
Telecom Dictionary - Definitions of terms
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
G
Gain - The ratio of output current, voltage, or power to input current, voltage, or power, respectively. Note 1: Gain is usually expressed in dB. Note 2: If the ratio is less than unity, the gain, expressed in dB, will be negative, in which case there is a loss between input and output.
Gain Hit - See hit. A transient disturbance to, or momentary interruption of, a communication channel, power supply (especially that provided via a commercial electric power distribution network or grid, but not limited to same), etc.
Gain Medium - An active medium, device, or system in which amplification of input occurs with or without feedback. Note: Gain media include amplifiers, lasers, and avalanche photodiodes (APDs).
Gain of an Antenna - Synonym antenna gain. - The ratio of the power required at the input of a loss-free reference antenna to the power supplied to the input of the given antenna to produce, in a given direction, the same field strength at the same distance. Note 1: Antenna gain is usually expressed in dB. Note 2: Unless otherwise specified, the gain refers to the direction of maximum radiation. The gain may be considered for a specified polarization. Depending on the choice of the reference antenna, a distinction is made between:
- absolute or isotropic gain (Gi), when the reference antenna is an isotropic antenna isolated in space;
- gain relative to a half-wave dipole (Gd) when the reference antenna is a half-wave dipole isolated in space and with an equatorial plane that contains the given direction;
- gain relative to a short vertical antenna (Gr), when the reference antenna is a linear conductor, much shorter than one quarter of the wavelength, normal to the surface of a perfectly conducting plane which contains the given direction. Synonyms antenna gain, power gain of an antenna.
Galactic Radio Noise - Synonym cosmic noise. - Random noise that originates outside the Earth's atmosphere. Note: Cosmic noise characteristics are similar to those of thermal noise. Cosmic noise is experienced at frequencies above about 15 MHz when highly directional antennas are pointed toward the Sun or to certain other regions of the sky such as the center of the Milky Way Galaxy.
Gamma Correction - In video, the insertion of a nonlinear output-input characteristic for the purpose of changing the system transfer characteristic. Note: Historically, gamma correction was a precompensation applied to the video signal at the camera to correct for the nonlinearities of the CRT (i.e., the power function of the electron gun) and, as such, it was the inverse of the electron gun function. It is now widely used, however, to describe "the total of all transfer function manipulations" (i.e., including departures from a true power-law function), whether inherent or intentionally introduced to act upon the video signal for the purpose of reducing the bandwidth for signal processing, making the image on the final display conform to preconceived artistic objectives, or providing noise suppression, or even bit-rate reduction.
GAN (global area network) - A network that (a) is composed of different interconnected computer networks and (b) covers an unlimited geographical area. Note: Loosely synonymous with an internet (as opposed to the Internet (with an uppercase "I"), which designates one specific network).
Gap - A period of low energy content signals present of a digital speech interpolation device.
Gap Loss - 1. The power loss that occurs when an optical signal is transferred from one fiber to another that is axially aligned with it, but longitudinally separated from it. Note: The gap allows light from the "transmitting" fiber to spread out as it leaves the fiber endface. When it strikes the "receiving" fiber, some of the light will enter the cladding, where it is quickly lost. 2. An analogous form of coupling loss that occurs between an optical source, e.g., an LED, and an optical fiber. Note: Gap loss is not usually significant at the optical detector, because the sensitive area of the detector is normally somewhat larger than the cross section of the fiber core. Unless the separation is substantial, all light emerging from the fiber, even though it diverges, will still strike the detector. Synonym longitudinal offset loss.
Gap-Loss Attenuator - An optical attenuator that exploits the principle of gap loss to reduce the optical power level when inserted in-line in the fiber path; e.g., to prevent saturation of the receiver. Note: Gap-loss attenuators should be used in-line near the optical transmitter.
Gaps - Periods of no speech activity or low-energy content signals present in the access channel of a wideband packet network.
Garble - 1. An error in transmission, reception, encryption, or decryption that changes the text of a message or any portion thereof in such a manner that it is incorrect or undecryptable. 2. In a telephone circuit or channel, readily audible but unintelligible interference from another circuit or channel. Note: Garble may, for example, take place in an FDM telephone carrier system in which an interfering signal from another channel or system is demodulated in such a fashion that it has an objectionable audio power level but is nonetheless unintelligible.
Gate - 1. A device having one output channel and one or more input channels, such that the output channel state is completely determined by the input channel states, except during switching transients. 2. One of many types of combinational logic elements having at least two inputs; e.g., AND, OR, NAND, and NOR.
Gateway - A system that translates incompatible networks or applications. Gateway is also commonly used to refer to any system that provides access to another system. A gateway is a network point that acts as an entrance to another network. On the Internet, a node or stopping point can be either a gateway node or a host (end-point) node. Both the computers of Internet users and the computers that serve pages to users are host nodes. The computers that control traffic within your company's network or at your local Internet service provider (ISP) are gateway nodes.
In the network for an enterprise, a computer server acting as a gateway node is often also acting as a proxy server and a firewall server. A gateway is often associated with both a router, which knows where to direct a given packet of data that arrives at the gateway, and a switch, which furnishes the actual path in and out of the gateway for a given packet.
1. In a communications network, a network node equipped for interfacing with another network that uses different protocols. Note 1: A gateway may contain devices such as protocol translators, impedance matching devices, rate converters, fault isolators, or signal translators as necessary to provide system interoperability. It also requires that mutually acceptable administrative procedures be established between the two networks. Note 2: A protocol translation/mapping gateway interconnects networks with different network protocol technologies by performing the required protocol conversions. 2. [An] interface providing a compatibility between networks by converting transmission speeds, protocols, codes, or security measures. 3. Loosely, a computer configured to perform the tasks of a gateway.
Gating - 1. The process of selecting only those portions of a wave between specified time intervals or between specified amplitude limits. 2. The controlling of signals by means of combinational logic elements. 3. A process in which a predetermined set of conditions, when established, permits a second process to occur.
Gaussian Beam - A beam of light whose electric field intensity distribution is gaussian. Note: When such a beam is circular in cross section the intensity at distance r from the center, E (r), is given by
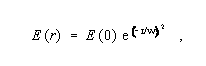
where E (0) is the electrical field strength at the beam center, i.e., at r = 0; and w is the value of r at which the intensity is 1/e of its value on the axis.
Gaussian Filter - A filter having a response curve (magnitude versus frequency) that approximates an ideal gaussian curve.
Gaussian Pulse - A pulse that has a waveform described by the gaussian distribution. Note: In the time domain, the amplitude of the waveform is given by
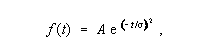
where A is the maximum amplitude, and
is the pulse half-duration at the 1/e points.
GBH - Abbreviation for group busy hour. The busy hour for a given trunk group.
Gb/s - Abbreviation for gigabytes per second. See International System of Units.
GCT - Abbreviation for Greenwich Civil Time. See Coordinated Universal Time.
GDF - Abbreviation for group distribution frame.
Gel - 1. A substance, resembling petroleum jelly in viscosity, that surrounds a fiber, or multiple fibers, enclosed in a loose buffer tube. Note: This gel serves to lubricate and support the fibers in the buffer tube. It also prevents water intrusion in the event the buffer tube is breached. 2. Index-matching material in the form of a gel. Synonyms index-matching gel, matching gel.
General Purpose Computer - A computer designed to perform, or that is capable of performing, in a reasonably efficient manner, the functions required by both scientific and business applications. Note: A general purpose computer is often understood to be a large system, capable of supporting remote terminal operations, but it may also be a smaller computer, e.g., a desktop workstation.
General Purpose Interface (GPI) - An equipment-interface device (usually computer equipment) with some number of digital lines, usually a multiple of eight, which may be used for input, output, or both, depending on the function. Note: The digital lines may be individually controlled, although nothing precludes using them in combination.
General Purpose Network - See common user network. - A system of circuits or channels allocated to furnish communication paths between switching centers to provide communication service on a common basis to all connected stations or subscribers.
Generation - In audio and video analog recording, pertaining to the number of duplication steps between an original recording and a given copy. Note 1: A second generation duplicate is a copy of the original master and a third generation duplicate is a copy of a copy of the original master, etc. Note 2: Relative to digital duplication, the copy is almost always identical to the original, so the term generation is irrelevant.
Generation Loss - In analog recording, cumulative deterioration of signal quality introduced as a consequence of limitations of the recording electronics and storage medium, when successive copies of an original recording are made, each from the preceding copy. Note 1: Examples of signal deterioration attributable to generation loss are increased distortion, increased noise, change in frequency response, and change in the relative phase of one frequency component with respect to another. Note 2: As a specific example, in the recording of television baseband signals, generation loss may manifest itself in the loss of fine detail, color distortion, erratic synchronization, etc. In audio recording, generation loss may manifest itself as audible distortion or loss of frequency response. Note 3: Generation loss is limited to analog recording because digital recording and reproduction may be performed in a manner that is essentially free from generation loss. Digital signals may be reshaped before being rerecorded, so successive generations are extremely faithful to one another, with possible exceptions attributable primarily to occasional uncompensated flaws that may be present in the recording medium. The degree to which this affects the outcome (signal quality) depends on the specific recording technique involved, but it is usually negligible. In digital recording, essentially all of the distortion introduced in the recording and playback process takes place in (a) the analog-to-digital conversion that occurs during the initial recording, and (b) the digital-to-analog process that occurs during playback. Note 4: Generation loss in digital recordings can quickly become non-negligible unless all transfers of the recording take place solely in the digital domain and lossless compression / decompression is used.
Genlock - The synchronization of two television signals at the vertical, horizontal, and chroma phase levels such that the signals may be cut, mixed, or cross-faded without noticeable roll, jump, or chroma shift. Note: Modern usage accomplishes this with a frame synchronizer/ time base corrector, but it may also be accomplished by a closed loop method or an open loop method, the latter using a pair of rubidium clocks and a video delay line to maintain chroma lock.
Geometric Optics - The branch of optics that describes light propagation in terms of rays. Note 1: Rays are bent at the interface between two dissimilar media, and may be curved in a medium in which the refractive index is a function of position. Note 2: The ray in geometric optics is perpendicular to the wavefront in physical optics. Synonym ray optics.
Geometric Spreading - See inverse-square law , which is the physical law stating that irradiance, i.e., the power per unit area in the direction of propagation, of a spherical wavefront varies inversely as the square of the distance from the source, assuming there are no losses caused by absorption or scattering. Note: For example, the power radiated from a point source, e.g., an omnidirectional isotropic antenna, or from any source at very large distances from the source compared to the size of the source, must spread itself over larger and larger spherical surfaces as the distance from the source increases. Diffuse and incoherent radiation are similarly affected.
Geostationary Orbit - A circular orbit in the equatorial plane, any point on which revolves about the Earth in the same direction and with the same period as the Earth's rotation. Note: An object in a geostationary orbit will remain directly above a fixed point on the equator at a distance of approximately 42,164 km from the center of the Earth, i.e., approximately 35,786 km above mean sea level.
Classification Orbital Altitude (km above the earth) LEO 500-2,000 MEO 8,000-20,000 Geostationary Orbit 35,786 Geostationary Satellite - A geosynchronous satellite whose circular and direct orbit lies in the plane of the Earth's equator and which thus remains fixed relative to the Earth; by extension, a satellite that remains approximately fixed relative to the Earth.
Geostationary Satellite Orbit - The orbit in which a satellite must be placed to be a geostationary satellite.
Geosynchronous Orbit - Any orbit about the Earth, which orbit has a period equal to the period of rotation of the Earth about its axis, and in the same sense, i.e., direction, as the rotation of the Earth.
Germanium Photodiode - A germanium-based PN- or PIN-junction photodiode. Note 1: Germanium photodiodes are useful for direct detection of optical wavelengths from approximately 1
m to several tens of
m. Note 2: Germanium-based detectors are noisier than silicon-based detectors. Silicon-based detectors are therefore usually preferred for wavelengths shorter than 1
m.
GETS - Abbreviation for Government Emergency Telecommunications Service (GETS). - A special federal government telecommunications service that provides National Security and Emergency Preparedness (NS/EP) users with priority switched voice and voiceband data communications during periods of emergency or crisis. GETS uses existing features and services of the Public Switched Network (PSN) with selected NS/EP augmentations and enhancements. Access to GETS requires a telephone calling card with personal identification number. GETS is maintained in a constant state of readiness to make maximum use of all available PSN telephone resources should network congestion or damage occur during an emergency or crisis. GETS calls receive priority over other traffic through special features such as trunk queuing, exemption from restrictive network management controls and Alternate Carrier Routing (ACR) on approximately 85% of all local carrier access lines. Comparable features provide priority treatment and enhanced routing in the interexchange networks. While GETS calls receive priority for next available path, they do not preempt other traffic. The Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) -High Probability of Completion (HPC) Network Capability standard is applied to provide NS/EP call identification and priority signaling.
GFP (global functional plane) - The plane in the intelligent network conceptual model that defines service independent building blocks (SIBs) used in providing service features.
Ghost - In the transmission or recording of raster-scanned analog television signals, an artifact manifested as a weak, ghost-like secondary image, offset (in the direction of the scan) with respect to the position of the primary image. Note: Ghosting is probably most familiar as a consequence of multipath rf reception of a broadcast television signal. The slight delay in the arrival time of the reflected signal results in the display of a secondary image that follows the primary. In the playback of a tape-recorded program, ghosting may also be introduced by print-through in the magnetic tape medium.
Ghosting - See ghost.
GHz (Gigahertz) - A unit of frequency denoting 109 Hz.
gif - (or .gif) Abbreviation for graphical interchange format. A file-name extension indicating a certain digital image file format suitable for efficiently importing image data into computer files or for transmitting or displaying the formatted image on a computer monitor or printing it out.
Gigaflop - A billion, i.e., 109, floating point operations per second.
Gigahertz (GHz) - A unit of frequency denoting 109 Hz.
GII - Abbreviation for global information infrastructure. The totality of worldwide infrastructure elements that combine the three industry sectors of (a) telecommunications, (b) computer (information) technology, and (c) consumer electronics to extend the capabilities of the NII (national information infrastructure) worldwide.
Glare - Deprecated synonym for call collision. See also dual seizure. - 1. The contention that occurs when a terminal and data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE) specify the same channel at the same time to transfer a call request and handle an incoming call. Note: When call collision occurs, the DCE proceeds with the call request and cancels the incoming call. 2. The condition that occurs when a trunk or channel is seized at both ends simultaneously, thereby blocking a call. Synonym dual seizure.
Glare Master - The Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) switch designated as control switch for circuits in the both-way circuit group. For the same circuits, the other switch is referred to as the slave. On detecting glare, the control switch proceeds to complete the call for which it has already sent an initial address message (IAM). The IAM received from the slave is discarded. The call being processed by the slave is backed off and the switch path released. A release message is not sent.
Glass - 1. In the strict sense, a state of matter. 2. In fiber-optic communication, any of a number of noncrystalline, amorphous inorganic substances, formed, by heating, from metallic or semiconductor oxides or halides, and used as the material for fibers. Note: The most common glasses are based on silicon dioxide (SiO2).
Glide Slope Facility - In aeronautical navigation, an instrument approach landing facility that furnishes vertical guidance information to an aircraft from its approach altitude down to the surface of the runway.
Global - 1. Pertaining to, or involving, the entire world. 2. Pertaining to that which is defined in one subsection of an entity and used in at least one other subsection of the same entity. 3. In computer, data processing, and communications systems, pertaining to what is applicable to an area beyond the immediate area of consideration. Note: Examples of global entities are (a) in computer programming, an entity that is defined in one subdivision of a computer program and used in at least one other subdivision of that program and (b) in personal computer systems and their software packages, a setting, definition, or condition that applies to the entire software system.
Global Address - In a communications network, the predefined address that is used as an address for all users of that network, and that may not be the address of an individual user, or subgroup of users, of the network.
Global Area Network (GAN) - A network that (a) is composed of different interconnected computer networks and (b) covers an unlimited geographical area. Note: Loosely synonymous with an internet (as opposed to the Internet (with an uppercase "I"), which designates one specific network).
Global Functional Plane (GFP) - The plane in the intelligent network conceptual model that defines service independent building blocks (SIBs) used in providing service features.
Global Information Infrastructure - See GII. The totality of worldwide infrastructure elements that combine the three industry sectors of (a) telecommunications, (b) computer (information) technology, and (c) consumer electronics to extend the capabilities of the NII (national information infrastructure) worldwide.
Global Positioning System (GPS): See GPS. A satellite-based global navigation system that consists of (a) a constellation of 24 satellites in orbit 11,000 nmi above the Earth, (b) several on-station (i.e., in-orbit) spares, and (c) a ground-based control segment. The satellites transmit signals that are used for extremely accurate three-dimensional (latitude, longitude, and elevation) global navigation (position determination), and for the dissemination of precise time. GPS-derived position determination is based on the arrival times, at an appropriate receiver, of precisely timed signals from the satellites that are above the user's radio horizon.
Global Status - 1. The set of attributes of an entity, described at a particular time, when that set is extended to every occurrence of that entity within a prescribed boundary. 2. The complete set of attributes necessary to describe an entity at a particular time.
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) - A public, all-digital cellular network that is standardized worldwide and that uses (a) TDMA techniques for multiplexing at approximately 900 MHz, (b) compressed voice at about 13 kb/s, (c) 16 kb/s circuit-switching technology, and (d) error-correcting algorithms.
Global Title (GT): A "logical" or "virtual" address used for routing Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) messages using signaling connection control part (SCCP) capabilities. To complete message routing, a GT must be translated to a SS7 point code and subsystem number.
Glyph - Any graphic symbol not in the ASCII character set.
GMT - Abbreviation for Greenwich Mean Time. Obsolete term. See Coordinated Universal Time. - Mean solar time at the meridian of Greenwich, England, formerly used as a basis for standard time throughout the world.
Go-Ahead Message - Synonym go-ahead notice. - In a tape-relay communications system, a service message, usually sent to a relay station or to a tributary station, that contains a request to the operator to resume transmitting over a specified channel or channels. Synonyms start notice.
Go-Ahead Notice - In a tape-relay communications system, a service message, usually sent to a relay station or to a tributary station, that contains a request to the operator to resume transmitting over a specified channel or channels. Synonyms go-ahead message, start message, start notice.
Go-Ahead Tone - In communications systems, an audible signal transmitted by a system indicating that the system is ready to receive a message or signal.
Gold Code - In spread-spectrum systems, a code that is generated by summing, using modulo-two addition, the outputs of two spread-spectrum code-sequence generators.
Go List - Synonyms bookmark list, history list, hotlist.
Gopher - A system of clients and servers, in menu format, that allows for navigation on the Internet. A menu-based information searching tool that allows users to access various types of databases, such as FTP archives and white pages databases. Note 1: Gopher is most often used as an Internet browser. Note 2: Gopher software uses the client-server model.Gopherspace - That part of the cyberspace to which the user has access by means of gopher software. Note: The use of gopher software has declined rapidly in recent years as the use of Web software has increased.
GOS - Abbreviation for grade of service. - 1. The probability of a call's being blocked or delayed more than a specified interval, expressed as a decimal fraction. Note: Grade of service may be applied to the busy hour or to some other specified period or set of traffic conditions. Grade of service may be viewed independently from the perspective of incoming versus outgoing calls, and is not necessarily equal in each direction. 2. In telephony, the quality of service for which a circuit is designed or conditioned to provide, e.g., voice grade or program grade. Note: Criteria for different grades of service may include equalization for amplitude over a specified band of frequencies, or in the case of digital data transported via analog circuits, equalization for phase also.
GOSIP - Acronym for Government Open Systems Interconnection Profile. A definition of Federal Government functional requirements for open systems computer network products, including a common set of Open System Interconnection (OSI) data communication protocols that enables systems developed by different vendors to interoperate and enable the users of different applications on these systems to exchange information. Note 1: The OSI protocols were developed primarily by ISO and CCITT (now, ITU-T). Note 2: The GOSIP is a subset of the OSI protocols and is based on agreements reached by vendors and users of computer networks participating in the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Implementors Workshop.
Government Emergency Telecommunications Service (GETS) - A special federal government telecommunications service that provides National Security and Emergency Preparedness (NS/EP) users with priority switched voice and voiceband data communications during periods of emergency or crisis. GETS uses existing features and services of the Public Switched Network (PSN) with selected NS/EP augmentations and enhancements. Access to GETS requires a telephone calling card with personal identification number. GETS is maintained in a constant state of readiness to make maximum use of all available PSN telephone resources should network congestion or damage occur during an emergency or crisis. GETS calls receive priority over other traffic through special features such as trunk queuing, exemption from restrictive network management controls and Alternate Carrier Routing (ACR) on approximately 85% of all local carrier access lines. Comparable features provide priority treatment and enhanced routing in the interexchange networks. While GETS calls receive priority for next available path, they do not preempt other traffic. The Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) -High Probability of Completion (HPC) Network Capability standard (ANSI T1.631-1993) is applied to provide NS/EP call identification and priority signaling.
Government Open Systems Interconnection Profile - See GOSIP. A definition of Federal Government functional requirements for open systems computer network products, including a common set of Open System Interconnection (OSI) data communication protocols that enables systems developed by different vendors to interoperate and enable the users of different applications on these systems to exchange information. Note 1: The OSI protocols were developed primarily by ISO and CCITT (now, ITU-T). Note 2: The GOSIP is a subset of the OSI protocols and is based on agreements reached by vendors and users of computer networks participating in the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Implementors Workshop.
GPI - Abbreviation for general purpose interface. An equipment-interface device (usually computer equipment) with some number of digital lines, usually a multiple of eight, which may be used for input, output, or both, depending on the function. Note: The digital lines may be individually controlled, although nothing precludes using them in combination. See general purpose interface.
GPS - Abbreviation for global positioning system. A satellite-based global navigation system that consists of (a) a constellation of 24 satellites in orbit 11,000 nmi above the Earth, (b) several on-station (i.e., in-orbit) spares, and (c) a ground-based control segment. The satellites transmit signals that are used for extremely accurate three-dimensional (latitude, longitude, and elevation) global navigation (position determination), and for the dissemination of precise time. GPS-derived position determination is based on the arrival times, at an appropriate receiver, of precisely timed signals from the satellites that are above the user's radio horizon.
Graceful Degradation - Degradation of a system in such a manner that it continues to operate, but provides a reduced level of service rather than failing completely.
Graded-Index Fiber - An optical fiber with a core having a refractive index that decreases with increasing radial distance from the fiber axis. Note: The most common refractive index profile for a graded-index fiber is very nearly parabolic. The parabolic profile results in continual refocusing of the rays in the core, and compensates for multimode distortion.
Graded-Index Profile - In the core of an optical fiber, a plot of the variation of refractive index such that the refractive index decreases with increasing radial distance from the fiber axis.
Grade of Service (GOS) - 1. The probability of a call's being blocked or delayed more than a specified interval, expressed as a decimal fraction. Note: Grade of service may be applied to the busy hour or to some other specified period or set of traffic conditions. Grade of service may be viewed independently from the perspective of incoming versus outgoing calls, and is not necessarily equal in each direction. 2. In telephony, the quality of service for which a circuit is designed or conditioned to provide, e.g., voice grade or program grade. Note: Criteria for different grades of service may include equalization for amplitude over a specified band of frequencies, or in the case of digital data transported via analog circuits, equalization for phase also.
Gradient - In graphics, especially computer graphics, that which characterizes an area in which a smooth transition between one color and another, or between black and white (i.e., contrast), takes place.
Grandfathered Systems - Systems, including but not limited to: (a) PBX and key telephone systems, directly connected to the public switched telephone network on June 1, 1978, that may remain permanently connected thereto without registration unless subsequently modified, and (b) systems that are of the same type as those connected to the public switched telephone network on July 1, 1978, that were added before January 1, 1980, and that may remain permanently connected thereto without registration unless subsequently modified.
Grandfathered Terminal Equipment - Terminal equipment (other than PBX and key telephone systems) and protective circuitry connected to the public switched telephone network before July 1, 1978, that may remain connected thereto for life without registration unless subsequently modified.
Graphical User Interface - See gui. A computer environment or program that displays, or facilitates the display of, on-screen options, usually in the form of icons (pictorial symbols) or menus (lists of alphanumeric characters) by means of which users may enter commands. Note 1: Options are selected by using the appropriate hardware (e.g., mouse, designated keyboard keys, or touchpad) to move a display cursor to, or on top of, the icon or menu item of interest. The application or function so represented may then be selected (e.g., by clicking a mouse button, pressing the "enter" key, or by touching the touchpad). Note 2: Pronounced "gooey."
Graphic Character - 1. A visual representation of a character, other than a control character. 2. In the ASCII code, a character other than an alphanumeric character, intended to be written, printed, or otherwise displayed in a form that can be read by humans. Note 1: Graphic characters are contained in rows 2 through 7 of the ASCII code table. Note 2: The space and delete characters are considered to be graphic characters.
Graphics - The art or science of conveying information through the use of display media, such as graphs, letters, lines, drawings, and pictures. Note: Graphics includes the transmission of coded images such as facsimile.
Graphics Pipe - In computer science and technology, the special hardware within the computer optimized for the display of real-time 3D graphics.
Gray Code - A binary code in which consecutive decimal numbers are represented by binary expressions that differ in the state of one, and only one, one bit. Synonym reflected code.
Gray Scale - An optical pattern consisting of discrete steps or shades of gray between black and white.
Great Circle - A circle defined by the intersection of the surface of the Earth and any plane that passes through the center of the Earth. Note: On the idealized surface of the Earth, the shortest distance between two points lies along a great circle.
Greenwich Civil Time (GCT) - Synonym Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). Obsolete term. See Coordinated Universal Time. - Mean solar time at the meridian of Greenwich, England, formerly used as a basis for standard time throughout the world.
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) - Mean solar time at the meridian of Greenwich, England, formerly used as a basis for standard time throughout the world. Obsolete term. Synonym Greenwich Civil Time. See Coordinated Universal Time.
Ground - 1. An electrical connection to earth through an earth-electrode subsystem. 2. In an electrical circuit, a common return path that usually (a) is connected to an earth-electrode subsystem and (b) is extended throughout a facility via a facility ground system consisting of the signal reference subsystem, the fault protection subsystem, and the lightning protection subsystem. 3. In an electrical circuit, a common return path that (a) may not necessarily be connected to earth and (b) is the zero voltage reference level for the equipment or system.
Ground Absorption - The dissipation of rf energy by the earth.
Ground Constants - The electrical parameters of earth, such as conductivity, permittivity, and magnetic permeability. Note 1: The values of these parameters vary with the local chemical composition and density of the earth. Note 2: For a propagating electromagnetic wave, such as a surface wave propagating along the surface of the Earth, these parameters vary with frequency and direction.
Ground Current - In the presence of an electrical fault, the current that flows in the protective ground wire of a power distribution system.
Ground Loop - In an electrical system, an unwanted current that flows in a conductor connecting two points that are nominally at the same potential, i.e., ground, but are actually at different potentials. Note 1: For example, the electrical potential at different points on the surface of the Earth can vary by hundreds of volts, primarily from the influence of the solar wind. Such an occurrence can be hazardous, e.g., to personnel working on long grounded conductors such as metallic telecommunications cable pairs. Note 2: A ground loop can also exist in a floating ground system, i.e., one not connected to an Earth ground, if the conductors that constitute the ground system have a relatively high resistance, or have, flowing through them, high currents that produce a significant voltage ("I•R") drop. Note 3: Ground loops can be detrimental to the operation of the electrical system.
Ground Plane - An electrically conductive surface that serves as the near-field reflection point for an antenna. Note: A ground plane may consist of a natural (e.g., Earth or sea) surface, an artificial surface of opportunity (e.g., the roof of a motor vehicle), or a specially designed artificial surface (e.g., the disc of a discone antenna).
Ground Potential - The zero reference level used to apply and measure voltages in a system. Note: A potential difference may exist between this reference level and the ground potential of the Earth, which varies with locality, soil conditions, and meteorological phenomena.
Ground-Return Circuit - 1. A circuit using a common return path that is at ground potential. Note: Earth may serve as a portion of the ground-return circuit. 2. A circuit in which there is a common return path, whether or not connected to earth.
Ground Start - A line or equipment that establishes a dial tone by completing a circuit between one of the wires of the line and earth ground. Ground start circuits are used mainly for PBX applications. Loop start equipment will not operate if connected directly to a ground start line. A method of signaling from a terminal or subscriber loop to a switch, in which method one side of a cable pair is temporarily grounded.
Ground-Start Signaling - A type of analog voicegrade access line signaling that requires the customer interface (CI) to provide a ground on the ring conductor at the network interface (NI) to initiate service requests.
Ground Wave - In radio transmission, a surface wave that propagates close to the surface of the Earth. Note 1: The Earth has one refractive index and the atmosphere has another, thus constituting an interface that supports surface wave transmission. These refractive indices are subject to spatial and temporal changes. Note 2: Ground waves do not include ionospheric and tropospheric waves.
Ground Window - The interface or transition point between the isolated and integrated ground planes. The ground window can be a dimensional area around a bus bar or the bus bar itself. After passing through the ground window, there shall be no additional paths to ground, intentional or unintentional, inside the isolated ground plane.
Group - 1. In frequency-division multiplexing, a specific number of associated voice channels, either within a supergroup or as an independent entity. Note 1: In wideband systems, a group usually consists of 12 voice channels and occupies the frequency band from 60 kHz to 108 kHz. Note 2: this is ITU-T group B (formerly CCITT group B). Note 3: ITU-T Basic Group A, for carrier telephone systems, consists of 12 channels occupying upper sidebands in the 12-kHz to 60-kHz band. Basic Group A is no longer mentioned in ITU-T Recommendations. Note 4: A supergroup usually consists of 60 voice channels, i.e., 5 groups of 12 voice channels each, occupying the frequency band from 312 kHz to 552 kHz. Note 5: A mastergroup consists of 10 supergroups or 600 voice channels. Note 6: The ITU-T standard mastergroup consists of 5 supergroups. The U.S. commercial carrier standard mastergroup consists of 10 supergroups. Note 7: The terms "supermaster group" or "jumbo group" are sometimes used to refer to 6 mastergroups. 2. A set of characters forming a unit for transmission or cryptographic treatment.
Group Address - In a communications network, a predefined address used to address only a specified set of users. Synonym collective address.
Group Alerting and Dispatching System - A service feature that (a) enables a controlling telephone to place a call to a specified number of telephones simultaneously, (b) enables the call to be recorded, (c) if any of the called lines is busy, enables the equipment to camp on until the busy line is free, and (d) rings the free line and plays the recorded message.
Group Busy Hour (GBH): The busy hour for a given trunk group.
Group Delay - 1. The rate of change of the total phase shift with respect to angular frequency, d
/d
, through a device or transmission medium, where
is the total phase shift, and
is the angular frequency equal to 2
f, where f is the frequency. 2. In an optical fiber, the transit time required for optical power, traveling at a given mode's group velocity, to travel a given distance. Note: For optical fiber dispersion measurement purposes, the quantity of interest is group delay per unit length, which is the reciprocal of the group velocity of a particular mode. The measured group delay of a signal through an optical fiber exhibits a wavelength dependence due to the various dispersion mechanisms present in the fiber.
Group Delay Time - In a group of waves that have slightly different individual frequencies, the time required for any defined point on the envelope (i.e., the envelope determined by the additive resultant of the group of waves) to travel through a device or transmission facility.
Group Distribution Frame (GDF) - In frequency-division multiplexing, a distribution frame that provides terminating and interconnecting facilities at the group level, i.e., group modulator output and group demodulator input circuits of FDM carrier equipment. Note: The basic spectrum of the FDM group is 60 kHz to 108 kHz.
Group Index (N): In fiber optics, for a given mode propagating in a medium of refractive index
, the velocity of light in vacuum, c, divided by the group velocity of the mode. Note: For a plane wave of wavelength
, the group index may also be expressed,
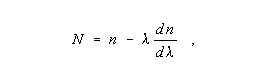
where n is the phase index of wavelength
.
Grouping Factor - Synonym blocking factor. - The number of records in a block. Note: The blocking factor is calculated by dividing the block length by the length of each record contained in the block. If the records are not of the same length, the average record length may be used to compute the blocking factor.
Group 1. . . 4 facsimile - See facsimile.
Group Patch Bay - See patch bay.
Group Velocity - 1. The velocity of propagation of an envelope produced when an electromagnetic wave is modulated by, or mixed with, other waves of different frequencies. Note: The group velocity is the velocity of information propagation and, loosely, of energy propagation. 2. In optical fiber transmission, for a particular mode, the reciprocal of the rate of change of the phase constant with respect to angular frequency. Note: The group velocity equals the phase velocity if the phase constant is a linear function of the angular frequency,
= 2
f, where f is the frequency. 3. In optical-fiber transmission, the velocity of the modulated optical power.
Groupware - Network-compatible software applications that facilitate shared work on information and documents.
GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) - A digital mobile telephone system that is widely used in Europe and other parts of the world. GSM uses a variation of time division multiple access (TDMA) and is the most widely used of the three digital wireless telephone technologies (TDMA, GSM, and CDMA). GSM digitizes and compresses data, then sends it down a channel with two other streams of user data, each in its own time slot. It operates at either the 900
MHz or 1800 MHz frequency band.GSM is the de facto wireless telephone standard in Europe. GSM has over 120 million users worldwide and is available in 120 countries, according to the GSM MoU Association. Since many GSM network operators have roaming agreements with foreign operators, users can often continue to use their mobile phones when they travel to other countries.
American Personal Communications (APC), a subsidiary of Sprint, is using GSM as the technology for a broadband personal communications service (PCS). The service will ultimately have more than 400 base stations for the palm-sized handsets that are being made by Ericsson, Motorola, and Nokia. The handsets include a phone, a text pager, and an answering machine.
GSM together with other technologies is part of an evolution of wireless mobile telemmunication that includes High-Speed Circuit-Switched Data (
HCSD ), General Packet Radio System (GPRS), Enhanced Data GSM Environment (EDGE), and Universal Mobile Telecommunications Service (UMTS).G /T - Abbreviation for antenna gain-to-noise-temperature.
Guard - In computer security, a functional unit that provides a security filter between two data processing systems operating at different security levels or between a user terminal and a database to filter out data that the user is not authorized to access.
Guard Band - See frequency guard band, time guard band.
Guarded Frequency - A transmission frequency that is not to be jammed or interfered with because of the value of the information being derived from it. Note: For example, a guarded frequency will not be jammed when the tactical, strategic, and technical information that can be obtained from the transmissions outweighs the potential operational gain achieved by jamming.
Gui - Acronym for graphical user interface. A computer environment or program that displays, or facilitates the display of, on-screen options, usually in the form of icons (pictorial symbols) or menus (lists of alphanumeric characters) by means of which users may enter commands. Note 1: Options are selected by using the appropriate hardware (e.g., mouse, designated keyboard keys, or touchpad) to move a display cursor to, or on top of, the icon or menu item of interest. The application or function so represented may then be selected (e.g., by clicking a mouse button, pressing the "enter" key, or by touching the touchpad). Note 2: Pronounced "gooey."
Guided Mode - Synonym bound mode. In an optical fiber, a mode that (a) has a field intensity that decays monotonically in the transverse direction everywhere external to the core and (b) does not lose power to radiation. Note: Except for single-mode fibers, the power in bound modes is predominantly contained in the core of the fiber.
Guided Ray - In an optical fiber, a ray that is confined primarily to the core. Note: A guided ray satisfies the relation given by
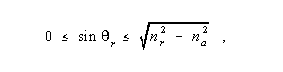
where
r is the angle the ray makes with the fiber axis, r is the radial position, i.e., radial distance, of the ray from the fiber axis, nr is the refractive index at the radial distance r from the fiber axis, and na is the refractive index at the core radius, a, i.e., at the core-cladding interface. Guided rays correspond to bound modes, i.e., guided modes, in terms of modes rather than rays. Synonyms bound ray, trapped ray.
Guided Wave - A wave having (a) energy concentrated near a boundary, or between substantially parallel boundaries, separating materials of different properties and (b) a direction of propagation effectively parallel to these boundaries.
Fax Switch Products
|
*Note: All prices include shipping and handling in the continental US and most of Canada. We reserve the right to charge up to the actual price of shipping on all orders outside the continental United States. Customer is responsible for any taxes, duties or brokerage charges that may apply. All orders shipped UPS Ground unless specified. For air and express shipments, appropriate charges will be applied to your order.
Need Help?
- Call now for free phone consultation at 1-866-337-0965.
Click here if you want to share 2 devices on 1 line and don't know which device to choose.
Click here if you want to share 3 or more devices on one line and don't know what type to choose.
"Albert Einstein Presents Fax Switch "
"Dancing Bear Fax Switch Presentation"
![]()
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
If you didn't find what you need here?
Please visit our sister company, SuperPhoneStore.com for wholesale to the public telephones, phone accessories or the latest electronics. We have over 4500 different products in stock from over 200 premier manufacturers.