
Telecom Dictionary - Definitions of terms
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
R
Raceway - Within a building, an enclosure, i.e., channel, used to contain and protect wires, cables, or bus bars.
Rack - A frame upon which one or more units of equipment are mounted. Note: DOD racks are always vertical.
Racon - See radar beacon.
rad - Acronym for radiation absorbed dose. The basic unit of measure for expressing absorbed radiant energy per unit mass of material. Note 1: A rad corresponds to an absorption of 0.01 J/kg, i.e., 100 ergs/g. Note 2: The absorbed radiant energy heats, ionizes, and/or destroys the material upon which it is incident.
Radar - Acronym for radio detection and ranging. 1. A radio detection system that transmits short bursts (pulses) of rf energy and detects their echoes from objects (targets) such as aircraft or ships. Note: The round-trip propagation time for the echo return may be used to determine the target's range (distance from the radar's antenna). If the transmitting antenna has a narrow beam (the usual case), the azimuth or elevation of the target may also be determined. Synonym primary radar. 2. A radio detection device that provides information on range, azimuth, and/or elevation of objects. 3. A radiodetermination system based on the comparison of reference signals with radio signals reflected, or retransmitted, from the position to be determined.
Radar Beacon (racon) - 1. A transmitter - receiver associated with a fixed navigational mark which, when triggered by a radar, automatically returns a distinctive signal which can appear on the display of the triggering radar, providing range, bearing and identification information. 2. A receiver-transmitter combination which sends out a coded signal when triggered by the proper type of pulse, enabling determination of range and bearing information by the interrogating station or aircraft.
Radar Blind Range - The range that corresponds to the situation in which a radar transmitter is on and hence the receiver must be off, so that the radar transmitted signal does not saturate, i.e., does not blind, its own receiver. Note: Radar blind ranges occur because there is a time interval between transmitted pulses that corresponds to the time required for a pulse to propagate to the object, i.e., to the target, and its reflection to travel back. This causes an attempt to measure the range just as the radar transmitter is transmitting the next pulse. However, the receiver is off, therefore this particular range cannot be measured. The width of the range value that cannot be measured depends on the duration of the time that the radar receiver is off, which depends on the duration of the transmitted pulse. The return-time interval could be coincident with the very next radar-transmitted pulse, i.e., the first pulse following a transmitted pulse, or the second, or the third, and so on, giving rise to a succession of blind ranges. The blind ranges are given by r m = ( m c)/(2 fn ), where r m is the blind range for a given value of m , m is a positive integer that indicates which of the blind ranges is being determined, c is the velocity of electromagnetic wave propagation in vacuum (approximately 3 × 10 8 m/s), f is the radar pulse repetition rate, and n is the refractive index of the transmission medium (nearly 1 for air). The radar blind range is independent of the radar radio frequency ( rf ) of the radar pulse.
Radian (rad.) - A unit of plane angle measure equal to the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle. Note: One radian is equal to 360°/2
, which is approximately 57° 17' 44.6".
Radiant Power - The rate of flow of electromagnetic energy, i.e., radiant energy. Note 1: Radiant power is usually expressed in watts, i.e., joules per second. Note 2: The modifier is often dropped and "power" is used to mean "radiant power". Deprecated synonyms flux, radiant flux.
Radiant Energy - Energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. Note 1: Radiant energy may be calculated by integrating radiant power with respect to time. Note 2: Radiant energy is usually expressed in joules.
Radiant Flux - Deprecated synonym for radiant power.
Radiation - 1. In communication, the emission of energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. 2. The outward flow of energy from any source in the form of radio waves.
Radiation Mode - For an optical fiber, an unbound mode. Note: In an optical fiber, a radiation mode is one having fields that are transversely oscillatory everywhere external to the waveguide, and which exists even at the limit of zero wavelength. Specifically, a radiation mode is one for which
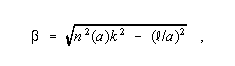
where
is the imaginary part (phase term) of the axial propagation constant, integer
is the azimuthal index of the mode, n (a) is the refractive index, where a is the core radius, and k is the free-space wave number, k = 2
/
, where
is the wavelength. Radiation modes correspond to refracted rays in the terminology of geometric optics. Synonym unbound mode.
Radiation Pattern - 1. The variation of the field intensity of an antenna as an angular function with respect to the axis. Note: A radiation pattern is usually represented graphically for the far-field conditions in either horizontal or vertical plane. 2. In fiber optics, the relative power distribution at the output of a fiber or active device as a function of position or angle. Note 1: The near-field radiation pattern describes the radiant emittance (W•m-2) as a function of position in the plane of the exit face of an optical fiber. Note 2: The far-field radiation pattern describes the irradiance as a function of angle in the far-field region of the exit face of an optical fiber. Note 3: The radiation pattern may be a function of the length of the fiber, the manner in which it is excited, and the wavelength. Synonym directivity pattern.
Radio - 1. Telecommunication by modulation and radiation of electromagnetic waves. 2. A transmitter, receiver, or transceiver used for communication via electromagnetic waves. 3. A general term applied to the use of radio waves.
Radiobeacon Station - A station in the radionavigation service the emissions of which are intended to enable a mobile station to determine its bearing or direction in relation to the radiobeacon station.
Radiocommunication - Telecommunication by means of radio waves.
Radiocommunication Service - A service as defined in this Section [of the Radio Regulations] involving the transmission, emission and/or reception of radio waves for specific telecommunication purposes. In these regulations, unless otherwise stated, any radiocommunication service relates to terrestrial radiocommunication.
Radio Detection and Ranging - See radar.
Radiodetermination - The determination of the position, velocity and/or other characteristics of an object, or the obtaining of information relating to these parameters, by means of the propagation properties of radio waves.
Radiodetermination-Satellite Service - A radiocommunication service for the purpose of radiodetermination involving the use of one or more space stations. This service may also include feeder links necessary for its own operation.
Radio Field Intensity - Synonym field strength. 1. The magnitude of an electric, magnetic, or electromagnetic field at a given point. Note: The field strength of an electromagnetic wave is usually expressed as the rms value of the electric field, in volts per meter. The field strength of a magnetic field is usually expressed in amperes per meter 2. The electric field strength in the horizontal plane.
Radio Frequency - See RF. Of, or pertaining to, any frequency within the electromagnetic spectrum normally associated with radio wave propagation. Note: For designation of subdivisions, see electromagnetic spectrum and its associated diagram.
Radio Horizon - The locus of points at which direct rays from an antenna are tangential to the surface of the Earth. Note: If the Earth were a perfect sphere and there were no atmospheric anomalies, the radio horizon would be a circle. In practice, the distance to the radio horizon is affected by the height of the transmitting antenna, the height of the receiving antenna, atmospheric conditions, and the presence of obstructions, e.g., mountains.
Radiolocation - Radiodetermination used for purposes other than those of radionavigation.
Radiological Monitoring - Synonym monitoring. - 1. The act of listening, carrying out surveillance on, and/or recording the emissions of one's own or allied forces for the purposes of maintaining and improving procedural standards and security, or for reference, as applicable. 2. The act of listening, carrying out surveillance on, and/or recording of enemy emissions for intelligence purposes. 3. The act of detecting the presence of radiation and the measurement thereof with radiation measuring instruments.
Radionavigation - 1. Radiolocation intended for the determination of position or direction or for obstruction warning in navigation. 2. Radiodetermination used for the purposes of navigation, including obstruction warning.
Radionavigation-Satellite Service - A radiodetermination-satellite service used for the purpose of radionavigation. This service may also include feeder links necessary for its operation.
Radio Paging - The use of a pocket-size radio receiver capable of alerting its wearer that there is a phone call, either from a displayed phone number or to a predesignated number. Note: Radio paging may be considered a subset of paging. Synonym beeping.
Radio Regulations Board: A permanent organization of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) that implements frequency assignment policy and maintains the Master International Frequency Register (MIFR). Note: Formerly International Frequency Registration Board (IFRB).
Radio Wave - An electromagnetic wave of a frequency arbitrarily lower than 3000 GHz. Synonym Hertzian wave.
RAM - Acronym for random access memory. - A read /write, nonsequential-access memory used for the storage of instructions and data. Note 1: RAM access time is essentially the same for all storage locations. Note 2: RAM is characterized by a shorter access time than disk or tape storage. Note 3: RAM is usually volatile.
Random Access Memory (RAM) - A read /write, nonsequential-access memory used for the storage of instructions and data. Note 1: RAM access time is essentially the same for all storage locations. Note 2: RAM is characterized by a shorter access time than disk or tape storage. Note 3: RAM is usually volatile.
Random Noise - Noise consisting of a large number of transient disturbances with a statistically random time distribution. Note: Thermal noise is an example of random noise.
Raster - A predetermined pattern of scanning lines within a display space. Note: An example of a raster is the pattern followed by an electron beam scanning the screen of a television camera or receiver.
Raster Graphics - Synonym [loosely] bitmapped graphics.
Ratio-Squared Combiner - A diversity combiner in which (a) the signals from each channel are added together, (b) the gain of each channel is made proportional to the rms signal level and inversely proportional to the mean square noise level in that channel, and (c) the same proportionality constant is used for all channels. Synonym maximal-ratio combiner.
Ray - A geometric representation of a lightwave by a line normal to the electromagnetic wavefront; i.e., in the direction of propagation of the wave.
Rayleigh Scattering - Of an electromagnetic wave propagating in a material medium, scattering caused by refractive-index inhomogeneities that are small compared to the wavelength. Note 1: Rayleigh scattering losses vary as the reciprocal of the fourth power of the wavelength. Note 2: Ionospheric scattering is caused partly by Rayleigh scattering.
Ray Optics - Synonym geometric optics. The branch of optics that describes light propagation in terms of rays. Note 1: Rays are bent at the interface between two dissimilar media, and may be curved in a medium in which the refractive index is a function of position. Note 2: The ray in ray optics is perpendicular to the wavefront in physical optics.
RBOC - Regional Bell Operating Company. In December 1983, a federal judge ordered AT&T to divide their 22 telephone companies into seven regional operating companies. The United States Department of Justice placed several restrictions on the RBOCs: they were not allowed to provide long distance, equipment manufacturing, or information services.
Read - [A] fundamental operation in an information system (IS) that results only in the flow of information from an object to a subject.
Real Time Protocol (RTP) - Also known as Real Time Transport Protocol. Controls the transmission of packets of data that demands low latency (such as audio and video). Supports real-time transmission over IP networks and streaming as one means of delivery.
Received Noise Power - 1. The calculated or measured noise power, within the bandwidth being used, at the receive end of a circuit, channel, link, or system. 2. The absolute power of the noise measured or calculated at a receive point. Note: The related bandwidth and the noise weighting must also be specified. 3. The value of noise power, from all sources, measured at the line terminals of telephone set's receiver. Note: Either flat weighting or some other specific amplitude-frequency characteristic or noise weighting characteristic must be associated with the measurement.
Receiver - The sink or terminator of any signal on a transmission medium.
Recipient - The switch or network to which a subscriber's directory number has been ported.
Recording Density - Synonym bit density.The number of bits recorded per unit length, area, or volume. Note: Recording Density is the reciprocal of bit pitch.
Record Traffic - 1. Traffic that is recorded, in permanent or quasipermanent form, by the originator, the addressee, or both. 2. Traffic that is permanently or semipermanently recorded in response to administrative procedures or public law.
Recovery - In a database management system, the procedures and capabilities available for reconstruction of the contents of a database to a state that prevailed before the detection of processing errors and before the occurrence of a hardware or software failure that resulted in the destruction of some or all of the stored data.
RED - Rural Economic Development. A program administered by TDS Telecom and other phone companies which includes advocating for rural development funding at the Federal and State levels. This program is designed to support local companies’ efforts with economic development projects in their communities.
Redundancy - 1. In the transmission of data, the excess of transmitted message symbols over that required to convey the essential information in a noise-free circuit. Note: Redundancy may be introduced intentionally (as in the case of error detection or correction codes) or inadvertently (such as by oversampling a band-limited signal, inefficient formats, etc.). 2. In a communication system, surplus capability usually provided to improve the reliability and quality of service.
Redundant Connectivity - A system of backup connections that ensures the network will continue functioning even if a problem is encountered on one of the connections.
Reference Antenna - An antenna that may be real, virtual, or theoretical, and has a radiation pattern that can be used as a basis of comparison with other antenna radiation patterns. Note: Examples of reference antennas are unit dipoles, half-wave dipoles, and isotropic, i.e., omnidirectional antennas.
Reference Point - In ISDN, a logical point between two, nonoverlapping functional groups. Note: When equipment is placed at a reference point, that reference point is designated an interface.
Reflected Code - Synonym Gray code. - A binary code in which consecutive decimal numbers are represented by binary expressions that differ in the state of one, and only one, one bit.
Reflecting Layer - In the ionosphere, a layer that has a free-electron density sufficient to reflect radio waves. Note 1: The principal reflecting layers are the E, F1, and F2 layers in the daylight hemisphere. Note 2: A critical frequency is associated with the reflection by each layer.
Reflection - The abrupt change in direction of a wave front at an interface between two dissimilar media so that the wave front returns into the medium from which it originated. Note 1: Reflection may be specular (i.e., mirror-like) or diffuse (i.e., not retaining the image, only the energy) according to the nature of the interface. Note 2: Depending on the nature of the interface, i.e., dielectric-conductor or dielectric-dielectric, the phase of the reflected wave may or may not be inverted.
Reflection Loss - 1. At a discontinuity or impedance mismatch, e.g., in a transmission line, the ratio of the incident power to the reflected power. Note 1: Reflection loss is usually expressed in dB. Note 2: The reflection loss, L r, is given by
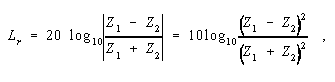
where Z 1 and Z 2 are the respective impedances, and the vertical bars designate absolute magnitude. 2. In an optical fiber, the loss that takes place at any discontinuity of refractive index, especially at an air-glass interface such as a fiber endface, at which a fraction of the optical signal is reflected back toward the source. Note: This reflection phenomenon is also called " Fresnel reflection loss," or simply,"Fresnel loss." At normal incidence, the fraction of reflected power is expressed by the formula,
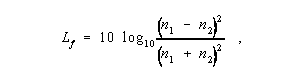
where n 1 and n 2 are the respective indices of refraction.
Refractive index (
, n) - Of a medium, the ratio of the velocity of propagation of an electromagnetic wave in vacuum to its velocity in the medium. Synonym index of refraction. Note: When the Greek character eta is unavailable, the letter n is used to represent the refractive index.
Refractive Index Contrast - In an optical fiber, a measure of the relative difference in refractive index of the core and cladding. Note: Refractive index contrast,
, is given by
= (n 1 2-n 2 2)/(2n 1 2), where n 1 is the maximum refractive index in the core and n 2 is the refractive index of the homogeneous cladding.
Refractive Index Profile - Of the cross section of an optical fiber, the description, i.e., plot, of the value of the refractive index as a function of distance from the fiber axis along a diameter. Synonyms index profile, refraction profile.
Refractive Index Profile - Index Profile
Regeneration - 1. In a regenerative repeater, the process by which digital signals are amplified, reshaped, retimed, and retransmitted. Synonym positive feedback. 2. In a storage or display device, the restoration of stored or displayed data that have deteriorated. Note: For example, conventional cathode-ray tube displays must be continually regenerated for the data to remain displayed. 3. In computer graphics, the sequence of events needed to generate a display image from its representation in storage.
Regenerative Repeater - A repeater, designed for digital transmission, in which digital signals are amplified, reshaped, retimed, and retransmitted. Synonym regenerator.
Regenerator - 1. - A repeater, designed for digital transmission, in which digital signals are amplified, reshaped, retimed, and retransmitted. Synonym regenerative repeater. 2. A device that reconstructs and retransmits a received pulse train.
Register - 1. A device, accessible to one or more input circuits, that accepts and stores data. Note: A register is usually used only as a device for temporary storage of data. 2. A temporary-memory device used to receive, hold, and transfer data (usually a computer word) to be operated upon by a processing unit. Note: Computers typically contain a variety of registers. General purpose registers may perform many functions, such as holding constants or accumulating arithmetic results. Special purpose registers perform special functions, such as holding the instruction being executed, the address of a storage location, or data being retrieved from or sent to storage.
Registration - 1. The accurate positioning of, or the degree of accuracy in the positioning of, an entity relative to (a) another entity, or (b) an independent frame of reference. Note: For example, in color graphics applications involving the superposition of several colored rasters, such as in a CRT display, good registration (usually termed " convergence " in this context) is of paramount importance if the resulting image is not to have false colors, especially around the edges of objects. 2. In telephony, see FCC registration program. 3. In computer networking, the official assignment of a name (Internet Protocol address) to an information object or device, in a way that makes the assignment unduplicated anywhere else in the network and makes the device available for other devices to communicate with.
Relative Address - In computer and data processing programming, an address that is expressed as a difference in relation to a base address.
Relative Spectral Width - See spectral width. The wavelength interval over which the magnitude of all spectral components is equal to or greater than a specified fraction of the magnitude of the component having the maximum value. Note 1: In optical communications applications, the usual method of specifying spectral width is the full width at half maximum. This method may be difficult to apply when the spectrum has a complex shape. Another method of specifying spectral width is a special case of root-mean-square deviation where the independent variable is wavelength,
, and f (
) is a suitable radiometric quantity. Note 2: The relative spectral width ,
/
, is frequently used where
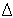
is obtained according to note 1, and
is the center wavelength.
Relative Transmission Level - The ratio of the signal power, at a given point in a transmission system, to a reference signal power. Note: The ratio is usually determined by applying a standard test tone at zero transmission level point (or applying adjusted test tone power at any other point) and measuring the gain or loss to the location of interest. A distinction should be made between the standard test tone power and the expected median power of the actual signal required as the basis for the design of transmission systems.
Relay - 1. To retransmit a received message from one station to another station. 2. An electromechanical or semiconductor switch (i.e., solid-state relay) in which a current or voltage applied across one port or terminal controls electrical currents or voltages that appear across another terminal or terminals.
Reliability - 1. The ability of an item to perform a required function under stated conditions for a specified period of time. 2. The probability that a functional unit will perform its required function for a specified interval under stated conditions. 3. The continuous availability of communication services to the general public, and emergency response activities in particular, during normal operating conditions and under emergency circumstances with minimal disruption.
Remote Access - 1. Pertaining to communication with a data processing facility from a remote location or facility through a data link. 2. A PABX service feature that allows a user at a remote location to access by telephone PABX features, such as access to wide area telephone service (WATS) lines. Note: For remote access, individual authorization codes are usually required.
Remote Clock - 1. A clock that is remote from a particular facility, such as a communications station or node, with which it is associated. 2. A clock that is remote from another clock to which it is to be compared.
Remote Linked Registration - A feature by which a linked registration for one specified terminal address can be carried out from another terminal address.
Remote Terminal - The location at which there is a transition between a telecommunications carrier facility and the local lines serving the individual customers.
Reorder Tone - See busy signal. In telephony, an audible or visual signal that indicates that the called number is occupied or otherwise unavailable.
Repeat Dialing - You can activate this feature by dialing a code and the last outgoing call placed by you will be automatically redialed. If the telephone number called is not busy, the call will complete. If the telephone number called is busy, you will hear a confirmation tone, you can then hang up. Once you hang up, the network will monitor the busy/idle status of both lines every 45 seconds for up to 30 minutes. During that time, the network will ring your home telephone number once the telephone number called is no longer busy.
Dials a busy telephone number for 30 minutes and rings your phone when the dialed number is clear. After reaching a busy number, hang up, then pick up the phone again and dial *66 to activate. To cancel Repeat Dial press*86 . Repeat Dial does not work with long distance calls or 800 numbers.
Repeater - 1. An analog device that amplifies an input signal regardless of its nature, i.e., analog or digital. 2. A digital device that amplifies, reshapes, retimes, or performs a combination of any of these functions on a digital input signal for retransmission. Note: The term "repeater" originated with telegraphy and referred to an electromechanical device used to regenerate telegraph signals. Use of the term has continued in telephony and data communications. 3. A fixed transmitter that retransmits the signals of other stations.
Requests - See click-through. - The process of clicking on a Web advertisement and going directly to the advertiser's Web site. Synonyms ad clicks, clicks.
Request-To-Send Signal - A signal that is generated by a receiver in order to condition a remote transmitter to commence transmission.
Reradiation -1. Radiation, at the same or different wavelengths, i.e., frequencies, of energy received from an incident wave. 2. Undesirable radiation of signals locally generated in a radio receiver. Note: Radiation might cause interference or reveal the location of the device.
Rerouting - Recommencement of route selection from the first point of routing control, when congestion is encountered at some intermediate switching point in the connection that is to be established.
Resident - Pertaining to computer programs that remain on a particular storage device.
Residual Error Rate - Synonym undetected error ratio. The ratio of the number of bits, unit elements, characters, or blocks incorrectly received and undetected, to the total number of bits, unit elements, characters, or blocks sent.
Resolution - In computers, resolution is the number of pixels (individual points of color) contained on a display monitor, expressed in terms of the number of pixels on the horizontal axis and the number on the vertical axis. The sharpness of the image on a display depends on the resolution and the size of the monitor. The same pixel resolution will be sharper on a smaller monitor and gradually lose sharpness on larger monitors because the same number of pixels are being spread out over a larger number of inches.
A given computer display system will have a maximum resolution that depends on its physical ability to focus light (in which case the physical dot size - the dot pitch - matches the pixel size) and usually several lesser resolutions. For example, a display system that supports a maximum resolution of 1280 by 1023 pixels may also support 1024 by 768, 800 by 600, and 640 by 480 resolutions. Note that on a given size monitor, the maximum resolution may offer a sharper image but be spread across a space too small to read well.
Display resolution is not measured in dots per inch as it usually is with printers. However, the resolution and the physical monitor size together do let you determine the pixels per inch. Typically, PC monitors have somewhere between 50 and 100 pixels per inch. For example, a 15-inch VGA (see display modes) monitor has a resolution of 640 pixels along a 12-inch horizontal line or about 53 pixels per inch. A smaller VGA display would have more pixels per inch.
Resonance - In an electrical circuit, the condition that exists when the inductive reactance and the capacitive reactance are of equal magnitude, causing electrical energy to oscillate between the magnetic field of the inductor and the electric field of the capacitor. Note 1: Resonance occurs because the collapsing magnetic field of the inductor generates an electric current in its windings that charges the capacitor and the discharging capacitor provides an electric current that builds the magnetic field in the inductor, and the process is repeated. Note 2: At resonance, the series impedance of the two elements is at a minimum and the parallel impedance is a maximum. Resonance is used for tuning and filtering, because resonance occurs at a particular frequency for given values of inductance and capacitance. Resonance can be detrimental to the operation of communications circuits by causing unwanted sustained and transient oscillations that may cause noise, signal distortion, and damage to circuit elements. Note 3: At resonance the inductive reactance and the capacitive reactance are of equal magnitude. Therefore,
L = 1/
C, where
= 2
f, in which f is the resonant frequency in hertz, L is the inductance in henrys, and C is the capacity in farads when standard SI units are used. Thus,
Restoration - Of an impaired (degraded) or unserviceable telecommunications service or facility, action taken to repair it and return it to service. Note: Permanent or temporary restoration may be accomplished by various means, such as patching, rerouting, substitution of component parts, etc.
Return Loss - The ratio, at the junction of a transmission line and a terminating impedance or other discontinuity, of the amplitude of the reflected wave to the amplitude of the incident wave. Note 1: Return loss is usually expressed in dB. Note 2: Return loss is a measure of the dissimilarity between impedances in metallic transmission lines and loads, or between refractive indices in dielectric media, e.g., optical fibers. Note 3: In a metallic transmission line, return loss is given by
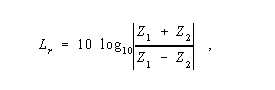
where Z 1 is the impedance toward the source and Z 2 is the impedance toward the load, and the vertical bars indicate magnitude. Note 4: For dielectric media, e.g., optical fibers, see reflection loss.
RF - Also rf. Abbreviation for radio frequency. Of, or pertaining to, any frequency within the electromagnetic spectrum normally associated with radio wave propagation. Note: For designation of subdivisions, see electromagnetic spectrum and its associated diagram.
Ringback - A tone produced by telephone processing equipment that signals to the caller that the called party is being rung. Automatic Call Processors produce a ringback tone to the caller when ringing a device.
Ringback Tone- A tone produced by telephone processing equipment that signals to the caller that the called party is being rung. Automatic Call Processors produce a ringback tone to the caller when ringing a device.
Ringing - Oscillations that occur in the output of systems after a sudden change in the input.
Ringing Cycle - In traditional telephony, a nominal period (usually approximately 6 seconds) composed of alternate (a) ringing signals (ringing current) and (b) a silent interval.
Ringing Signal - 1. The alternating current (ac) component of the alerting signal. 2. An ac signal applied across the network interface (NI) of such magnitude, frequency, and duration to cause an electromechanical ringer to ring. Used to alert the customer installation (CI) of an incoming call.
Ring Topology - See network topology. A network topology in which every node has exactly two branches connected to it.
RJ-11 - The most common telephone jack is the RJ-11 jack, which can have six conductors but usually is implemented with four. The RJ-11 jack is likely to be the jack that your household or office phones are plugged into from the ordinary "untwisted" wire (sometimes called "gray satin" or "flat wire") people are most familiar with. In turn, the jacks connect to the "outside" longer wires known as twisted pair that connect to the telephone company central office or to a private branch exchange (PBX).
The four wires are usually characterized as a red and green pair and a black and white pair. The red and green pair typically carry voice or data. On an outside phone company connection, the black and white pair may be used for low-voltage signals such as phone lights. On a PBX system, they may be used for other kinds of signaling. See telephone jacks.
A computer that uses a dial-up modem to connect to a network is usually plugged into an RJ-11 jack.
RJ-11 Wiring Standard - A specific wiring arrangement for using a g-position modular connector to attach exactly one telephone line. The two wires of the telephone line are attached to the two center contacts of an RJ-11 modular jack (the wires are often color-coded red and green). All connections to your automatic call processor must be wired according to this RJ-11 standard. See telephone jacks.
RJ-14 - The RJ-14 is similar to the RJ-11, but the four wires are used for two phone lines. Typically, one set of wires (for one line) contains a red wire and a green wire. The other set contains a yellow and black wire. Each set carries one analog "conversation" (voice or data). See telephone jacks.
RJ-14 Wiring Standard - Utilizes a six position modular connector wired to two separate telephone lines. This application is used almost exclusively on dual line telephones. Line 1 is attached to the center two contacts (like RJ-ll), and Line 2 is attached to the next outer two contacts (often color-coded yellow and black). See RJ-14. See telephone jacks.
RJ-45 - The RJ-45 is a single-line jack for digital transmission over ordinary phone wire, either untwisted or twisted. The interface has eight pins or positions. For connecting a modem, printer, or a data PBX at a data rate up to 19.2 Kbps, you can use untwisted wire. For faster transmissions in which you're connecting to an Ethernet 10BASET network, you need to use twisted pair wire. (Untwisted is usually a flat wire like common household phone extension wire. Twisted is often round.)
There are two varieties of RJ-45: keyed and unkeyed. Keyed has a small bump on its end and the female complements it. Both jack and plug must match.
Roaming Service - Is the ability to get access to the Internet when away from home at the price of a local call or at a charge considerably less than the regular long-distance charges. For example, if you normally get access to the Internet from an access provider in Brooklyn, New York and are travelling to Hong Kong, you can call a designated access provider in Hong Kong. Instead of paying long distance charges to your local provider in Brooklyn, you pay the local phone connection charge in Hong Kong and possibly a modest additional charge for the service.
Robot - Computer software that runs continuously and responds automatically to a user's activity. Note: Some robots are created for the benefit of the user, such as those that send information when a user requests it, those that perform automated searches, and those that monitor messages in a forum and delete messages that are repetitive or violate the forum's rules of netiquette. Other robots are created to harm the user (e.g., a computer virus) or spam the user (e.g., a program that, whenever a user posts a message to a forum, automatically sends a response to the user containing unrelated advertisements).
Robotic Librarian - Synonym droid.
Roll Over - A service provided by most phone companies that allows several lines to be tied together. A single number is generally dialed by all callers. If that line is busy, the phone company will "roll-over" the call to another line in that group. Also called "hunt-group" or "rotary".
ROM - Acronym for read-only memory.
Roofing Filter - A low-pass filter used to reduce unwanted higher frequencies.
Room Noise Level - Synonym ambient noise level.
Room Preset - In multimedia and virtual reality, information that may be used to select a video source, and then control the video source to provide the desired view. The ability to provide presets is optional and may not be supported in all terminals.
Root - In computer science, the highest level of a hierarchy.
Root-Mean-Square (rms) Deviation - A single quantity,
rms, characterizing a function, f (x), given by
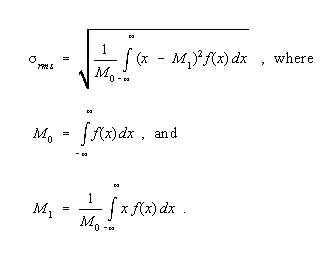
Note: The term "rms deviation" is also used in probability and statistics, where the normalization, M 0, is unity. Here, the term is used in a more general sense.
Root-Mean-Square (rms) Pulse Broadening - The temporal rms deviation of the impulse response of a system.
Root-Mean-Square (rms) Pulse Duration - A special case of root-mean-square deviation where the independent variable is time and f ( t ) describes the pulse waveform.
Rope Lay Conductor - A conductor composed of a central core surrounded by one or more layers of helically wound groups of wires.
Rotary - An ambiguous term. "Rotary Group" means a roll-over group, and "Rotary Dialing" means pulse dialing.
Rotary Dial - A signaling mechanism--usually incorporated within a telephone set--that when rotated and released, generates dc pulses required for establishing a connection in a telephone system.
Rotary Dialing - means pulse dialing.
Rotary Group -A service provided by most phone companies that allows several lines to be tied together. A single number is generally dialed by all callers. If that line is busy, the phone company will "roll-over" the call to another line in that group. Also called "hunt-group", "rollover" and more recently "busy-line transfer".
Rotary Hunting - Hunting in which all the numbers in the hunt group are selected in a prescribed order. Note: In modern electronic switching systems, the numbers in the hunt group are not necessarily selected in consecutive order.
Rotary Switching - In telephone systems, an electro-mechanical switching method whereby the selecting mechanism consists of a rotating element using several groups of wipers, brushes, and contacts.
Rotational Position Sensing: [In magnetic media,] A technique used to locate a given sector, a desired track, and a specific record by continuous comparison of the read / write head position with appropriate synchronization signals.
Rounding - Deleting the least-significant digits of a number and applying some rule of correction to the part retained.
Round-Trip Delay Time -1. The elapsed time for transit of a signal over a closed circuit. Note: Round-trip delay time is significant in systems that require two-way interactive communication such as voice telephony or ACK / NAK data systems where the round-trip time directly affects the throughput rate. It may range from a very few microseconds for a short line-of-sight ( LOS ) radio system to many seconds for a multiple- link circuit with one or more satellite links involved. This includes the node delays as well as the media transit time. 2. In primary or secondary radar systems, the time required for a transmitted pulse to reach a target and for the echo or transponder reply to return to the receiver.
Route - 1. In communications systems operations, the geographical path that is followed by a call or message over the circuits that are used in establishing a chain of connections. 2. To determine the path that a message or call is to take in a communications network. Note: In a Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) internet, each IP datagram is routed separately. The route a datagram follows may include many gateways and many physical networks. 3. To construct the path that a call or message is to take in a communications network in going from one station to another or from a source user end instrument to a destination user end instrument.Route Diversity - The allocation of circuits between two points over more than one geographic or physical route with no geographic points in common.
Route Index - A pointer to a specific trunk group.
Route List - A specific list of trunk groups.
Route Matrix - In communications network operations, a record that indicates the interconnections between pairs of nodes in the network, and is used to produce direct routes, alternate routes, and available route tables from point to point.
Router - Highly sophisticated systems that connect local area networks (LANs). The router reads the network layer address of all packets transmitted by a network, and forwards only those addressed to another network.
Route Verification - Procedures that permit a signaling point to determine the accuracy and consistency of its routing data by sending a test message and analyzing the response message to determine whether the sent message traversed the expected route.
Routine - A computer program, called by another program, that may have some general or frequent use.
Routine Message - A category of precedence to be used for all types of messages that justify transmission by rapid means unless of sufficient urgency to require a higher precedence.
Routing - The process of determining and prescribing the path or method to be used for establishing telephone connections or forwarding messages.
Routing Address - Synonym routing number, routing table.
Routing Diagram - In a communications system, a diagram that (a) shows all links between all switchboards, exchanges, switching centers, and stations in the system, such as the links between primary relay , major relay, minor relay, and tributary stations as well as supplementary links, (b) is used to identify the stations and links, and (c) is used to indicate tape-relay routes, transfer circuits, refile circuits, radio links, operational status, line conditions, and other network information required for network operations and management.
Routing Directory - See routing table.
Routing Indicator (RI) -1. A group of letters assigned to indicate: (a) the geographic location of a station; (b) a fixed headquarters of a command, activity, or unit at a geographic location; and (c) the general location of a tape relay or tributary station to facilitate the routing of traffic over the tape relay networks. 2. In a message header, an address, i.e., group of characters, that specify routing instructions for the transmission of the message to its final destination. Note: Routing indicators may also include addresses of intermediate points.
Routing Label - The part of the message label that is used for message routing in the signaling network. It includes the destination point code, the originating point code, and the signaling link selection field.
Routing Number - Synonym routing address, routing table.
Routing Protocol - In an internet, a service protocol that is used (by routers, but not by hosts) to maintain routing tables; routing protocols are classified as either (a) interior gateway protocols, or (b) exterior gateway protocols.
Routing Table - A matrix associated with a network control protocol, which gives the hierarchy of link routing at each node.
RQ - Abbreviation for repeat-request. See ARQ.
RSL - Abbreviation for received signal level.
RTA - Abbreviation for remote trunk arrangement.
RTP - (Real Time Protocol) - Also known as Real Time Transport Protocol. Controls the transmission of packets of data that demands low latency (such as audio and video). Supports real-time transmission over IP networks and streaming as one means of delivery.
RTTY - Abbreviation for radio teletypewriter.
Rubidium Clock - A clock containing a quartz oscillator stabilized by a rubidium standard.
Rubidium Standard - A frequency standard in which a specified hyperfine transition of electrons in rubidium-87 atoms is used to control the output frequency. Note: A rubidium standard consists of a gas cell, which has an inherent long-term instability. This instability relegates the rubidium standard to its status as a secondary standard.
Run - The execution of one or more computer jobs or programs.
Run-Length Encoding - A redundancy -reduction technique for facsimile in which a run of consecutive picture elements having the same state ( gray scale or color) is encoded into a single code word.
Rural Radio Service - A public radio service rendered by fixed stations on frequencies below 1000 MHz used to provide (1) Basic Exchange Telecommunications Radio Service, which is public message communication service between a central office and subscribers located in rural areas, (2) public message communication service between landline central offices and different exchange areas which it is impracticable to interconnect by any other means, or (3) private line telephone, telegraph, or facsimile service between two or more points to which it is impracticable to extend service via landline.
Rural Subscriber Station -1. A fixed station in the rural radio service used by a subscriber for communication within a central office station. 2. One or more fixed transmitters in the rural radiotelephone service that receive service from central office transmitters.
RUS - Rural Utilities Service. The RUS is an agency of the United States Department of Agriculture. It’s a source of financing and technical assistance for rural telecommunication systems.RWI - Abbreviation for radio and wire integration.
RX - Abbreviation for receive, receiver.
RZ - Abbreviation for return-to-zero.
Fax Switch Products
|
*Note: All prices include shipping and handling in the continental US and most of Canada. We reserve the right to charge up to the actual price of shipping on all orders outside the continental United States. Customer is responsible for any taxes, duties or brokerage charges that may apply. All orders shipped UPS Ground unless specified. For air and express shipments, appropriate charges will be applied to your order.
Need Help?
- Call now for free phone consultation at 1-866-337-0965.
Click here if you want to share 2 devices on 1 line and don't know which device to choose.
Click here if you want to share 3 or more devices on one line and don't know what type to choose.
"Albert Einstein Presents Fax Switch "
"Dancing Bear Fax Switch Presentation"
![]()
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
You didn't find what you need here?
Please visit our sister company, SuperPhoneStore.com for wholesale to the public telephones, phone accessories or the latest electronics. We have over 4500 different products in stock from over 200 premier manufacturers. Check it out!