frequency limit that can be used for transmission between two points at a specified time. Note: MUF is a median frequency applicable to 50% of the days of a month, as opposed to 90% cited for the lowest usable high frequency (LUF) and the optimum traffic frequency (FOT).
Multicarrier Modulation (MCM) - A technique of transmitting data by dividing the data into several interleaved bit streams and using these to modulate several carriers. Note: MCM is a form of frequency-division multiplexing.
Multicast Backbone (Mbone) - See Mbone. A part of the Internet designed to support IP multicasting by coordinating the transmission of messages to a single destination instead of allowing packets to travel by different routes.
Multicasting - DTV technology that allows each digital broadcast station to split its digital bandwidth into two or more individual channels of programming and/or data services (For example, on Channel 7, you could watch sub-channel 7-1, 7-2, 7-3 or 7-4).
Multichannel - Pertaining to communications, usually full-duplex communications, on more than one channel. Note: Multichannel transmission may be accomplished by time-division multiplexing, frequency-division multiplexing, phase-division multiplexing, or space diversity.
Multi-Channel Sound - Feature of DTV that permits numerous streams of sound to be transmitted for a given program, providing stereo, surround sound, and even other languages.
Multi-LinkInc.com - Multi-LinkInc.com is a division of Higgins International that distributes Multi-Link Fax switches and remote activated power products to individuals and companies worldwide.
Multimedia Communication System - A system that handles more than one media stream in a synchronized way from the user's point of view. The system may allow interconnection of multiple parties, multiple connections, and the addition or deletion of resources and users within a single communication session.
Multimode Distortion - A distortion mechanism, occurring in multimode fibers, in which the signal is spread in time because the velocity of propagation of the optical signal is not the same for all modes. Note 1: In the ray-optics analogy, multimode distortion in a step-index optical fiber may be compared to multipath propagation of a radio signal. The direct signal is distorted by the arrival of the reflected signal a short time later. In a step-index optical fiber, rays taking more direct paths through the fiber core, i.e., those which undergo the fewest reflections at the core-cladding boundary, will traverse the length of the fiber sooner than those rays which undergo more reflections. This results in distortion of the signal. Note 2: Multimode distortion limits the bandwidth of multimode fibers. For example, a typical step-index fiber with a 50-
m core would be limited to approximately 20 MHz for a one-kilometer length, i.e., a bandwidth of 20 MHz•km. Note 3: Multimode distortion may be considerably reduced, but never completely eliminated, by the use of a core having a graded refractive index. The bandwidth of a typical off-the-shelf graded-index multimode fiber, having a 50-
m core, may approach 1 GHz•km or more. Multimode graded-index fibers having bandwidths approaching 3 GHz•km have been produced. Note 4: Because of its similarity to dispersion in its effect on the optical signal, multimode distortion is sometimes incorrectly referred to as " intermodal dispersion," " modal dispersion," or " multimode dispersion." Such usage is incorrect because multimode distortion is not a truly dispersive effect. Dispersion is a wavelength-dependant phenomenon, whereas multimode distortion may occur at a single wavelength. Synonyms intermodal delay distortion, intermodal distortion.
Multimode Optical Fiber - An optical fiber that supports the propagation of more than one bound mode. Note: A multimode optical fiber may be either a graded-index (GI) fiber or a step-index (SI) fiber.
Multiparty Line - Synonym party line. In telephone systems, an arrangement in which two or more user end instruments, usually telephones, are connected to the same loop. Note: If selective ringing is not used, individual users may be alerted by different ringing signals, such as a different number of rings or a different combination of long and short rings. Party lines remain primarily in rural areas where loops are long. Privacy is limited and congestion often occurs.
Multipath - The propagation phenomenon that results in radio signals' reaching the receiving antenna by two or more paths. Note 1: Causes of multipath include atmospheric ducting, ionospheric reflection and refraction, and reflection from terrestrial objects, such as mountains and buildings. Note 2: The effects of multipath include constructive and destructive interference, and phase shifting of the signal. Note 3: In facsimile and television transmission, multipath causes jitter and ghosting.
Multiplex (MUX) - See multiplexing. The combining of two or more information channels onto a common transmission medium. Note: In electrical communications, the two basic forms of multiplexing are time-division multiplexing (TDM) and frequency-division multiplexing (FDM). In optical communications, the analog of FDM is referred to as wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM).
Multiplexer (MUX) - A device that combines multiple inputs into an aggregate signal to be transported via a single transmission channel. Synonym multiplexing equipment.
Multiplexing (MUXing) - The combining of two or more information channels onto a common transmission medium. Note: In electrical communications, the two basic forms of multiplexing are time-division multiplexing (TDM) and frequency-division multiplexing (FDM). In optical communications, the analog of FDM is referred to as wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM).
Multiplexing Equipment - Synonym multiplexer. - A device that combines multiple inputs into an aggregate signal to be transported via a single transmission channel.
Multiplex Hierarchy - In frequency-division multiplexing, the rank of frequency bands occupied:
12 channels group 5 groups (60 channels) super group 5 super groups (300 channels) master group (CCITT--now, ITU-T) 10 super groups (600 channels) master group (U.S. standard) 6 U.S. master groups (3600 channels) jumbo group Multipoint - Synonym multiple.
Multipoint Circuit - A circuit that interconnects three or more separate points.
Must-Carry - The legal obligation of cable companies to carry the analog or digital signals of over-the-air local broadcasters.
MW - Abbreviation for microwave. - Loosely, an electromagnetic wave having a wavelength from 300 mm to 10 mm (1 GHz to 30 GHz). Note: Microwaves exhibit many of the properties usually associated with waves in the optical regime, e.g., they are easily concentrated into a beam.
MX Record - Abbreviation for mail exchange record. - An entry in a domain name system database that directs the routing of mail by mail transfer agents.
Fax Switch Products
|
*Note: All prices include shipping and handling in the continental US and most of Canada. We reserve the right to charge up to the actual price of shipping on all orders outside the continental United States. Customer is responsible for any taxes, duties or brokerage charges that may apply. All orders shipped UPS Ground unless specified. For air and express shipments, appropriate charges will be applied to your order.
Need Help?
- Call now for free phone consultation at 1-866-337-0965.
Click here if you want to share 2 devices on 1 line and don't know which device to choose.
Click here if you want to share 3 or more devices on one line and don't know what type to choose.
"Albert Einstein Presents Fax Switch "
"Dancing Bear Fax Switch Presentation"
![]()
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
You didn't find what you need here?
Please visit our sister company, SuperPhoneStore.com for wholesale to the public telephones, phone accessories or the latest electronics. We have over 4500 different products in stock from over 200 premier manufacturers.