
Telecom Dictionary - Definitions of terms
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
T
T - Abbreviation for tera (1012). See International System of Units.
T-1 - - A leased line connection that can carry 1,544,000 bits per second. The T-1 carrier is the most commonly used digital transmission service in the United States, Canada, and Japan. It consists of 24 separate channels using pulse code modulation (PCM) signals with time-division multiplexing (TDM). T-1 lines were originally designed to transmit digitized voice signals. Current applications also include digital data transmission. T1 lines originally used copper wire but now also include optical and wireless media. A T-1 Outstate System has been developed for longer distances between cities.
Internet access providers are commonly connected to the Internet as a point-of-presence (POP) on a T1 line owned by a major telephone network. Many businesses also use T1 lines to connect to an Internet access provider.
See T-carrier.
T-3 - A leased line connection that can carry 44,736,000 bits per second. The T-3 carrier is a digital transmission that consists of 672 individual channels, each of which supports 64 Kbps using pulse code modulation (PCM) signals with time-division multiplexing (TDM). T-3 lines were originally designed to transmit digitized voice signals. Current applications also include digital data transmission. T3 lines originally used copper wire but now also include optical and wireless media. A T-3 Outstate System has been developed for longer distances between cities.Internet access providers are sometimes connected to the Internet as a point-of-presence (POP) on a T3 line owned by a major telephone network. Some businesses also use T3 lines to connect to an Internet access provider.
T1 (carrier) - The generic designator for any of several digitally multiplexed telecommunications carrier systems. Note 1: The designators for T-carrier in the North American digital hierarchy correspond to the designators for the digital signal (DS) level hierarchy. See the associated table below. Note 2: T-carrier systems were originally designed to transmit digitized voice signals. Current applications also include digital data transmission. Note 3: If an "F" precedes the "T", a fiber optic cable system is indicated at the same rates. Note 4: The table below lists the designators and rates for current T-Carrier systems. Note 5: The North American and Japanese hierarchies are based on multiplexing 24 voice-frequency channels and multiples thereof, whereas the European hierarchy is based on multiplexing 30 voice-frequency channels and multiples thereof. - See T-carrier.
T1 Line - A full-duplex digital transmission facility that is composed of transmission media (optical or metallic) and regenerators that carry one DS1 signal.
T3 (carrier) - A dedicated leased phone line connection supporting data rates of 44,736,000 bits per second. A T-3 line actually consists of 672 individual channels, each of which supports 64 Kbps.
T-3 lines are used mainly by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) connecting to the Internet backbone and for the backbone itself.
T-3 lines are sometimes referred to as DS3 lines. - See T-carrier.
T3 Line - A full-duplex digital transmission facility that is composed of transmission media (optical or metallic) and regenerators that carry one DS3 signal.
Tactical Automatic Digital Switching System (TADSS) - A transportable store-and-forward message-switching system used for rapid deployment in support of tactical forces.
Tactical Command and Control (C2) Systems - The equipment, communications, procedures, and personnel essential to a commander for planning, directing, coordinating, and controlling tactical operations of assigned forces pursuant to assigned missions.
Tactical Communications - Communications in which information of any kind, especially orders and decisions, are conveyed from one command, person, or place to another within the tactical forces, usually by means of electronic equipment, including communications security equipment, organic to the tactical forces. Note: Tactical communications do not include communications provided to tactical forces by the Defense Communications System (DCS), to nontactical military commands, and to tactical forces by civil organizations.
Tactical Communications System - A communications system that (a) is used within, or in direct support of, tactical forces, (b) is designed to meet the requirements of changing tactical situations and varying environmental conditions, (c) provides securable communications, such as voice, data, and video, among mobile users to facilitate command and control within, and in support of, tactical forces, and (d) usually requires extremely short installation times, usually on the order of hours, in order to meet the requirements of frequent relocation.
Tactical Data Information Link (TADIL) - A standardized communications link, approved by the Joint Staff, that is suitable for transmission of digital information, and is characterized by standardized message formats and transmission characteristics.
Tactical Data Information Link--A (TADIL--A) - A netted link in which one unit acts as a net control station and interrogates each unit by roll call. Note: Once interrogated, that unit transmits its data to the net. This means that each unit receives all the information transmitted. This is a direct transfer of data and no relaying is involved.
Tactical Data Information Link--B (TADIL--B) - A point-to-point data link between two units which provides for simultaneous transmission and reception of data (duplex).
Tactical Load - For the host service tactical forces, the total power requirements for communications, including the requirements for weapons, detection, command and control systems, and related support functions. Note: The tactical load is a part of the operational load.
TADIL - Acronym for tactical data information link.
TADSS - Acronym for Tactical Automatic Digital Switching System.
Tagged Image File Format (TIFF) - A file format used to store an image using the particular data structure of the file.
TAI - Abbreviation for International Atomic Time.
Tail Circuit - 1. A circuit which connects the serial lines of two modems together. 2. A communications line from the end of a major transmission link, such as a microwave link, satellite link, or LAN, to the end-user location. Note: A tail circuit is a part of a user-to-user connection.
Tailgate - To gain unauthorized physical access by following an authorized person through a controlled door.
Tailing - In facsimile systems, the excessive prolongation of the decay of the signal. Synonym hangover.
Take - See clip. 1. In moving picture or television technology, a relatively short, continuous set of frames (often including the associated audio, if any), stored on a recording medium. Synonyms clip, scene. 2. In audio, a short, uninterrupted sound track. Note: Both audio and video clips may be part of a digitized information package, e.g., on a Web page. 3. To limit to a predetermined level (e.g., at the output of an otherwise linear amplifier) the amplitude of an otherwise linear signal. Note: In contrast with an analog compression circuit, which reduces the dynamic range of a signal but retains its basic waveform, a clipping circuit treats (processes, amplifies) a signal in a linear fashion unless the output level reaches a certain threshold, which it may not exceed, and at which it remains unless the input decreases to a level at which the processed output level is lower than the clipping level.
Takeoff Angle - Synonym departure angle. - The angle between the axis of the main lobe of an antenna pattern and the horizontal plane at the transmitting antenna.
Tampering - 1. Penetration or modification of internal operations, or the insertion of active or passive tapping mechanisms, to determine the nature of, or monitor or record , e.g., secret data. 2. Unauthorized modification altering the proper functioning of INFOSEC equipment. 3. Unauthorized modification of sensitive systems or sensitive information.
Tandem - 1. Pertaining to an arrangement or sequencing of networks, circuits, or links, in which the output terminals of one network, circuit, or link are connected directly to the input terminals of another network, circuit, or link. Note: For example, concatenated microwave links constitute a tandem connection. 2. A switching system in the message network that establishes trunk-to-trunk connections. Tandems may be further identified as local tandems, LATA tandems, or access tandems.
Tandem Area - The general areas served by the local offices having direct trunks to or from the tandem office. This area may consist of one or more communities or may include only a portion of a relatively large city.
Tandem Center - In a switched public telecommunications network, a facility that connects trunks to trunks and does not connect any local loops.
Tandem Circuit - A general classification of circuits or trunks between a tandem central office unit and any other central office or switchboard. Synonym tandem trunk.
Tandem Connection - A call switched at a tandem office.
Tandem Office - A central office unit used primarily as an intermediate switching point for traffic between local central offices within the tandem area. Where qualified by a modifying expression, or other explanation, this term may be applied to an office employed for both the interconnection of local central offices within the tandem area and for the interconnection of these local offices with other central offices, e.g., long haul tandem office.
Tandem Signaling - One of the most difficult conditions for speech coders to perform well in is the case where a digital speech-coded signal is transmitted from the mobile to the base station, and then demodolated into an analog signal which is then speech coded for retransmission as a digital signal over a land line or wireless link. This situation, called tandem signaling, tends to exaggerate the bit errors originally received at the base station. Tandem signaling is difficult to protect against, but is an important evaluation criterion in the evaluation of speech coders. As wireless systems proliferate, there will be a greater demand for mobile-to-mobile communications, and such links will, by definition, involve at least two independent, noisy tandems.
Tandem Tie Trunk Network (TTTN) - An arrangement that permits sequential connection of tie trunks between PBX and Centrex® locations by using tandem operation. Note: Tandem operation permits two or more dial tie trunks to be connected at a tandem center to form a through connection.
Tandem Trunk - Synonym tandem circuit. - A general classification of circuits or trunks between a tandem central office unit and any other central office or switchboard.
Tap - 1. To draw energy from a circuit. 2. To monitor, with or without authorization, the information that is being transmitted via a communications circuit. 3. To extract a portion of the signal from an optical fiber or communications link. Note: One method of tapping an optical fiber is to bend it to a relatively short radius, thus promoting radiation of a portion of the optical signal.
Tapered Fiber - An optical fiber in which the cross section, i.e., cross-sectional diameter or area, varies, i.e., increases or decreases, monotonically with length.
Tape Relay - A method of retransmitting TTY traffic from one channel to another, in which messages arriving on an incoming channel are recorded in the form of perforated tape, this tape then being either fed directly and automatically into an outgoing channel, or manually transferred to an automatic transmitter for transmission on an outgoing channel.
Target Language - In computing, data processing, and communications systems, a language into which statements are translated. Note: Translators, assemblers, and compilers prepare target language programs, usually machine-language programs, from source language programs, usually high-level language programs written by programmers.
Tariff - Documents filed by a telephone company with a state public utility commission and the FCC describing its services and the payments to be charged for the services. The published schedule of rates or charges for a specific unit of equipment, facility, or type of service such as might be provided by a telecommunications common carrier.
TASI - Acronym for time-assignment speech interpolation.
TAT - Abbreviation for transatlantic telecommunications (cable). Note: TAT formerly stood for transatlantic telephone (cable).
T-carrier - In telecommunications, T-carrier is the generic designator for any of several digitally multiplexed telecommunications carrier systems originally developed by Bell Labs and used in North America and Japan. The basic unit of the T-carrier system is the DS0, which has a transmission rate of 64 kbit/s, and is commonly used for one voice circuit. Note 1: The designators for T-carrier in the North American digital hierarchy correspond to the designators for the digital signal (DS) level hierarchy. See the associated table below. Note 2: T-carrier systems were originally designed to transmit digitized voice signals. Current applications also include digital data transmission. Note 3: If an "F" precedes the "T", a fiber optic cable system is indicated at the same rates. Note 4: The table below lists the designators and rates for current T-Carrier systems. Note 5: The North American and Japanese hierarchies are based on multiplexing 24 voice-frequency channels and multiples thereof, whereas the European hierarchy is based on multiplexing 30 voice-frequency channels and multiples thereof.
The E-carrier system, where 'E' stands for European, is incompatible with the T-carrier and is used just about everywhere else in the world besides North America and Japan. It typically uses the E1 line rate and the E3 line rate. The E2 line rate is less commonly used.
TCB - Abbreviation for trusted computing base. - [The] totality of protection mechanisms within a computer system, including hardware, firmware, and software, the combination of which is responsible for enforcing a security policy. Note: The ability of a trusted computing base to enforce correctly a unified security policy depends on the correctness of the mechanisms within the trusted computing base, the protection of those mechanisms to ensure their correctness, and the correct input of parameters related to the security policy.
TCF - Abbreviation for technical control facility. - A physical plant, or a designated and specially configured part thereof, that (a) contains the equipment necessary for ensuring fast, reliable, and secure exchange of information, (b) typically includes distribution frames and associated panels, jacks, and switches and monitoring, test, conditioning, and orderwire equipment, and (c) allows telecommunications systems control personnel to exercise operational control of communications paths and facilities, make quality analyses of communications and communications channels, monitor operations and maintenance functions, recognize and correct deteriorating conditions, restore disrupted communications, provide requested on-call circuits, and take or direct such actions as may be required and practical to provide effective telecommunications services.
T-Coupler - A passive optical coupler having three ports (three fibers). Note 1: Two isolated inputs may be combined into one output; or one input, into two isolated outputs. Note 2: The amount of coupling loss, usually expressed in dB, between ports is determined by the design and construction of the coupler. [After FAA] Synonyms directional coupler, splitter, tee coupler.
TCP - Abbreviation for Transmission Control Protocol. In the Internet Protocol suite, a standard, connection-oriented, full-duplex, host-to-host protocol used over packet-switched computer communications networks. Note 1: TCP corresponds closely to the ISO Open Systems Interconnection--Reference Model (OSI--RM) Layer 4 (Transport Layer). Note 2: The OSI--RM uses TP-0 or TP-4 protocols for transmission control. See Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
TCP/IP - Abbreviation for Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol. Two interrelated protocols that are part of the Internet protocol suite. Note 1: TCP operates on the OSI Transport Layer and breaks data into packets. IP operates on the OSI Network Layer and routes packets. Note 2: TCP/IP was originally developed by the U.S. Department of Defense.
TCP/IP Suite - The suite of interrelated protocols associated with Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol. Note 1: The TCP/IP Suite includes, but is not limited to, protocols such as TCP, IP, UDP, ICMP, FTP, and SMTP. Note 2: Additional application and management protocols are sometimes considered part of the TCP/IP Suite. This includes protocols such as SNMP.
TCS - Abbreviation for trusted computer system. 1. [An] information system (IS) employing sufficient hardware and software assurance measures to allow simultaneous processing of a range of classified or sensitive information. 2. A data processing system that provides sufficient computer security to allow for concurrent access to data by users with different access rights and to data with different security classification and security categories.
TCU - Abbreviation for teletypewriter control unit. - A device that controls and coordinates operations between teletypewriters and message switching centers.
TDD - Abbreviation for Telecommunications Device for the Deaf. - A machine that uses typed input and output, usually with a visual text display, to enable individuals with hearing or speech impairments to communicate over a telecommunications network.
TDEA Decryption Operation - the transformation of a 64-bit block I into a 64-bit block O that is defined as follows: O = DK1(EK2(DK3(I))). The standard specifies the following keying options for bundle (K1, K2, K3)
- Keying Option 1 - K1, K2, and K3 are independent keys;
- Keying Option 2 - K1 and K2 are independent keys and K3 = K1;
- Keying Option 3 - K1 = K2 = K3.
TDM - Abbreviation for time-division multiplexing. - 1. Digital multiplexing in which two or more apparently simultaneous channels are derived from a given frequency spectrum, i.e., bit stream, by interleaving pulses representing bits from different channels. Note: Successive pulses represent bits from successive channels, e.g., voice channels in a T1 system. 2. A multiplexing technique whereby two or more channels are derived from a transmission medium by dividing access to the medium into sequential intervals. Each channel has access to the entire bandwidth of the medium during its interval. This implies that one transmitter uses one channel to send several bit streams of information.
TDMA - Abbreviation for time-division multiple access. - 1. A communications technique that uses a common channel (multipoint or broadcast) for communications among multiple users by allocating unique time slots to different users. Note: TDMA is used extensively in satellite systems, local area networks, physical security systems, and combat-net radio systems. 2. A multiple access technique whereby users share a transmission medium by being assigned and using (one at a time) for a limited number of time division multiplexed channels; implies that several transmitters use one channel for sending several bit streams.
TE - Abbreviation for transverse electric. See transverse electric mode. A mode whose electric field vector is normal to the direction of propagation. Note: TE modes may be useful modes in waveguides. In an optical fiber, TE and TM modes correspond to meridional rays.
Technical Area - In the military community, an area in which temperature, humidity, or access is controlled because it contains equipment, such as communications, computing, control, or support equipment, that requires such controls.
Technical Control Facility (TCF) - A physical plant, or a designated and specially configured part thereof, that (a) contains the equipment necessary for ensuring fast, reliable, and secure exchange of information, (b) typically includes distribution frames and associated panels, jacks, and switches and monitoring, test, conditioning, and orderwire equipment, and (c) allows telecommunications systems control personnel to exercise operational control of communications paths and facilities, make quality analyses of communications and communications channels, monitor operations and maintenance functions, recognize and correct deteriorating conditions, restore disrupted communications, provide requested on-call circuits, and take or direct such actions as may be required and practical to provide effective telecommunications services.
Technical Control Hubbing Repeater - Synonym data conferencing repeater. - A device that enables any one user of a group of users to transmit a message to all other users in that group.
Technical Load - The portion of the operational load required for communications, tactical operations, and ancillary equipment including necessary lighting, air-conditioning, or ventilation required for full continuity of communications.
Technical Vulnerability - In information handling, a hardware, software, or firmware weakness, or design deficiency, that leaves a system open to assault, harm, or unauthorized exploitation, either externally or internally, thereby resulting in unacceptable risk of information compromise, information alteration, or service denial.
TED - Abbreviation for trunk encryption device. - A bulk encryption device used to provide secure communications over a wideband digital transmission link. Note: A TED is usually located between the output of a trunk group multiplexer and a wideband radio or cable facility.
Tee Coupler - A passive coupler that has three ports. Synonyms directional coupler, splitter, T-coupler.
TEK - Abbreviation for traffic encryption key. - [A] key used to encrypt plain text or to superencrypt previously encrypted text and/or to decrypt cipher text.
Teleaction Service - In Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) applications, a telecommunications service that uses very short messages with very low data transmission rates between the user and the network.
Telecommand - The use of telecommunication for the transmission of signals to initiate, modify or terminate functions of equipment at a distance.
Telecommunication - 1. Any transmission, emission, or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic systems. 2. Any transmission, emission, or reception of signs, signals, writings, images, sounds, or information of any nature by wire, radio, visual, or other electromagnetic systems.
Telecommunication Administration - An administration, or the part of a combined postal and telecommunication administration, concerned with the provision of telecommunication service.
Telecommunication Architecture - See network architecture. - 1. The design principles, physical configuration, functional organization, operational procedures, and data formats used as the bases for the design, construction, modification, and operation of a communications network. 2. The structure of an existing communications network, including the physical configuration, facilities, operational structure, operational procedures, and the data formats in use.
Telecommunications - Telecommunications is any process that enables one or more users to pass to one or more other users information of any nature delivered in any usable form, by wire, radio, visual, or other electrical, electromagnetic, optical means. The word is derived from the Greek tele, "far off," and the Latin communicare "to share."
Telecommunications Center - See communications center. - 1. An agency charged with the responsibility for handling and controlling communications traffic. The center normally includes message center, transmitting, and receiving facilities. 2. A facility that (a) serves as a node for a communications network, (b) is equipped for technical control and maintenance of the circuits originating, transiting, or terminating at the node, (c) may contain message-center facilities, and (d) may serve as a gateway.
Telecommunications Closet - In a premises distribution system, a telecommunications closet is an area for connecting the horizontal and backbone wiring and for containing active or passive PDS equipment.
Telecommunications Device for the Deaf (TDD) - A machine that uses typed input and output, usually with a visual text display, to enable individuals with hearing or speech impairments to communicate over a telecommunications network.
Telecommunication Sector - The sector that includes the telecommunications service providers, network operators, regulators, manufacturers, subscribers, and users.
Telecommunications Facilities - The aggregate of equipment, such as radios, telephones, teletypewriters, facsimile equipment, data equipment, cables, and switches, used for providing telecommunications services.
Telecommunications Infrastructure - The organizations, personnel, procedures, facilities, and networks employed to transmit and receive information by electrical or electronic means. Note 1: Telecommunications facilities include, but are not necessarily limited to, terrestrial radio, metallic and optical fiber cables, artificial Earth satellite communications, radio and television stations (traditional broadcast as well as cable and satellite broadcast), public switched telephone network (s), etc. Note 2: Examples of advanced telecommunications infrastructure facilities are direct broadcast satellite (DBS), digital audio broadcasting (DAB), Advanced Digital Television, and the Global Positioning System (GPS), which is used extensively for precise navigation and timing.
Telecommunications Link - A communications facility or channel, including feeder and local distribution plant, having a termination in a center in the telecommunications network. Examples of such a link include (but are not necessarily restricted to): optical-fiber cable, coaxial cable, metallic cables, transmitting and receiving antenna.
Telecommunications Load Equipment - Equipment powered from a primary or secondary distribution of a centralized dc power system owned or operated by exchange and interexchange carriers.
Telecommunications Management Network (TMN) - A network that interfaces with a telecommunications network at several points in order to receive information from, and to control the operation of, the telecommunications network. Note: A TMN may use parts of the managed telecommunications network to provide for the TMN communications.
Telecommunications Network - A telecommunications network is a system of interconnected facilities designed to carry traffic from a variety of telecommunications services. The network has two different but related aspects. In terms of its physical components, it is a facilities network. In terms of the variety of telecommunications services that it provides, it can support a set of many traffic networks, each representing a particular interconnection of facilities.
Telecommunications Relay Center Fee/Charge/Surcharge - This state fee helps pay for the relay center that transmits and translates calls for people who are deaf, hard-of-hearing or speech disabled. Mandated nationally by Congress with the passage of the Americans with Disabilities Act, it may also be called “Telecommunication Devices for the Deaf Tax.”
Telecommunications Security - See communications security. Measures and controls taken to deny unauthorized persons information derived from telecommunications and to ensure the authenticity of such telecommunications. Note: Communications security includes cryptosecurity, transmission security, emission security, and physical security of COMSEC material. [INFOSEC]
- (a) cryptosecurity: [The] component of communications security that results from the provision of technically sound cryptosystems and their proper use. [NIS]
- (b) emission security: Protection resulting from all measures taken to deny unauthorized persons information of value which might be derived from intercept and analysis of compromising emanations from crypto-equipment, AIS, and telecommunications systems. [NIS]
- (c) physical security: The component of communications security that results from all physical measures necessary to safeguard classified equipment, material, and documents from access thereto or observation thereof by unauthorized persons. [JP 1-02]
- (d) transmission security: [The] component of communications security that results from the application of measures designed to protect transmissions from interception and exploitation by means other than cryptanalysis.
Telecommunications Service - 1. Any service provided by a telecommunication provider. 2. A specified set of user-information transfer capabilities provided to a group of users by a telecommunications system. Note: The telecommunications service user is responsible for the information content of the message. The telecommunications service provider has the responsibility for the acceptance, transmission, and delivery of the message.
Telecommunications Service Priority (TSP) Service - A regulated service provided by a telecommunications provider, such as an operating telephone company or a carrier, for NS/EP telecommunications. Note: The TSP service replaced Restoration Priority (RP) service effective September 1990.
Telecommunications Service Priority (TSP) System - A system that provides a means for telecommunications users to obtain priority treatment from service providers for the NS/EP telecommunications requirements. Note: The TSP system replaced the Restoration Priority (RP) system effective September 1990.
Telecommunications Service Priority (TSP) System User - Any individual, organization, or activity that interacts with the NS/EP TSP System.
Telecommunications System - See communications system. A collection of individual communications networks, transmission systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and data terminal equipment (DTE) usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole. Note: The components of a communications system serve a common purpose, are technically compatible, use common procedures, respond to controls, and operate in unison.
Telecommunications System Operator - The organization responsible for providing telecommunications services to users.
Teleconference - The live exchange of information among persons and machines remote from one another but linked by a telecommunications system. Note: The telecommunications system may support the teleconference by providing audio, video, and data services by one or more means, such as telephone, telegraph, teletype, radio, and television.
Telegram - Written matter intended to be transmitted by telegraphy for delivery to the addressee. This term also includes radiotelegrams unless otherwise specified. In this definition the term telegraphy has the same general meaning as defined in the [1979 General Worldwide Administrative Radio Conference] Convention.
Telegraph - See telegraphy. A form of telecommunication which is concerned in any process providing transmission and reproduction at a distance of documentary matter, such as written or printed matter or fixed images, or the reproduction at a distance of any kind of information in such a form. For the purposes of the Radio Regulations, unless otherwise specified therein, telegraphy shall mean a form of telecommunication for the transmission of written matter by the use of a signal code.
Telegraphy - A form of telecommunication which is concerned in any process providing transmission and reproduction at a distance of documentary matter, such as written or printed matter or fixed images, or the reproduction at a distance of any kind of information in such a form. For the purposes of the Radio Regulations, unless otherwise specified therein, telegraphy shall mean a form of telecommunication for the transmission of written matter by the use of a signal code.
Telemeter - A measuring, transmitting, and receiving device used in telemetry. Any scientific instrument for observing events at a distance and transmitting the information back to the observer.
Telemetered, Telemetering, Telemeters - To measure, transmit, and receive (data) automatically from a distant source, as from a spacecraft or an electric power grid.
Telemetry - 1. The use of telecommunication for automatically indicating or recording measurements at a distance from the measuring instrument. 2. The transmission of non-voice signals for the purpose of automatically indicating or recording measurements at a distance from the measuring instrument.
Telephone - A user end instrument that is used to transmit and receive voice-frequency signals.
Telephone Book - A directory of the names of telephone subscribers with their telephone numbers and often their addresses. A directory containing an alphabetical list of telephone subscribers and their telephone numbers.
Telephone Booth - A small enclosure containing a public telephone. Also a slang term referring to one of the many phone terminals on the floor of the New York Stock Exchange that is used by floor traders to receive orders.
Telephone Exchange - Synonym for central office. A central system of switches and other equipment that establishes connections between individual telephones. Also called switchboard. A workplace that serves as a telecommunications facility where lines from telephones can be connected together to permit communication.
In the field of telecommunications, a telephone exchange (US: telephone switch) is a piece of equipment that connects phone calls. It is what makes your phone calls "work" in the sense of making connections and relaying the speech information.
The term exchange can also be used to refer to an area served by a particular switch. And more narrowly, it can refer to the first three digits of the local number. In the past, the first two or three digits would map to a mnemonic exchange name, e.g. 869–1234 was formerly TOwnsend 9–1234, and before that (in some localities) might have been TOWnsend 1234 (only the capital letters and numbers being dialed). In December of 1930, New York City became the first locality in the United States to adopt the two-letter, five-number format; it remained alone in this respect until after World War II, when other municipalities across the country began to follow suit (in some areas, most notably much of California, telephone numbers in the 1930s and early 1940s consisted of only six digits, two letters which began the exchange name followed by four numbers, as in DUnkirk 0799).
Prior to the mid-1950s, the number immediately following the name could never be a "0" or "1;" indeed, "0" was never pressed into service at all, except in the immediate Los Angeles area (the "BEnsonhurst 0" exchange mentioned in an episode of the popular TV sitcom The Honeymooners was fictitious). In 1955, the Bell System attempted to standardize the process of naming exchanges by issuing a "recommended list" of names to be used for the various number combinations. In 1961, New York Telephone introduced "selected-letter" exchanges, in which the two letters did not mark the start of any particular name (example: FL 6-9970), and by 1965 all newly-connected phone numbers nationwide consisted of numerals only (Wichita Falls, Texas had been the first locality in the United States to implement the latter, having done so in 1958; meanwhile, pre-existing numbers continued to be displayed the old way in many places well into the 1970s). The United Kingdom never adopted the two-letter, five-number format, remaining with the three-letter, four-number format until converting to all-numeric phone numbers in 1968.
In the United States, the word exchange can also have the technical meaning of a local access and transport area under the Modification of Final Judgment (MFJ).
Telephone Jack - In the U. S., telephone jacks are also known as registered jacks, sometimes described as RJ-XX, and are a series of telephone connection interfaces (receptacle and plug) that are registered with the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC). They derive from interfaces that were part of AT&T's Universal Service Order Codes (USOC) and were adopted as part of FCC regulations (specifically Part 68, Subpart F. Section 68.502). The term jack sometimes means both receptacle and plug and sometimes just the receptacle.
RJ-11
The most common telephone jack is the RJ-11 jack, which can have six conductors but usually is implemented with four. The RJ-11 jack is likely to be the jack that your household or office phones are plugged into from the ordinary "untwisted" wire (sometimes called "gray satin" or "flat wire") people are most familiar with. In turn, the jacks connect to the "outside" longer wires known as twisted pair that connect to the telephone company central office or to a private branch exchange (PBX).The four wires are usually characterized as a red and green pair and a black and white pair. The red and green pair typically carry voice or data. On an outside phone company connection, the black and white pair may be used for low-voltage signals such as phone lights. On a PBX system, they may be used for other kinds of signaling.
A computer that uses a dial-up modem to connect to a network is usually plugged into an RJ-11 jack.
RJ-14
The RJ-14 is similar to the RJ-11, but the four wires are used for two phone lines. Typically, one set of wires (for one line) contains a red wire and a green wire. The other set contains a yellow and black wire. Each set carries one analog "conversation" (voice or data).RJ-45
The RJ-45 is a single-line jack for digital transmission over ordinary phone wire, either untwisted or twisted. The interface has eight pins or positions. For connecting a modem, printer, or a data PBX at a data rate up to 19.2 Kbps, you can use untwisted wire. For faster transmissions in which you're connecting to an Ethernet 10BASET network, you need to use twisted pair wire. (Untwisted is usually a flat wire like common household phone extension wire. Twisted is often round.)There are two varieties of RJ-45: keyed and unkeyed. Keyed has a small bump on its end and the female complements it. Both jack and plug must match.
Telephone Line Sharing - A technology that allows a single phone line to share incoming and outgoing access for multiple devices. Typically Telephone Line Sharing Technology allows voice (phones and answering machine) and a fax machine or fax modem to operate on a shared phone line. Other applications include any variation of voice, a fax machine, fax/modem and/or modem(s).
Incoming calls are automatically routed to the proper device(s). If the call comes in and it is a fax call, the call is automatically routed to the fax machine or fax modem. If the call is a modem call, it is routed to the correct modem. Voice calls are routes to phone(s) and/or answering machine. May require a security access code (SAC) in the dialing string to automatically switch to the modem.
Since the need for to subscribe to a separate "fax line" from the local telephone company is eliminated, the return on investment (ROI) is very high. The initial cost of the device is returned in savings in a few months. After that you will save the monthly bills associated with fax, data or voice lines. For almost every business, a telephone line sharing technology is a smart investment.
Telephone Network - The system of wires, fiber-optic cables, satellites and transmission towers that transmit telephone messages from caller to receiver.
Telephone Number - The unique network address that is assigned to a telephone user, i.e., subscriber, for routing telephone calls.
Telephone Plug - A telephone plug is a type of male connector used to connect a telephone to the telephone wiring in a home or business, and in turn to a local telephone network. It is inserted into its female counterpart, a telephone "jack", commonly fixed to a wall or baseboard. The standard for telephone plugs varies from country to country, though the RJ11 "modular connector" has become by far the most common.
A connection standard, such as "RJ11", specifies not only the physical connector, but how it is wired (the "pinout"). Modular connectors are specified for the Registered Jack series of connectors, as well as for Ethernet and other connectors, such as 4P4C (4 position, 4 contacts) modular connectors, the de facto standard on handset cables, often improperly referred to as "RJ" connectors
Telephone Switch - A large-scale computer used to route telephone calls in a central office. Such devices are made by Lucent, Nortel and others.
Telephone Tag - A series of unsuccessful calls exchanged by two people who are attempting to contact each other by telephone.
Telephonic - 1. Of or relating to telephones. 2. Transmitted or conveyed by telephone.
Telephony - 1. The branch of science devoted to the transmission, reception, and reproduction of sounds, such as speech and tones that represent digits for signaling. Note 1: Transmission may be via various media, such as wire, optical fibers, or radio. Note 2: Analog representations of sounds may be digitized, transmitted, and, on reception, converted back to analog form. Note 3: "Telephony" originally entailed only the transmission of voice and voice-frequency data. Currently, it includes new services, such as the transmission of graphics information. 2. A form of telecommunication set up for the transmission of speech or, in some cases, other sounds. 3. The technology and manufacture of telephone equipment. 4. The transmission of sound between distant stations, especially by radio or telephone.
Meaning "sound over distance," it refers to electronically transmitting the human voice. In the beginning, telephony dealt only with analog signals in the circuit-switched networks of the telephone companies. It later referred to a mix of analog and digital circuits, but still with the telephone industry. Starting in the 1990s, telephony began to embrace sending voice over IP (VoIP) networks, which is now deployed by common carriers, private enterprises and independent VoIP providers.
Telephoto - 1. Of or relating to a photographic lens or lens system used to produce a large image of a distant object. 2. Of or relating to an instrument that electrically transmits photographs. 3. Pertaining to pictures transmitted via a telecommunications system.
Telephotograph - 1. A telephoto. 2. A photograph transmitted and reproduced over a distance.
Telephotography - 1. The process or technique of photographing distant objects, using a telephoto lens on a camera. 2. The technique or process of transmitting charts, pictures, and photographs over a distance.
Teleprinter - A typewriter-like terminal with a keyboard and built-in printer. It can be a desktop or portable unit. Teleprinters were quite common years ago as input terminals for computers, but have given way to the video screen. Teleprinter-like devices are still used in retail applications where receipts are necessary.
Teleprinters were widely used starting with the very first computers. They lived well into the 1970s as a computer input device. Any keyboard and printing unit can be called a teleprinter.
Paper tape was widely used on teleprinters to record incoming data. The reel of tape in this picture is on the lower left side of the unit. (Image courtesy of General Electric Company.)
A teletypewriter that can only receive data and does not have a keyboard for transmission.
Teleprocessing - The combining of telecommunications and computer operations interacting in the automatic processing, reception, and transmission of data and/or information. [JP 1-02] Note: Teleprocessing includes human-machine interface equipment.
Teleran - An air-traffic control system in which the image of a ground-based radar unit is televised to aircraft in the vicinity so that pilots may see their positions in relation to other aircraft.
Teletext - An electronic communications system in which printed information is broadcast by television signal to sets equipped with decoders. An international store-and-forward essentially error-free communications service that is defined by the CCITT (now the ITU-T), has a data signaling rate (DSR) of 2400 b/s over switched telephone networks, and has a communications protocol that supports the CCITT Group 4 facsimile service.
Teletraining - Training that (a) in which usually live instruction is conveyed in real time via telecommunications facilities, (b) that may be accomplished on a point-to-point basis or on a point-to-multipoint basis, and (c) may assume many forms, such as a teleseminar, a teleconference, or an electronic classroom, usually including both audio and video. Synonyms distance learning, distance training, electronic classroom, virtual instruction.
Teletype - A trademark used for a teletypewriter.
Teletypewriter (TTY) - A printing telegraph instrument that has a signal-actuated mechanism for automatically printing received messages. An electromechanical typewriter that either transmits or receives messages coded in electrical signals carried by telegraph or telephone wires. Note 1: A TTY may have a keyboard similar to that of a typewriter for sending messages. Note 2: Radio circuits carrying TTY traffic are called "RTTY circuits" or "RATT circuits."
Teletypewriter Control Unit (TCU) - A device that controls and coordinates operations between teletypewriters and message switching centers.
Teletypewriter Exchange Service (TWX) - A switched teletypewriter service in which suitably arranged teletypewriter stations are provided with lines to a central office for access to other such stations.
Teletypewriter Signal Distortion - The shifting of signal pulse transitions from their proper positions relative to the beginning of the start pulse. Note: The magnitude of the distortion is expressed in percent of a perfect unit pulse length. Synonym start-stop TTY distortion.
Television (TV) - A form of telecommunication for the transmission of transient images of fixed or moving objects.Note 1: The picture signal is usually accompanied by the sound signal. Note 2: In North America, TV signals are generated, transmitted, received, and displayed in accordance with the NTSC standard.
Telex - 1. A communications system consisting of teletypewriters connected to a telephonic network (automatic exchanges) to send and receive signals. 2. A message sent or received by such a system.
(TELetypewriter EXchange) An international, dial-up data communications service administered in the U.S. by AT&T, MCI and other providers. Developed in the U.S. and other European countries in the 1930s, it was the first data communications service that used typewriter-like terminals (teletypewriters). Prior to Telex, telegrams and cablegrams were the primary method for delivering a text message. By the 1960s, Telex became a worldwide, real time, data communications service. Although diminishing each year, Telex is still used for commerce in more than 200 countries.
Telex started out transmitting Baudot code at 50 bps. Although upgraded, it is still a low-speed data service. It was originally administered worldwide by various carriers and the local PTTs. Western Union handled the U.S., and in 1971, purchased and integrated the Bell System's TWX service. AT&T acquired Western Union's Telex service in 1991.
Telex Machine - A character printer connected to a telegraph that operates like a typewriter
Telnet - A program that allows Internet users to login to computers other than their host. Telnet also refers to the act of doing so. The TCP/IP standard network virtual terminal protocol that is used for remote terminal connection service and that allows a user at one site to interact with systems at other sites as if that user terminal were directly connected to computers at those sites.
TEM - Abbreviation for transverse electric and magnetic mode. - A mode whose electric and magnetic field vectors are both normal to the direction of propagation. Note: The TEM mode is the most useful mode in a coaxial cable.
TEMPEST - 1. [A] Short name referring to investigation, study, and control of compromising emanations from information systems (IS) equipment. 2. To shield against compromising emanations.
Temporal Application - A video application requiring high temporal resolution, i.e., reduced jerkiness, possibly at the expense of reduced spatial resolution. Note: An example of temporal applications is the ability to accurately discern moving image features such as facial expressions and lip movements.
Temporal Edge Noise - In a video display, that form of edge busyness that is characterized by time-varying sharpness at the edges of objects.
Terminal - A device capable of sending, receiving, or sending and receiving information over a communications channel.
Terminal Access Controller (TAC) - A host computer that accepts terminal connections, usually from dial-up lines, and that allows the user to invoke Internet remote log-on procedures, such as Telnet.
Terminal Adapter - An interfacing device employed at the "R" reference point in an ISDN environment that allows connection of a non-ISDN terminal at the physical layer to communicate with an ISDN network. Note: Typically, a terminal adapter will support standard RJ-11 telephone connection plugs for voice and RS-232C, V.35 and RS-449 interfaces for data.
Terminal Data - Data maintained for each terminal including the current terminal location (and capabilities).
Terminal Deregistration - The process by which a wireless terminal's previous location registration is canceled.
Terminal Endpoint (TE) Functional Group - A functional group that includes functions broadly belonging to Layer 1 and higher layers of the ITU-T Recommendation X.200 Reference Model. Note 1: The functions of a TE functional group are performed on various types of equipment, or combinations of equipment, such as digital telephones, data terminal equipment, and/or integrated work stations. Note 2: Examples of TE functions are protocol-handling, maintenance, interface, and connection functions.
Terminal Equipment - 1. Communications equipment at either end of a communications link, used to permit the stations involved to accomplish the mission for which the link was established. 2. In radio-relay systems, equipment used at points where data are inserted or derived, as distinct from equipment used only to relay a reconstituted signal. 3. Telephone and telegraph switchboards and other centrally located equipment at which communications circuits are terminated. 4. Equipment that originates or terminates signals at the specified rate.
Terminal Identifier - A code identifying a specific terminal.Terminal Impedance - 1. The impedance as measured at the unloaded output terminals of transmission equipment or a line that is otherwise in normal operating condition. 2. The ratio of voltage to current at the output terminals of a device, including the connected load.
Terminal Mobility - In commercial wireless networks, the ability of a terminal, while in motion, to access telecommunication services from different locations, and the capability of the network to identify and locate that terminal.
Terminal Mobility Controller - A device that provides the control logic for terminal authentication, location management, alerting, and routing to radio personal terminal / radio terminations (RPT/RTs).
Terminal Mobility Management - In personal communications service (PCS), (a) providing authentication of terminal information, (b) maintaining terminal location and capability information for each terminal, and (c) providing translation between terminal identification and location (routing address) for the completion of calls to terminals.
Terminal Registration - The process of associating a terminal with a terminal registration area.
Terminal Registration Area - A territory in which a wireless terminal is registered for terminal mobility.
Terminal Service Profile (TSP) - Information that the service provider maintains for a given user to characterize the services offered by the network to that user. A TSP may be allocated to an interface or to a particular user equipment or a group of user equipment.
Terminal Type - The variety of terminal or the originator (e.g., dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) phone, ISDN terminal).
Terminating Endpoint - In a wideband packet node, the part of the node that receives packetized traffic, depacketizes it, and then plays it back as channelized traffic.
Terminating Network Function - Of a UPT call, any network function associated with the termination of the call to the destination terminal.
Termination - 1. The load connected to a transmission line, circuit, or device. Note: For a uniform transmission line, if the termination impedance is equal to the characteristic impedance of the line, wave reflections from the end of the line will be avoided. 2. In hollow metallic waveguides, the point at which energy propagating in the waveguide continues in a nonwaveguide propagation mode into a load. 3. An impedance, often resistive, that is connected to a transmission line or piece of equipment as a dummy load, for test purposes.
Terminus - A device used to terminate, position, and hold an optical fiber within a connector.
Ternary Signal - A signal that can assume, at any given instant, one of three significant conditions, such as power level, phase position, pulse duration, or frequency. Note: Examples of ternary signals are (a) a pulse that can have a positive, zero, or negative voltage value at any given instant, (b) a sine wave that can assume phases of 0°, 120°, or 240° relative to a clock pulse, and (c) a carrier wave that can assume any one of three different frequencies depending on three different modulation signal significant conditions.
Terrestrial Broadcasting - A broadcast signal transmitted over-the-air to an antenna.
Terrestrial Microwave Radio - Terrestrial microwave radio is a transmission systems consisting of at least two radio transmitter/receivers (transceivers) connected to high gain antennas (directional antennas which concentrate electromagnetic or radiowave energy in narrow beams) focused in pairs on each other. The operation is point-to-point, that is, communications are established between two and only two antennas (installations) with line-of-sight visibility. This can be contrasted to point-to- multipoint systems like broadcast radio or television.
Terrestrial Radiocommunication - Any radiocommunication other than space radiocommunication or radio astronomy.
Terrestrial Station - A station effecting terrestrial radiocommunication. In these [Radio] Regulations, unless otherwise stated, any station is a terrestrial station.
Test and Validation - Physical measurements taken (a) to verify conclusions obtained from mathematical modeling and analysis or (b) for the purpose of developing mathematical models.
Test Antenna - An antenna of known performance characteristics used in determining transmission characteristics of equipment and associated propagation paths.
Test Key - Key intended for testing of COMSEC equipment or systems.
Test Point - A point within a piece of equipment or an equipment string that provides access to signals for the purpose of fault isolation.
Test Tone - A tone sent at a predetermined level and frequency through a transmission system for test purposes, such as for facilitating measurements and for aligning gains and losses in the system.
Text Format vs. HTML Format - Some Web applications, such as e-mail or Web pages, can either be viewed in Text or HTML formats. Text formats generally display only the words (text) in an e-mail or on a Web page and not graphics, such as artwork or photos. HTML format allows display of both text and graphics.
TGM - Abbreviation for trunk group multiplexer.
THD - Abbreviation for total harmonic distortion. - Of a signal, the ratio of (a) the sum of the powers of all harmonic frequencies above the fundamental frequency to (b) the power of the fundamental frequency. Note 1: The THD is usually expressed in dB. Note 2: Measurements for calculating the THD are made at the output of a device under specified conditions.
Thermal Noise: The noise generated by thermal agitation of electrons in a conductor. The noise power, P, in watts, is given by P = kT
f, where k is Boltzmann's constant in joules per kelvin, T is the conductor temperature in kelvins, and
f is the bandwidth in hertz. Note 1: Thermal noise power, per hertz, is equal throughout the frequency spectrum, depending only on k and T. Note 2: For the general case, the above definition may be held to apply to charge carriers in any type of conducting medium. Synonym Johnson noise.
Thermal Radiation - 1. Electromagnetic radiations emitted from a heat or light source as a consequence of its temperature; it consists essentially of ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiations. [JP1] 2. The heat and light produced by a nuclear explosion.
Thermodynamic Temperature - A measure, in kelvins (K), proportional to the thermal energy of a given body at equilibrium. Note 1: A temperature of 0 K is called "absolute zero," and coincides with the minimum molecular activity (i.e., thermal energy) of matter. Note 2: Thermodynamic temperature was formerly called "absolute temperature." Note 3: In practice, the International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90) serves as the basis for high-accuracy temperature measurements in science and technology.
The Stick - Business quality Single Line Automatic Call Processor. Line sharing device for small or home business as well large corporations and organizations. Automatically routes calls to the assigned device. The Stick allows up to three telecommunication devices plus an answering machine to share one single phone line. This is our most popular fax switch. For more information: The Stick brochure , The Stick online manual.
THF - Abbreviation for tremendously high frequency. See electromagnetic spectrum.
Thin Client (computing) - A server-centric computing model in which the application software, data, and CPU power resides on a network server rather than on the client computer (s). Note 1: This computing philosophy allows administrators to purchase one relatively powerful and expensive server and be confident that any external terminal, regardless of its power or sophistication, can run applications on the server. Most "shopping" Web pages, for example, are thin-client applications (i.e., the client needs nothing more than a browser and a connection to the network to be able to search the "shopping" page and to order products). Local area networks can use thin-client modeling to install only one copy of necessary programs onto the main server for many clients on the network to use. Note 2: Server software is required to interface clients with the software on the server. Synonyms Internet appliance (computing), Internet box (computing), network computer.
Thin-Client Software - Computer programs that reside on a server and react to external requests from a client. Note: This is in contrast to software that is installed on each client computer in a network. Software that resides only on a single server can be maintained and updated with minimal effort.
Thin-Film Laser - A laser that is constructed by thin-film deposition techniques on a substrate for use as a light source, is usually used to drive thin-film optical waveguides, and may be used in integrated optical circuits.
Thin-Film Optical Modulator - A modulator that consists of multilateral films of material of different optical characteristics, is capable of modulating transmitted light by using electro-optic, electro-acoustic, or magneto-optic effects to obtain signal modulation, and may be used as a component in integrated optical circuits.
Thin-Film Optical Multiplexer - A multiplexer that consists of multi layered films of material of different optical characteristics, is capable of multiplexing transmitted light by using electro-optic, electro-acoustic, or magneto-optic effects to obtain signal multiplexing, and may be used as a component in integrated optical circuits.
Thin-Film Optical Switch - A switch that consists of multi layered films of material of different optical characteristics, that is capable of switching transmitted light by using electro-optic, electro-acoustic, or magneto-optic effects to obtain signal switching, and is usually used as a component in integrated optical circuits. Note: Thin-film optical switches may support only one propagation mode.
Thin-Film Optical Waveguide - A slab-dielectric waveguide that consists of multi layered films of material of different optical characteristics, is capable of guiding an optical signal, and may be used as a component in integrated optical circuits.
Third-Order Intercept Point - A point (a) that is an extrapolated convergence--not directly measurable--of intermodulation distortion products in the desired output and (b) that indicates how well a receiver performs in the presence of strong nearby signals. Note: Determination of a third-order intercept point is accomplished by using two test frequencies that fall within the first intermediate frequency mixer passband. Usually, the test frequencies are about 20 to 30 kHz apart.
Third Window - Of silica-based optical fibers, the transmission window at approximately 1.55 m. Note: The third window is the minimum-loss window in silica-based fibers.
Thread - In computer conferencing, a set of sequential messages containing closely related information.
Threat - 1. Capabilities, intentions, and attack methods of adversaries to exploit, or any circumstance or event with the potential to cause harm to, information or an information system. [NIS] 2. Any circumstance or event with the potential to harm an information system (IS) through unauthorized access, destruction, disclosure, modification of data, and/or denial of service.
Threat Analysis - Examination of information to identify the elements comprising a threat.
Threat Assessment - [A] formal description and evaluation of threat to an information system (IS).
Three-Way Calling - A switching system service feature that permits users to add a third party to an established connection at a different number during a call, without the assistance of an attendant or operator.
Allows you to speak to two separate people at the same time. To use, start by placing a call to the first
person. Once that person is on the line, press the switch hook or “flash” button briefly. This places the
first party on hold and gives you a dial tone to reach the second person. Then dial the second number.
Once the second person answers press the switch hook to connect everyone.Threshold - 1. The minimum value of a signal that can be detected by the system or sensor under consideration. 2. A value used to denote predetermined levels, such as those pertaining to volume of message storage, i.e., in-transit storage or queue storage, used in a message switching center. 3. The minimum value of the parameter used to activate a device. 4. The minimum value a stimulus may have to create a desired effect.
Threshold Current - In a laser, the driving current corresponding to lasing threshold.
Threshold Extension - See FM threshold extension. - A change in the value of the FM threshold of a receiver. Note: FM threshold extension may be obtained by decreasing the operational bandwidth, thus decreasing the received noise power and allowing the threshold of the desired signal to occur at a lower signal input level.
Threshold Frequency - In opto-electronics, the frequency of incident radiant energy below which there is no photo-emissive effect.
Through Group - A group of 12 voice-frequency channels transmitted as a unit through a carrier system.
Through-Group Equipment - In carrier telephone transmission, equipment that accepts the signal from a group receiver output and attenuates it to the proper signal level for insertion, without frequency translation, at the input of a group transmitter.
Throughput - 1. The number of bits, characters, or blocks passing through a data communication system, or portion of that system. Note 1: Throughput may vary greatly from its theoretical maximum. Note 2: Throughput is expressed in data units per period of time; e.g., in the DDN, as blocks per second. 2. The maximum capacity of a communications channel or system. 3. A measure of the amount of work performed by a system over a period of time, e.g., the number of jobs per day.
Through Supergroup - An aggregate of 60 voice-frequency channels, i.e., five groups, transmitted as a unit through a carrier system.
Through-Supergroup Equipment - In carrier telephone transmission, equipment that accepts the multiplexed signal from a supergroup receiver output, amplifies it without frequency translation, and provides the proper signal level to the input of a supergroup transmitter equipment.
THz - Abbreviation for terahertz. See electromagnetic spectrum.
TIA - Abbreviation for Telecommunications Industry Association.
Ticket - In computer security, a representation of one or more access rights that a possessor has to an object. Note: The ticket represents an access permission.
Ticketed Call - A call for which a record is made of certain facts concerning the call, such as the time it was placed, the duration, the call originator, call destination numbers, and, where applicable, the attendant's name or initials.
Ticket-Oriented - [In security, a] computer protection system in which each subject maintains a list of unforgeable bit patterns called tickets, one for each object a subject is authorized to access.
TIE - Acronym for time interval error. - 1. The time difference between a real clock and an ideal uniform time scale, after a time interval following perfect synchronization between the clock and the scale. 2. The variation in time delay of a given timing signal with respect to an ideal timing signal over a particular time period.
Tie Trunk - A telephone line that directly connects two private branch exchanges (PBXs).
TIFF (Tag Image File Format) - A common format for exchanging raster graphics (bitmap) images between application programs, including those used for scanner images. A TIFF file can be identified as a file with a ".tiff" or ".tif" file name suffix. The TIFF format was developed in 1986 by an industry committee chaired by the Aldus Corporation (now part of Adobe Software). Microsoft and Hewlett-Packard were among the contributors to the format. One of the most common graphic image formats, TIFF files are commonly used in desktop publishing, faxing, 3-D applications, and medical imaging applications.
TIFF files can be in any of several classes, including gray scale, color palette, or RGB full color, and can include files with JPEG,
LZW , or CCITT Group 4 standard run-length image compression.Time - 1. An epoch, i.e., the designation of an instant on a selected time scale, astronomical or atomic. It is used in the sense of time of day [JP1] 2. On a time scale, the interval between two events, or the duration of an event. 3. An apparently irreversible continuum of ordered events. 4. That which characterizes, or is characterized by, the observed and apparently irreversible continuum of ordered events.
Time Ambiguity - A situation in which more than one different time or time measurement can be obtained under the stated conditions.
Time-Assignment Speech Interpolation (TASI) - An analog technique used on certain long transmission links to increase voice-transmission capacity. Note: TASI works by switching additional users onto any channel temporarily idled because an original user has stopped speaking. When the original user resumes speaking, that user will, in turn, be switched to any channel that happens to be idle.
Time Block - An arbitrary grouping of several consecutive hours of a day, usually for a particular season, during which it is assumed that propagation data are statistically homogeneous.
Time Bomb - 1. In COMSEC, a logic bomb to be activated at a predetermined time. 2. [A] resident computer program that triggers an unauthorized act at a predefined time.
Time Code - A code used for the transmission and identification of time signals. Note: In telecommunications systems, the format of the time code must be specified.
Time Code Ambiguity - The shortest interval between successive repetitions of the same time code value. Note: For example, in a time code in which year-of-century is the most slowly changing field, the time code ambiguity would be 100 years; for a digital clock in which hours and minutes up to a maximum of 11:59 are displayed, the time code ambiguity would be 12 hours.
Time Code Resolution - The interval between two successive time code states. Note: Time code resolution is determined by the most rapidly changing symbol position within the time code. For example, for a digital clock that displays hours and minutes, the time code resolution would be 1 minute.
Time-Consistent Busy Hour (TCBH) - The identical hour each day during which, over a number of days, the highest average traffic is measured.
Time Diversity - Transmission in which signals representing the same information are sent over the same channel at different times. Note: Time diversity is often used over systems subject to burst error conditions, and at intervals adjusted to be longer than an error burst.
Time-Division Multiple Access (TDMA) - 1. A communications technique that uses a common channel (multipoint or broadcast) for communications among multiple users by allocating unique time slots to different users. Note: TDMA is used extensively in satellite systems, local area networks, physical security systems, and combat-net radio systems. 2. A multiple access technique whereby users share a transmission medium by being assigned and using (one at a time) for a limited number of time division multiplexed channels; implies that several transmitters use one channel for sending several bit streams.
Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM) - 1. Digital multiplexing in which two or more apparently simultaneous channels are derived from a given frequency spectrum, i.e., bit stream, by interleaving pulses representing bits from different channels. Note: Successive pulses represent bits from successive channels, e.g., voice channels in a T1 system. 2. A multiplexing technique whereby two or more channels are derived from a transmission medium by dividing access to the medium into sequential intervals. Each channel has access to the entire bandwidth of the medium during its interval. This implies that one transmitter uses one channel to send several bit streams of information.
Time Division Switch - A time division switch is a switch that implements the switch matrix using the TDM process, in a time-slot interchange (TSI) arrangement (usually denoted by T in combined time and space division switches).
Time-Division Switching - Switching of time-division multiplexed (TDM) channels by shifting bits between time slots in a TDM frame.
Time-Domain Reflectometer (TDR) - An electronic instrument used to characterize and locate faults in metallic cables (e.g., twisted pair, coax). Note 1: A TDR transmits a fast rise time pulse along the conductor. The resulting reflected pulse is measured at the input as a function of time and displayed on the instrument or plotted, as a function of cable length. Note 2: A TDR may be used to verify cable impedance characteristics, splice and connector location and associated losses, and estimate cable lengths.
Time-Gated Direct-Sequence Spread Spectrum - Direct-sequence spread spectrum where the transmitter is on only for a short fraction of a time interval. The on-time can be periodic or random within a time interval.
Time Guard Band - A time interval left vacant on a channel to provide a margin of safety against intersymbol interference in the time domain between sequential operations, such as detection, integration, differentiation, transmission, encoding, decoding, or switching.
Time Instability - The fluctuation of the time interval error caused by the instability of a real clock.
Time Interval Error (TIE) - 1. The time difference between a real clock and an ideal uniform time scale, after a time interval following perfect synchronization between the clock and the scale. 2. The variation in time delay of a given timing signal with respect to an ideal timing signal over a particular time period.
Time Jitter - Short-term variation or instability in the duration of a specified time interval.
Time Marker - A reference signal, often repeated periodically, enabling the correlation of specific events with a time scale, such as for establishing synchronization.
Time of Occurrence - The date of an event, i.e., the instant an event occurs, with reference to a specified time scale.
Time-Out - 1. A network parameter related to an enforced event designed to occur at the conclusion of a predetermined elapsed time. 2. A specified period of time that will be allowed to elapse in a system before a specified event is to take place, unless another specified event occurs first; in either case, the period is terminated when either event takes place. Note: A time-out condition can be canceled by the receipt of an appropriate time-out cancellation signal. 3. An event that occurs at the end of a predetermined period of time that began at the occurrence of another specified event. The time-out can be prevented by an appropriate signal.
Time Scale - 1. A time measuring system defined to relate the passage of temporal events since a selected epoch. Note: The internationally recognized time interval is the second. Time scales are graduated in intervals such as seconds, minutes, hours, days, and years, and in fractions of a second, such as milliseconds, nanoseconds, and picoseconds. 2. Time coordinates placed on the abscissa (x-axis) of Cartesian-coordinate graphs used for depicting waveforms and similar phenomena.
Time Scale Factor - A multiplier used to transform the real time of occurrence of an event or a problem into system time, such as that of a telecommunications system or a computer.
Time Server - The server maintaining and distributing the correct date and time over a computer network. Note: There is usually a special time-distribution protocol.
Time-Sharing - 1. The interleaving of two or more independent processes on one functional unit. 2. Pertaining to the interleaved use of computer time that enables two or more users to execute programs concurrently.
Time Slot - 1. Period of time during which certain activities are governed by specific regulations. [JP1] 2. A time interval that can be recognized and uniquely defined.
Time Stamp (TS) - 1. A data field in which is recorded (typically with a resolution of 1 millisecond) the cumulative variable queuing delay experienced by a packet in traversing the network. [After T1.509-1995] 2. With respect to a recorded network event, a data field in which is recorded the time (time of day or other instant of elapsed time) at which the event took place.
Time Standard - A stable device that emits signals at equal intervals such that their count may be used as a clock.
Time Tick - A time mark output of a clock system.
Time-Variant Value - In cryptography, a value that changes with each transaction or with each message value.
Timing Jitter - The short-term variations of the significant instants of a digital signal from their ideal positions in time. Here short term implies phase oscillations of frequency greater than or equal to 10 Hz. Timing jitter may lead to crosstalk and/or distortion of the original analog signal and is a potential source of slips at the input ports of digital switches. It may also cause slips and resultant errors in asynchronous digital multiplexes.
Timing Recovery - The derivation of a timing signal from a received signal.
Timing Signal - 1. The output of a clock. 2. A signal used to synchronize interconnected equipment.
Timing Tracking Accuracy - A measure of the ability of a timing synchronization system to minimize the clock difference between a master clock and any slaved clock.
T-Interface - For basic rate access in an Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) environment, a user-to-network interface reference point that (a) is characterized by a four-wire, 144-kb/s (2B+D) user rate, (b) accommodates the link access and transport layer function in the ISDN architecture, (c) is located at the user premises, (d) is distance sensitive to the servicing network terminating equipment, and (e) functions in a manner analogous to that of the Channel Service Units (CSUs) and the Data Service Units (DSUs).
Tip and Ring - An archaic term that gets its meaning from the old switchboard plugs. Each plug had a tip connector and a ring connector. Now, tip and ring refer to the two conductors that make up a single telephone line.
TLM - Abbreviation for telemetry.
TM - Abbreviation for transverse magnetic. See transverse magnetic mode.
TOD - Abbreviation for time of day. See time of occurrence.
Token - In certain local-area-network protocols, a group of bits that serves as a symbol of authority, is passed among data stations, and is used to indicate the station that is temporarily in control of the transmission medium.
Token-Bus Network - A bus network in which a token passing procedure is used.
Token Passing - A network access procedure in which a token passes from station to station and the only station allowed to transmit information is the station with the token.
Token Passing Bus LAN (IEEE 802.4) - A token passing bus LAN is a LAN using a deterministic access mechanism and topology in which all stations actively attached to the bus "listen" for a broadcast token or supervisory frame. Stations wishing to transmit must receive the token before doing so; however the next logical station to transmit may not be the next physical station on the bus. Access is controlled by pre-assigned priority algorithms.
Token Passing Ring LAN (IEEE 802.5) - A token passing ring LAN is a LAN using a deterministic access mechanism and topology, in which a supervisory frame (or token) is passed from station to adjacent station sequentially. Stations wishing to transmit must wait for the "free" token to arrive before transmitting data. In a token ring LAN the start and end points of the medium are physically connected, leading to a ring topology.
Token Ring Adapter - A network interface card (NIC) designed to attach a client workstation to a token ring computer network and operate as a token-passing interface.
Token-Ring Network - See network topology.
Toll Call - A call to any location outside the local service area. Otherwise known as a long distance call.
Tolerance - The permissible range of variation of some characteristic from its nominal value.
Tolerance Field - 1. The region between two curves, such as circles or rectangles, used to specify the tolerance on component size and geometry. 2. Pertaining to the cross section of an optical fiber, when used to specify the respective diameters and ovalities of, and concentricity error between, the core and cladding; two concentric annular regions which define the core-cladding boundary and the cladding outer boundary. Note: Dimensions are usually expressed in micrometers (
m). The larger annular region is defined by concentric circles of diameter [D C+
D C] and [D C-
D C], where D C is the nominal diameter of the cladding and
D C is the cladding diameter tolerance. The smaller annular region is defined by concentric circles of diameter [D c+
D c] and [D c-
D c], where D c is the nominal diameter of the core and
D c is the core diameter tolerance. When the core and cladding boundaries of the cross section of the fiber in question fall entirely within their respective defined areas, the fiber meets the specification. 3. Of the cross section of a given optical fiber, when used to characterize the respective diameters and ovalities of the core and cladding, and the concentricity error between the core and cladding; two such pairs of concentric circles, the concentric pairs not necessarily being concentric with one another. Note 1: One pair of concentric circles characterizes the core, and the other pair, the cladding. The cladding ovality is characterized by the smallest circle that circumscribes its cross section, and the largest circle that fits within its cross section. (The cross section is assumed, to a first approximation, to be elliptical in shape, so these defining circles will be concentric.) The core cross section is characterized by an analogous pair of circles, also concentric with one another, but not necessarily with those defining the cladding cross section. Note 2: The distance between the centers of the two concentric pairs (core pair and cladding pair) defines the offset between the core and cladding (the " core-cladding offset," also called the "concentricity error"). The width of the annulus defined by the cladding circles determines the ovality of the cladding, and the width of the annulus defined by the core determines the ovality of the core.
Toll Call - See long-distance call.
Toll Center - An office (or group of offices) within a city which generally handles the originating and incoming toll traffic for that city to or from other toll center areas and which handles through switched traffic. The toll center normally handles the inward toll traffic for its tributary exchanges and, in general, either handles the outward traffic originating at its tributaries or serves as the outlet to interexchange circuits for outward traffic ticketed and timed at its tributaries. Toll centers are listed as such in the Toll Rate and Route Guide.
Toll Center Area - The areas served by a toll center, including the toll center city and the communities served by tributaries of the toll center.
Toll Center Toll Office - A toll office (as contrasted to a local office) in a toll center city.
toll circuit - A general term applied to interexchange trunks used primarily for toll traffic.Toll Connecting Trunk - A general classification of trunks carrying toll traffic and ordinarily extending between a local office and a toll office, except trunks classified as tributary circuits. Examples of toll connecting trunks include toll switching trunks, recording trunks, and recording-completing trunks.
toll diversion - A system service feature by which users are denied the ability to place toll calls without the assistance of an attendant.Toll Office - A central office used primarily for supervising and switching toll traffic.
Toll Quality - The voice quality resulting from the use of a nominal 4-kHz telephone channel. Note: Toll quality may be quantized in terms of a specified bit error ratio.
Toll Switching Trunk - A trunk connecting one or more end offices to a toll center as the first stage of concentration for intertoll traffic. Note: Operator assistance or participation may be an optional function. In U.S. common carrier telephony service, a toll center designated "Class 4C" is an office where assistance in completing incoming calls is provided in addition to other traffic; a toll center designated "Class 4P" is an office where operators handle only outbound calls, or where switching is performed without operator assistance.
Tone - An electrically generated single-frequency sinusoidal oscillation.
Tone Detection Device - Tone detection devices "listen" for one of three things and then automatically route the incoming call to the correct phone connected device:
(1) FAX TONES which are also called CNG tones. FAX tones automatically route the call to the fax if they are present. All fax machines and fax devices usually automatically generate these tones to identify themselves.
(2) TOUCH TONES also called DTMF tones (DUAL TONE MULTIFREQUENCY). Modem calls are typically routed by DTMF placed in the dialing string from the connecting modem software. These extra digits are known as the security access codes (SAC)s.
(3) NO TONES - when there are no tones present (normal call), the device sends the call to the default device which is usually voice (phones, phone system, or answering machine) although the default device might be a fax device or modem when voice is not included the the application. Tone detection devices require no additional services from the phone company to operate.
Tone Detection Devices, save the owner significant monthly phone expenses by eliminating multiple phone lines. They automatically routing different types of calls (voice, fax, modem, etc.) to the correct type of phone connected equipment transparently to the caller over a single line.
Tone Diversity - In a voice frequency telegraph (VFTG) transmission system, the use of two channels to carry the same information. Note: Tone diversity is usually achieved by twinning the channels of a 16-channel VFTG to obtain 8 channels with dual diversity.
Tone Signaling - See dual-tone multifrequency signaling.
Tool - Synonym utility program.
Top-Level Domain Name - In Internet addressing, a domain name identifying the highest hierarchical level in the geographical or organizational structure of the addressing system in Internet. Note: In Internet, the top-level domain name is either an ISO country name, or an English abbreviation such as "com," "edu," "gov," "mil," "net," or "org."
Topography - The specification and arrangement in physical locations of actual communication and information system components which implement the topology.
Topology - See network topology.
Torn-Tape Relay - An antiquated tape relay system in which the perforated tape is manually transferred by an operator to the appropriate outgoing transmitter.
Total Channel Noise - The sum of random noise, intermodulation noise, and crosstalk. Note: Total channel noise does not include impulse noise because different techniques are required for its measurement.
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) - Of a signal, the ratio of (a) the sum of the powers of all harmonic frequencies above the fundamental frequency to (b) the power of the fundamental frequency. Note 1: The THD is usually expressed in dB. Note 2: Measurements for calculating the THD are made at the output of a device under specified conditions.
Total Internal Reflection - The reflection that occurs when light, in a higher refractive-index medium, strikes an interface, with a medium with a lower refractive index, at an angle of incidence (with respect to the normal) greater than the critical angle. See Snell's law
Total Line Length - In facsimile, the spot speed divided by the scanning line frequency. Note: The total line length may be greater than the length of the available line.
Touchpad - A pad that is electrically sensitive to touch, often used as the pointing device in laptops. You can also tap on it for clicks, but some people find that annoying if they bump the pad while typing.
Touch Panel - See touch-sensitive.
Touch Screen - See touch-sensitive.
Touch-Sensitive - Pertaining to a device that allows a user to interact with a computer system by touching an area on the surface of the device with a finger, pencil, or other object; for example, a touch-sensitive keypad or screen.
Touch Tone Dialing - See dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) signaling.
Trace Packet - In a packet-switching network, a unique packet that causes a report of each stage of its progress to be sent to the network control center from each visited system element.
Trace Program - A computer program that performs a check on another computer program by exhibiting the sequence in which the instructions are executed and usually the results of executing the instructions.
Track - On a data medium, a path associated with a single read / write head position as data move past the head.
Trackball - A ball that can be rotated about its center and that is used as an input device, e.g., to position a cursor. Synonym control ball.
Track Density - The number of tracks per unit length, measured in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the tracks are read.
Tracking Error - The deviation of a dependent variable with respect to a reference function.
Tracking Mode - An operational mode during which a system is operating within specified movement limits relative to a reference.
Tracking Phase - See tracking mode.
Traffic - 1. The information moved over a communication channel. 2. A quantitative measurement of the total messages and their length, expressed in CCS or other units, during a specified period of time.
Traffic Analysis - 1. In a communications system, the analysis of traffic rates, volumes, densities, capacities, and patterns specifically for system performance improvement. 2. [The] study of communications characteristics external to the text. 3. The analysis of the communications-electronic environment for use in the design, development, and operation of new communications systems. 4. In cryptology, the inference of information from observation and analysis of the presence, absence, amount, direction, and frequency of the traffic flow. 5. [The] Study of communications patterns.
Traffic Capacity - The maximum traffic per unit of time that a given telecommunications system, subsystem, or device can carry under specified conditions.
Traffic Encryption Key (TEK) - [A] key used to encrypt plain text or to superencrypt previously encrypted text and/or to decrypt cipher text.
Traffic Engineering - The determination of the numbers and kinds of circuits and quantities of related terminating and switching equipment required to meet anticipated traffic loads throughout a communications system.
Traffic-Flow Security - 1. The protection resulting from features, inherent in some crypto-equipment, that conceal the presence of valid messages on a communications circuit; normally achieved by causing the circuit to appear busy at all times. 2. Measures used to conceal the presence of valid messages in an on-line cryptosystem or secure communications system. Note: Encryption of sending and receiving addresses and causing the circuit to appear busy at all times by sending dummy traffic are two methods of traffic-flow security. A more common method is to send a continuous encrypted signal, whether or not traffic is being transmitted.
Traffic Intensity - A measure of the average occupancy of a facility during a specified period of time, normally a busy hour, measured in traffic units (erlangs) and defined as the ratio of the time during which a facility is occupied (continuously or cumulatively) to the time this facility is available for occupancy. Note: A traffic intensity of one traffic unit (one erlang) means continuous occupancy of a facility during the time period under consideration, regardless of whether or not information is transmitted. Synonym call intensity.
Traffic Load - The total traffic carried by a trunk or trunk group during a specified time interval.
Traffic Monitor - In a communications network, a service feature that provides basic data on the amount and type of traffic handled by the network.Traffic Over First Routes - A term applied to the routing of traffic and denoting routing via principal route for traffic between any two points as distinguished from alternate routes for such traffic.
Traffic Overflow - 1. That condition wherein the traffic offered to a portion of a communication system exceeds its capacity and the excess may be blocked or may be provided with alternate routing. 2. The excess traffic itself.
Traffic Padding - 1. In COMSEC, a countermeasure that generates spurious data in transmission media to make traffic analysis or decryption more difficult. 2. In reliability techniques, see pilot-make-busy circuit. 3. Generation of spurious communications or data units to disguise the amount of real data units being sent.
Traffic Register - See register.
Traffic Service Position System (TSPS) - A stored program electronic system associated with one or more toll switching systems which provides centralized traffic service position functions for several local offices at one location.
Traffic Unit - Synonym erlang.
Traffic Usage Recorder - A device for measuring and recording the amount of telephone traffic carried by a group, or several groups, of switches or trunks.
Trailer - Protocol control information located at the end of a protocol data unit (PDU).
Tranquility - [The] property whereby the security level of an object cannot change while the object is being processed by an information system (IS).
Transaction Capabilities (TC) - 1. A means based upon the OSI –Reference Model to support applications in telecommunications networks. 2. Protocol functions and procedures that control non-circuit related information exchange among signaling points in SS7 networks. It provides a general purpose approach to the introduction of new services within a network as well as a framework for service architecture for providing inter-network services. Transaction capabilities includes the application layer protocol called transaction capabilities application part (TCAP) as well as the supporting Presentation, Session, and Transport layers called the application service part (ASP).
Transaction Integrity - The degree to which a transaction flowing through a network reaches its intended destination without impairment of its function, content or meaning.
Transaction-Oriented Application - Applications that exchange messages that are time-critical, bursty, and often limited in length, to perform an indivisible or elemental unit of work for OAM&P (operations, administration, maintenance, and provisioning) applications.
Transceiver - 1. A device that performs, within one chassis, both transmitting and receiving functions. 2. In military communications, the combination of transmitting and receiving equipment that (a) is in a common housing, (b) usually is designed for portable or mobile use, (c) uses common circuit components for both transmitting and receiving, and (d) provides half-duplex operation.
Transcoding - The direct digital-to-digital conversion from one encoding scheme, such as voice LPC-10, to a different encoding scheme without returning the signals to analog form. Note: The transcoded signals, i.e., the digital representations of analog signals may be any digital representation of any analog signal, such as voice, facsimile, or quasi-analog signals.
Transcoding Gain - The factor by which the bit rate of a 64-kb/s channel is reduced when transcoding is used, e.g., when a transcoder conforming to ANSI T1.303 (i.e., ADPCM 32-kb/s) is used, the transcoding gain will equal 2. Transcoding gain equals 1 when no transcoding is used.
Transducer - A device for converting energy from one form to another for the purpose of measurement of a physical quantity or for information transfer.
TRANSEC - Abbreviation for transmission security. See communications security.
Transfer - To send information from one location and to receive it at another.
Transfer Allowed (TFA) - A procedure included in the signaling route management (functionality) that is used to inform a signaling point that a signaling route to a specific destination has become available.
Transfer Capacity - The maximum sustainable rate of information transfer.
Transfer Characteristics - Those intrinsic parameters of a system, subsystem, or equipment which, when applied to the input of the system, subsystem, or equipment, will fully describe its output.
Transfer Controlled (TFC) - A procedure included in the signaling route management (functionality) that is used to inform a signaling point of congestion status of a signaling route.Transfer Function - 1. A mathematical statement that describes the transfer characteristics of a system, subsystem, or equipment. 2. The relationship between the input and the output of a system, subsystem, or equipment in terms of the transfer characteristics. Note 1: When the transfer function operates on the input, the output is obtained. Given any two of these three entities, the third can be obtained. Note 2: Examples of simple transfer functions are voltage gains, reflection coefficients, transmission coefficients, and efficiency ratios. An example of a complex transfer function is envelope delay distortion. Note 3: For a negative feedback circuit, the transfer function, T, is given by
where e o is the output, e i is the input, G is the forward gain, and H is the backward gain, i.e., the fraction of the output that is fed back and combined with the input in a subtracter. 3. Of an optical fiber, the complex mathematical function that expresses the ratio of the variation, as a function of modulation frequency, of the instantaneous power of the optical signal at the output of the fiber, to the instantaneous power of the optical signal that is launched into the fiber. Note: The optical detectors used in communication applications are square-law devices. Their output current is proportional to the input optical power. Because electrical power is proportional to current, when the optical power input drops by one-half (3 dB), the electrical power at the output of the detector drops by three-quarters (6 dB).
Transfer Mode - In an integrated services digital network, (ISDN), a method of transmitting, multiplexing, and switching.
Transfer Prohibited (TFP) - A procedure included in the signaling route management (functionality) that is used to inform a signaling point of the unavailability of a signaling route.
Transfer Rate - See data transfer rate. - The rate at which data is transferred in some amount of bits per second.
Transfer Restricted (TFR) - A procedure included in the signaling route management (functionality) that is used to inform a signaling point of the restriction of a signaling route.
Transfer Syntax -That concrete syntax used in the transfer of data between open systems.
Transient - See dynamic variation.
Transistor -An electronic device that acts like an electrically activated switch but has no moving parts, so it can switch millions of times per second.
Transit Delay - Between two given points in an integrated services digital network (ISDN), the time between the moment that the first bit of a data unit, such as a frame or block, passes the first given point and the moment that bit passes the second given point, plus the transmission time of the data unit. Note: Transit delay is defined only between pairs of boundaries. Transit delay of a FPDU states at the time t1 at which the first bit of the FPDU crosses the first boundary, and ends at the time t2 at which the last bit of the FPDU crosses the second boundary. Transit delay = t2-t1.
Transit Network Identification - A network service feature that specifies the sequence of networks used to establish or partially establish a virtual circuit.
Transit Network Section - A network section between two internet circuit sections.
Transit Node - A node that interfaces with other nodes, and does not directly interface with customer equipment.
Transit Time - Synonym phase delay.
Transition - In a signal, the changing from one significant condition to another. Note: Examples of transitions are the changing from one voltage level to another in a data stream, the shifting from one phase position to another in phase-shift keying, and the translation from one frequency to another in frequency-shift keying.
Transition Frequency - The frequency associated with the difference between two discrete energy levels in an atomic system, given by
where f 2,1 is the frequency associated with the difference between two energy levels, E 2 and E 1(E 2> E 1), and is Planck's constant. Note: If a transition from E 2 to E 1 occurs, a photon with frequency f 2,1 is likely to be emitted. If the atomic system is at energy level E 1, and a photon of frequency f 2,1 is absorbed, the energy level will be raised to E 2.
Transition Zone - Synonym intermediate-field region.
Translate - In cryptography, the process of offset decrypting a key or set of keys using a transportation key shared with one center and then offset encrypting the same key or keys under a transportation key shared with a different center.
Translating Program - Synonym translator.
Translation Signaling Point (TSP) - A signaling point that performs SCCP (signal connection control part) global title translation. It is also known as SCCP Relay Node. The translation performed may be intermediate, in which case the TSP is referred to as "intermediate translation signaling point" (ITSP), or final, in which case the TSP is referred to as "final translation signaling point"
Translator - 1. A device that converts information from one system of representation into equivalent information in another system of representation. Note: An example of a translator in telephony is the device that converts dialed digits into call-routing information. 2. A computer program that translates from one language into another language and in particular from one programming language into another programming language. Synonym translating program. 3. In FM and TV broadcasting, a repeater station that receives a primary station's signal, amplifies it, shifts it in frequency, and rebroadcasts it. 4. A device that converts one frequency to another.
Transliterate - To convert the characters of one alphabet to the corresponding characters of another alphabet.
Transmission - 1. The dispatching, for reception elsewhere, of a signal, message, or other form of information. 2. The propagation of a signal, message, or other form of information by any means, such as by telegraph, telephone, radio, television, or facsimile via any medium, such as wire, coaxial cable, microwave, optical fiber, or radio frequency. 3. In communications systems, a series of data units, such as blocks, messages, or frames. 4. The transfer of electrical power from one location to another via conductors.
Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol - Two interrelated protocols that are part of the Internet protocol suite. Note 1: TCP operates on the OSI Transport Layer and breaks data into packets. IP operates on the OSI Network Layer and routes packets. Note 2: TCP/IP was originally developed by the U.S. Department of Defense.
Transmission Line - The material medium or structure that forms all or part of a path from one place to another for directing the transmission of energy, such as electric currents, magnetic fields, acoustic waves, or electromagnetic waves. Note: Examples of transmission lines include wires, optical fibers, coaxial cables, rectangular closed waveguides, and dielectric slabs.
Transmission Security (TRANSEC) - 1. See communications security. 2. [A] Component of COMSEC resulting from the application of measures designed to protect transmissions from interception and exploitation by means other than cryptanalysis.
Transmission Block - 1. A group of bits or characters transmitted as a unit and usually containing an encoding procedure for error control purposes. 2. In data transmission, a group of records sent, processed, or recorded as a unit. Note: A transmission block is usually terminated by an end-of-block character (EOB), end-of-transmission-block character (ETB), or end-of-text character (EOT or ETX).
Transmission Buffer - Storage (viz., buffer storage) in the signaling link control for signal units not yet transmitted.
Transmission Channel - See channel.
Transmission Coefficient - 1. The ratio of the transmitted field strength to the incident field strength of an electromagnetic wave when it is incident upon an interface surface between media with two different refractive indices. 2. In a transmission line, the ratio of the amplitude of the complex transmitted wave to that of the incident wave at a discontinuity in the line. 3. The probability that a portion of a communications system, such as a line, circuit, channel or trunk, will meet specified performance criteria. Note: The value of the transmission coefficient is inversely related to the quality of the line, circuit, channel or trunk.
Transmission Control Character - See control character.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) - One of the core protocols of the Internet protocol suite. Using TCP, applications on networked hosts can create connections to one another, over which they can exchange data. The protocol guarantees reliable and in-order delivery of sender to receiver data. TCP also distinguishes data for multiple, concurrent applications (e.g. Web server and email server) running on the same host.
TCP supports many of the Internet's most popular application protocols and resulting applications, including the World Wide Web, email and Secure Shell.
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) - A set of communications protocols or software necessary to access the Internet. A network protocol that controls host-to-host transmissions over packet-switched communication networks.
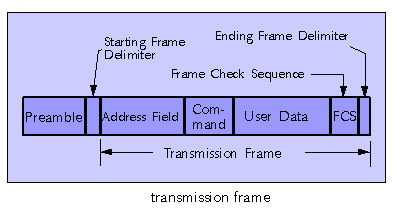
Transmission Frame - A data structure, beginning and ending with delimiters, that consists of fields predetermined by a protocol for the transmission of user data and control data.
Transmission Level - At a specified point in a telecommunications system, the power that is measured when a standard test signal, e.g., 0 dBm or -16 dBm at 1000 Hz, is transmitted from a corresponding reference point. Note: The transmission level is usually expressed in dBm.
Transmission Level Point (TLP) - In a telecommunications system, a test point, i.e., a point where a signal may be inserted or measured, and for which the nominal power of a test signal is specified. Note 1: In practice, the abbreviation, TLP, is usually used, and it is modified by the nominal level for the point in question. For example, where the nominal level is 0 dBm, the expression 0 dBm TLP, or simply, 0TLP, is used. Where the nominal level is -16 dBm, the expression -16 dBm TLP, or -16TLP, is used. Note 2: The nominal transmission level at a specified TLP is a function of system design and is an expression of the design gain or loss. Note 3: Voice-channel transmission levels, i.e., TLPs, are usually specified for a frequency of approximately 1000 Hz. Note 4: The TLP at a point at which an end instrument, e.g., a telephone set, is connected is usually specified as 0 dBm.
Transmission Line - The material medium or structure that forms all or part of a path from one place to another for directing the transmission of energy, such as electric currents, magnetic fields, acoustic waves, or electromagnetic waves. Note: Examples of transmission lines include wires, optical fibers, coaxial cables, rectangular closed waveguides, and dielectric slabs.
Transmission Loss - The decrease in power that occurs during transmission from one point to another. Note: Transmission loss is usually expressed in dB.
Transmission Medium - Any material substance, such as fiber-optic cable, twisted-wire pair, coaxial cable, dielectric-slab waveguide, water, and air, that can be used for the propagation of signals, usually in the form of modulated radio, light, or acoustic waves, from one point to another. Note: By extension, free space can also be considered a transmission medium for electromagnetic waves, although it is not a material medium.
Transmission Security (TRANSEC) - 1. See communications security. 2. [A] Component of COMSEC resulting from the application of measures designed to protect transmissions from interception and exploitation by means other than cryptanalysis.
Transmission Security Key (TSK) - [A] key that is used in the control of TRANSEC (transmission security) processes, such as frequency hopping and spread spectrum.
Transmission Service Channel - In video systems, the one-way transmission path between two designated points.
Transmission System - Part of a communication system organized to accomplish the transfer of information from one point to one or more other points by means of signals. Note: Examples of NATO-owned transmission systems are SATCOM, ACE HIGH and CIP-67.
Transmission Time - In facsimile, the interval between the start of picture signals and the detection of the end-of-message signal by the receiver for a single document.
Transmission Window - Synonym spectral window. See window.
Transmissivity - Obsolete. See transmittance.
Transmit-After-Receive Time Delay - The time interval from removal of rf energy at the local receiver input until the local transmitter is automatically keyed on and the transmitted rf signal amplitude has increased to 90% of its steady-state value. An Exception: High-frequency (HF) transceiver equipment is normally not designed with an interlock between receiver squelch and transmitter on-off key. The transmitter can be keyed on at any time, independent of whether or not a signal is being received at the receiver input.
Transmit Flow Control - In data communications systems, control of the rate at which data are transmitted from a terminal so that the data can be received by another terminal. Note 1: Transmit flow control may occur between data terminal equipment (DTE) and a switching center, via data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE), or between two DTEs. The transmission rate may be controlled because of network or DTE requirements. Note 2: Transmit flow control can occur independently in the two directions of data transfer, thus permitting the transfer rates in one direction to be different from the transfer rates in the other direction.
Transmit Objective Loudness Rating (TOLR) - The ratio in dB of the sound pressure produced by a speaker to the voltage produced by a telephone and loop as defined by ANSI /IEEE 661-1997.
Transmit Signal -The signal sent across an interface la or lb from the associated equipment.
Transmittance - The ratio of the transmitted power to the incident power. Note 1: In optics, transmittance is usually expressed as optical density or in percent. Note 2: Transmittance was formerly called " transmission."
Transmitter - The source or generator of any signal on a transmission medium.
Transmitter Attack-Time Delay - The interval from the instant a transmitter is keyed-on to the instant the transmitted radio frequency (rf) signal amplitude has increased to a specified level, usually 90% of its key-on steady-state value. Note: The transmitter attack-time delay excludes the time required for automatic antenna tuning.
Transmitter Central Wavelength Range (
tmax-
tmin): In optical communication, the total allowed range of transmitter central wavelengths caused by the combined worst-case variations due to manufacturing, temperature, aging, and any other significant factors.
Transmitter Power Output Rating - The power output of a radio transmitter under stated conditions of operation and measurement. Note: Power output ratings may be made against a number of criteria, e.g., peak envelope power, peak power, mean power, carrier power, noise power, or stated intermodulation level.
Transmitter-Receiver Pair - A one-way 15-kHz program system comprised of a transmitting terminal connected via a DS1 digital link to a receiving terminal.
Transmitter Release-Time Delay - The interval from the instant a transmitter is keyed-off to the instant the transmitted radio frequency (rf) signal amplitude has decreased to a specified level, usually 10% of its key-on steady-state value.
Transmultiplexer - Equipment that transforms signals derived from frequency-division multiplex equipment, such as group or supergroups, to time-division-multiplexed signals having the same structure as those derived from PCM multiplex equipment, such as primary or secondary PCM multiplex signals, and vice versa.
Transparency - 1. The property of an entity that allows another entity to pass thorough it without altering either of the entities. 2. In telecommunications, the property that allows a transmission system or channel to accept, at its input, unmodified user information, and deliver corresponding user information at its output, unchanged in form or information content. Note: The user information may be changed internally within the transmission system, but it is restored to its original form prior to the output without the involvement of the user. 3. The quality of a data communications system or device that uses a bit-oriented link protocol that does not depend on the bit sequence structure used by the data source. 4. An image fixed on a clear base by means of a photographic printing, chemical, or other process, especially adaptable for viewing by transmitted light.
Transparent Interface - An interface that allows the connection and operation of a system, subsystem, or equipment with another without modification of system characteristics or operational procedures on either side of the interface.
Transparent Loopback - A loopback in which the signal is transmitted beyond the loopback point (the forward signal).
Transparent Network - See transparency.
Transponder - 1. An automatic device that receives, amplifies, and retransmits a signal on a different frequency. 2. An automatic device that transmits a predetermined message in response to a predefined received signal. Note: An example of transponders is in identification-friend-or-foe systems and air-traffic-control secondary radar (beacon radar) systems. 3. A receiver-transmitter that will generate a reply signal upon proper interrogation.
Transport - 1. In telecommunications, to convey information from one location to another. 2. Facilities associated with the carriage of OC-1 or higher level signals.
Transportability - 1. In communications, the quality of equipment, devices, systems, and associated hardware that permits their being moved from one location to another to interconnect with locally available complementary equipment, devices, systems, associated hardware, or other complementary facilities. Note: Transportability implies the use of standardized components, such as standardized plugs and transmission media. 2. The capability of materiel to be moved by towing, self-propulsion, or carrier through any means, such as railways, highways, waterways, pipelines, oceans, and airways.
Transportable Station - A station which is transferred to various fixed locations but is not intended to be used while in motion.
Transport Layer - Layer 4. This layer responds to service requests from the Session Layer and issues service requests to the Network Layer. The purpose of the Transport Layer is to provide transparent transfer of data between end users, thus relieving the upper layers from any concern with providing reliable and cost-effective data transfer. See Open Systems Interconnection--Reference Model.
Transport Overhead - The overhead added to the STS SPE (synchronous transport signal-- synchronous payload envelope) for transport purposes. Transport overhead consists of line and section overhead.
Transposition - In INFOSEC, encryption that rearranges bits or characters according to some scheme. Note: The resulting ciphertext is called transposition cipher.
Transverse Electric and Magnetic (TEM) Mode - A mode whose electric and magnetic field vectors are both normal to the direction of propagation. Note: The TEM mode is the most useful mode in a coaxial cable.
Transverse Electric (TE) Mode - A mode whose electric field vector is normal to the direction of propagation. Note: TE modes may be useful modes in waveguides. In an optical fiber, TE and TM modes correspond to meridional rays.
Transverse Magnetic (TM) Mode - A mode whose magnetic field vector is normal to the direction of propagation. Note: TM modes may be useful in waveguides. In an optical fiber, TE and TM modes correspond to meridional rays.
Transverse Offset Loss - Synonym lateral offset loss. - 1. In fiber optics, a loss of optical power at a splice or connector, caused by a lateral, i.e., transverse, offset of the mating fiber cores, which offset causes an imperfect transfer of the optical signal from the "transmitting" fiber to the "receiving" fiber. Note: The effect of a given amount of lateral offset will depend on other parameters such as the relative diameters of the respective cores. For example: if, because of manufacturing tolerances, the "transmitting" core is smaller than the "receiving" core, the effect will be less than if both cores were the same size. 2. An analogous loss of optical power caused by lateral misalignment of the fiber and optical source.
Transverse Parity Check - A parity check performed on a group of binary digits recorded on parallel tracks of a data medium, such as a magnetic disk, tape, drum, or card.
Transverse Redundancy Check (TRC) - In synchronized parallel bit streams, a redundancy check (a) that is based on the formation of a block check following preset rules, (b) in which the check-formation rule applied to blocks is also applied to characters, and (c) in which the check is made on parallel bit patterns. Note 1: When the TRC is based on a parity bit applied to each character and block, the TRC can only detect, with limited certainty, whether or not there is an error. It cannot correct the error. Detection cannot be guaranteed because an even number of errors in the same character or block will escape detection, regardless of whether odd or even parity is used. Note 2: Two-dimensional arrays of bits may be used to represent characters or blocks in synchronized parallel data streams. When TRC is combined with longitudinal redundancy checking (LRC), individual erroneous bits can be corrected. Synonym vertical redundancy check.
Transverse Resolution - In a facsimile receiver, the dimension that (a) is perpendicular to a scanning line and (b) is the smallest recognizable detail of the image produced by the shortest signal capable of actuating the facsimile receiver under specified conditions.
Trapdoor - A hidden software or hardware mechanism, usually created for testing and troubleshooting, that may be used to circumvent computer security.
Trapped Electromagnetic Wave - An electromagnetic wave that enters a layer of material that is surrounded on both sides by a layer of material of a lesser refractive index such that, if the wave is traveling parallel or nearly parallel to the surfaces of the layers and hence the incident angles with the surfaces are greater than the critical angle, i.e., the angles are grazing with the surface, total internal reflection will occur on both sides and hence trap the wave. Note: Dielectric slabs, optical fibers, and layers of air can serve as an electromagnetic wave trap, thus confining the wave to a given direction of propagation and to a given point.
Trapped Mode - Synonym bound mode. In an optical fiber, a mode that (a) has a field intensity that decays monotonically in the transverse direction everywhere external to the core and (b) does not lose power to radiation. Note: Except for single-mode fibers, the power in trapped modes is predominantly contained in the core of the fiber.
Trapped Ray - In an optical fiber, a ray that is confined primarily to the core. Note: A guided ray satisfies the relation given by
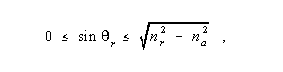
where
r is the angle the ray makes with the fiber axis, r is the radial position, i.e., radial distance, of the ray from the fiber axis, nr is the refractive index at the radial distance r from the fiber axis, and na is the refractive index at the core radius, a, i.e., at the core-cladding interface. Guided rays correspond to bound modes, i.e., guided modes, in terms of modes rather than rays. Synonyms bound ray, guided ray.
Traveling Wave - A wave that (a) propagates in a transmission medium, (b) has a velocity determined by the launching conditions and the physical properties of the medium, and (c) may be a longitudinal or transverse wave. Note 1: For the purposes of this definition, free space may be considered a medium, although it is not a physical medium. Note 2: A traveling wave is not a wave that is reduced to a standing wave by reflections from a distant boundary. Note 3: Examples of traveling waves are radio waves propagating in free space, lightwaves propagating in optical fibers, water waves on the surface of the ocean, and seismic waves.
Tree Network - See network topology.
Tree Search - In a tree structure, a search in which it is possible to decide, at each step, which part of the tree may be rejected without a further search.
Tree Structure - A hierarchical organization in which a given node is considered to be an ancestor of all the lower level nodes to which the given node is connected. Note 1: The root node, i.e., the base node, is an ancestor of all the other nodes. Note 2: In a tree structure there is one and only one path from any point to any other point.
Tree Topology - A network topology that, from a purely topologic viewpoint, resembles an interconnection of star networks in that individual peripheral nodes are required to transmit to and receive from one other node only, toward a central node, and are not required to act as repeaters or regenerators. Note 1: The function of the central node may be distributed. Note 2: As in the conventional star network, individual nodes may thus still be isolated from the network by a single-point failure of a transmission path to the node. Note 3: A single-point failure of a transmission path within a distributed node will result in partitioning two or more stations from the rest of the network. See network topology.
T Reference Point - In Integrated Services Digital Networks (ISDN), the conceptual point dividing NT2 and NT1 functional groupings in a particular ISDN arrangement.
Tremendously High Erequency (THF) - Frequencies from 300 GHz to 3000 GHz. See electromagnetic spectrum.
Triaxial Cable - A specialized form of coaxial cable, circular in cross-section and consisting of (a) a center conductor, often a solid wire but sometimes braided; separated by an insulating material from (b) a concentric solid or braided conductor which is in turn separated by an insulating material from (c) a third solid or braided conductor, concentric with the first two; and (d) a protective sheath.
Tributary Circuit - A circuit between a tributary office and a toll switchboard or intertoll dialing equipment in a toll center city.
Tributary Office - A local office which is located outside the exchange in which a toll center is located, which has a different rate center from its toll center and which usually tickets and times only a part of its originating toll traffic, but which may ticket or time all or none, of such traffic. The toll center handles all outward traffic not ticketed and timed at the tributary and normally switches all inward toll traffic from outside the tributary's toll center to the tributary. Tributary offices are indicated as such in the Toll Rate and Route Guide.
Tributary Station - 1. In a data network, a station other than the control station. 2. On a multipoint connection or a point-to-point connection using basic mode link control, any data station other than the control station.
Trim Effect - In a crystal oscillator, the degradation of frequency-vs.-temperature stability, and marked frequency offset, resulting from frequency adjustment which produces a rotation or distortion, or both, of the inherent frequency-vs.-temperature characteristic.
Triple Data Encryption Algorithm (TDEA) - An encryption algorithm whose key consists of three DES (Data Encryption Standard) keys, which is also referred to as a key bundle. Note 1: A DES key consists of 64 binary digits ("0"s or "1"s) of which 56 bits are randomly generated and used directly by the algorithm. (The other 8 bits, which are not used by the algorithm, may be used for error detection.) Note 2: Each TDEA encryption/decryption operation (as specified in ANSI X9.52) is a compound operation of DES encryption and decryption operations. Let EK(I) and DK(I) represent the DES encryption and decryption of I using DES key K respectively. The following operations are TDEA encryption operation: the transformation of a 64-bit block I into a 64-bit block O that is defined as follows: O = EK3(DK2(EK1(I))).
TDEA Decryption Operation - the transformation of a 64-bit block I into a 64-bit block O that is defined as follows: O = DK1(EK2(DK3(I))). The standard specifies the following keying options for bundle (K1, K2, K3)
- Keying Option 1 - K1, K2, and K3 are independent keys;
- Keying Option 2 - K1 and K2 are independent keys and K3 = K1;
- Keying Option 3 - K1 = K2 = K3.
Triple Precision - Characterized by the use of three computer words to represent a number in accordance with required precision.
Triplet - A byte composed of three bits. Synonym three-bit byte.
Tristimulus Values - In a given trichromatic system, the amounts of the three reference color stimuli required to match the light considered in a given chromatic system.
TRI-TAC - Acronym for tri-services tactical. See tactical communications.
TRI-TAC Equipment - Equipment that (a) accommodates the transition from current manual and analog systems to fully automated digital systems and (b) provides for message switching, voice communications circuit switching, and the use of secure voice terminals, digital facsimile systems, and user digital voice terminals.
Trojan Horse - 1. An apparently harmless program containing malicious logic that allows the unauthorized collection, falsification, or destruction of data. 2. [A] program containing hidden code allowing the unauthorized collection, falsification, or destruction of information.
Troposcatter - Synonym tropospheric scatter.
Troposphere - 1. The lower layers of atmosphere, in which the change of temperature with height is relatively large. It is the region where clouds form, convection is active, and mixing is continuous and more or less complete. 2. The layer of the Earth's atmosphere, between the surface and the stratosphere, in which temperature decreases with altitude and which contains approximately 80% of the total air mass. Note: The thickness of the troposphere varies with season and latitude. It is usually 16 km to 18 km thick over tropical regions, and less than 10 km thick over the poles.
Tropospheric Duct - See atmospheric duct.
Tropospheric Scatter - 1. The propagation of radio waves by scattering as a result of irregularities or discontinuities in the physical properties of the troposphere. [NTIA] [RR] [JP1] 2. A method of transhorizon communications using frequencies from approximately 350 MHz to approximately 8400 MHz. Note: The propagation mechanism is still not fully understood, though it includes several distinguishable but changeable mechanisms such as propagation by means of random reflections and scattering from irregularities in the dielectric gradient density of the troposphere, smooth-Earth diffraction, and diffraction over isolated obstacles (knife-edge diffraction). Synonym troposcatter.
Tropospheric Wave - A radio wave that is propagated by reflection from a place of abrupt change in the dielectric constant, or its gradient, in the troposphere. Note: In some cases, a ground wave may be so altered that new components appear to arise from reflection in regions of rapidly changing dielectric constant. When these components are distinguishable from the other components, they are called "tropospheric waves."
TRS Cable (Tip, Ring, Sleeve Cable) - An analog cable used to connect audio devices. It typically comes in 1/4" and 1/8" diameters. It is balanced, as opposed to the unbalanced signals of RCA cables.
True Color - The name given to 32-bit, 16.7 million color representation.
True Parity - This term has come about with the advent of logical parity memory. It simply means that the parity memory actually does something useful instead of just issuing positives over and over.
True Power - Synonym effective power.
TrueType - This is a font standard developed by Apple and used in Mac OS version 7. Later, Apple licensed the technology to Microsoft, which used it in Windows 3.1 and continues to use it today. However, Apple and Microsoft TrueType fonts are not compatible.
Truncated Binary Exponential Backoff - In carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) networks and in carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) networks, the algorithm used to schedule retransmission after a collision such that the retransmission is delayed by an amount of time derived from the slot time and the number of attempts to retransmit.
Truncation - The deletion or omission of a leading or a trailing portion of a string in accordance with specified criteria.
Truncation Error - In the representation of a number, the error introduced when one or more digits are dropped.
Trunk - A communication line between two switching systems. In other words, a telephone line. A line that connects to the telephone company CO (central office).
Trunk Circuit Identification Code (TCIC) - A unique identity assigned to each SS7 message trunk interconnecting two switches.
Trunk Encryption Device (TED) - A bulk encryption device used to provide secure communications over a wideband digital transmission link. Note: A TED is usually located between the output of a trunk group multiplexer and a wideband radio or cable facility.
Trunk Group - Two or more trunks of the same type between two given points.
Trunk Group Multiplexer (TGM) - A time-division multiplexer that combines individual digital trunk groups into a higher rate bit stream for transmission over wideband digital communications links.
Trunk Group Serial Number (TGSN) - A unique alphanumeric code used to identify a trunk group.
Trust - In cryptology and cryptosystems, that characteristic allowing one entity to assume that a second entity will behave exactly as the first entity expects. Note: Trust may apply only for some specific function. The critical role of trust in the authentication framework is to describe the relationship between an authenticating entity and a certification authority; an authenticating entity must be certain that it can trust the certification authority to create only valid and reliable certificates.
Trusted Computer System (TCS) - 1. [An] information system (IS) employing sufficient hardware and software assurance measures to allow simultaneous processing of a range of classified or sensitive information. 2. A data processing system that provides sufficient computer security to allow for concurrent access to data by users with different access rights and to data with different security classification and security categories.
Trusted Computing Base (TCB) - [The] totality of protection mechanisms within a computer system, including hardware, firmware, and software, the combination of which is responsible for enforcing a security policy. Note: The ability of a trusted computing base to enforce correctly a unified security policy depends on the correctness of the mechanisms within the trusted computing base, the protection of those mechanisms to ensure their correctness, and the correct input of parameters related to the security policy.
Trusted Distribution - [A] method for distributing trusted computing base (TCB) hardware, software, and firmware components that protects the TCB from modification during distribution.
Trusted Identification Forwarding - [The] identification method used in information system (IS) networks whereby the sending host can verify an authorized user on its system is attempting a connection to another host. The sending host transmits the required user authentication information to the receiving host.
Trusted Path - [The] Mechanism by which a person using a terminal can communicate directly with the trusted computing base (TCB). Trusted path can only be activated by the person or the TCB and cannot be imitated by untrusted
Trusted Process - [A] process that has privileges to circumvent the system security policy and has been tested and verified to operate only as intended.
Trusted Recovery - [The] ability to ensure recovery without compromise after a system failure.
Trusted Software - [The] software portion of a trusted computing base (TCB).
Trusted Third-Party - A security authority trusted by communicating entities with respect to specific security-related activities (e.g., for the purpose of authentication).
Truth Table - 1. An operation table for a logic operation. 2. A table that describes a logic function by listing all possible combinations of input values and indicating, for each combination, the output value.
TSEC Nomenclature - [In security, the] system for identifying the type and purpose of certain items of COMSEC material.
TSK - Abbreviation for transmission security key.
TSP - Abbreviation for Telecommunications Service Priority.
TSPS - Abbreviation for traffic service position system.
TSPS Complex - All groups of operator positions, wherever located, associated with the same TSPS stored program control units.
TSP System - See Telecommunications Service Priority system.
TTTN - Abbreviation for tandem tie trunk network.
TTY - Abbreviation for teletypewriter.
TTY/TDD - Telephone Typewriter and Telephone Device for the Deaf. A telecommunication device for the hearing impaired using teletypewriter principals. The users call a special operator number and third-party translation.
Tuning - Adjusting the parameters and components of a circuit so that it resonates at a particular frequency or so that the current or voltage is either maximized or minimized at a specific point in the circuit. Note: Tuning is usually accomplished by adjusting the capacitance or the inductance, or both, of elements that are connected to or in the circuit.
Tunneling - 1. In computer networking, a technique for connecting two networks via a third, while totally isolating the connected traffic from other traffic in the third network. [After 2382-pt.35] 2. Technology enabling one network to send its data via another network's connections. Tunneling works by encapsulating a network protocol within packets carried by the second network.
Tunneling Mode - Synonym leaky mode. In an optical fiber, a mode having a field that decays monotonically for a finite distance in the transverse direction but becomes oscillatory everywhere beyond that finite distance. Note: Leaky modes correspond to leaky rays in the terminology of geometric optics. Leaky modes experience attenuation, even if the waveguide is perfect in every respect.
Tunneling Ray - Synonym leaky ray. In an optical fiber, a ray for which geometric optics would predict total internal reflection at the boundary between the core and the cladding, but which suffers loss by virtue of the curved core boundary. Note: Leaky rays correspond to leaky (i.e., tunneling) modes in the terminology of mode descriptors.
Turing Machine - A mathematical model of a device that changes its internal state and reads from, writes on, and moves a potentially infinite tape, all in accordance with its present state, thereby constituting a model for computer-like behavior.
Turnaround Time - In a half-duplex circuit, the time required to reverse the direction of transmission from transmit to receive or vice versa.
Turnkey - Pertaining to a procurement process that (a) includes contractual actions at least through the system, subsystem, or equipment installation phase and (b) may include follow-on contractual actions, such as testing, training, logistical, and operational support. Note: Precise definition of the types of allowable contractual features are contained in the Federal Acquisition Regulations (FAR).
TWAIN (Toolkit Without An Interesting Name) - A set of operations that allow scanners to have a standard interface to software. This allows the use of your favorite graphics package with your favorite scanner without worrying if one will support the other. As long as both are TWAIN-complaint they will work together.
Twin Cable - A cable composed of two parallel conductors separated from each other by a ribbon-like insulator or encased by a foam insulator. Synonym twin-lead.
Twin-Lead - Synonym twin cable. A term that refers to a two-conductor ribbon cable commonly used as a transmission line for TV signals.
Twin-Lead Adapter - A device for connecting a Twin Lead cable to a coaxial cable.
Twinplex - A frequency-shift-keyed (FSK) carrier telegraphy system in which four unique tones, i.e., two pairs of tones, are transmitted over a single transmission channel, such as one twisted pair. Note: One tone of each pair represents a " mark " and the other a "space."
Twin Sideband Transmission - See independent-sideband transmission.
Twist - In telephony, a change, as a function of temperature, in the shape of the frequency-vs.-attenuation response curve, i.e., characteristic, of a transmission line.
Twisted Pair - A pair of individually insulated conductors (wires) twisted together and treated as an entity in the transmission of electrical signals or power (e.g., from an electronic power supply to a circuit). Note 1: In communications cables, the twisted pair is usually if not always composed of two individually insulated solid conductors (wires). In other applications, e.g., in a power-supply application, each of the insulated conductors may consist of stranded wire. Note 2: Because the wires are twisted together, interfering signals tend to create opposing electromagnetic forces at frequent intervals, reducing the effect of the interference on the signal or power supply voltage being conducted. Note 3: Twisted pairs may be used for bit rates up to 1 Mb/s over short distances (<100 m) and lower bit rates over longer distances. More sophisticated driver and receiver circuits facilitate similar or higher data rates over longer distances. Note 4: Unshielded twisted pairs (UTPs) are used extensively in telephone networks and in many data communications applications.
Twisted Pair Cable - See paired cable.
Two-Out-Of-Five Code - A binary-coded decimal notation in which (a) each decimal digit is represented by a binary numeral consisting of five binary digits of which two are of one kind, called "ones," and three are of the other kind, called "zeros" and (b) the usual weights assigned to the digit positions are 0-1-2-3-6, except that "zero" is represented as 01100.
Two-Part Code - Code consisting of an encoding section, in which the vocabulary items (with their associated code groups) are arranged in alphabetical or other systematic order; and a decoding section, in which the code groups (with their associated meanings) are arranged in a separate alphabetical or numeric order.
Two-Person Control - Continuous surveillance and control of positive control material at all times by a minimum of two authorized individuals, each capable of detecting incorrect and unauthorized procedures with respect to the task being performed, and each familiar with established security and safety requirements.
Two-Person Integrity (TPI) - [A] system of storage and handling designed to prohibit individual access to certain COMSEC keying material by requiring the presence of at least two authorized persons, each capable of detecting incorrect or unauthorized security procedures with respect to the task being performed.
Two-Pilot Regulation - In frequency-division multiplexed (FDM) systems, the use of two pilot frequencies within a band so that the differential change in attenuation with respect to temperature, i.e., twist, can be detected and compensated by a regulator.
Two-Sample Deviation - The square root of the Allan variance
Two-Sample Variance - Synonym Allan variance.
Two-Source Frequency Keying - Synonym frequency-exchange signaling.
Two-Tone Keying: - In telegraphy systems, keying in which the modulating wave causes the carrier to be modulated with a single tone for the " mark " and modulated with a different single tone for the "space."
Two-Tone Telegraph - See two-tone keying.
Two-way Alternate Operation - Synonym half-duplex operation.
Two-Way Simultaneous Operation - Synonym duplex operation.
Two-Wire Circuit - Also 2-wire circuit. A full-duplex communications circuit that utilizes only two metallic conductors, e.g., a single twisted pair.
TWX® - Acronym for teletypewriter exchange service.
TX - Abbreviation for transmitter, transmit.
Type 1 Product - Classified or controlled cryptographic item for securing classified and sensitive U.S. Government information, when appropriately keyed. The term refers only to products, and not to information, key, services, or controls. Type 1 products contain classified algorithms. They are available to U.S. Government users, their contractors, and federally sponsored non-U.S. Government activities subject to export restrictions in accordance with International Traffic in Arms Regulation.
Type 2 Product - Unclassified cryptographic equipment, assembly, or component, endorsed by the National Security Agency, for use in national security systems as defined in Title 40 U.S.C. Section 1452. [INFOSEC-99] Note: The term refers only to products, and not to information, key, services, or controls. Type 2 products may not be used for classified information, but contain classified National Security Agency algorithms that distinguish them from products containing the unclassified data algorithm. Type 2 products are subject to export restrictions in accordance with the International Traffic in Arms Regulation.
Type 3 Algorithm - [A] cryptographic algorithm that has been registered by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and published as a Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) for use in protecting unclassified sensitive, information or commercial information.
Type 4 Algorithm - [An] unclassified cryptographic algorithm that has been registered by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), but not published as a Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS).
Types of Calls -
- Local — A call within your local calling area covered by your local calling plan.
- Local Toll (Regional Toll) — A call beyond your local calling area, but not far enough to be long
distance. These calls are subject to per-minute charges, which vary by state.- In-State Long Distance — A call to a number outside your local calling area, but still within the borders of your state.
- State-to-State Long Distance — A call to a number in a different state.
Fax Switch Products
|
*Note: All prices include shipping and handling in the continental US and most of Canada. We reserve the right to charge up to the actual price of shipping on all orders outside the continental United States. Customer is responsible for any taxes, duties or brokerage charges that may apply. All orders shipped UPS Ground unless specified. For air and express shipments, appropriate charges will be applied to your order.
Need Help?
- Call now for free phone consultation at 1-866-337-0965.
Click here if you want to share 2 devices on 1 line and don't know which device to choose.
Click here if you want to share 3 or more devices on one line and don't know what type to choose.
"Albert Einstein Presents Fax Switch "
"Dancing Bear Fax Switch Presentation"
![]()
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
You didn't find what you need here?
Please visit our sister company, SuperPhoneStore.com for wholesale to the public telephones, phone accessories or the latest electronics. We have over 4500 different products in stock from over 200 premier manufacturers. Check it out!